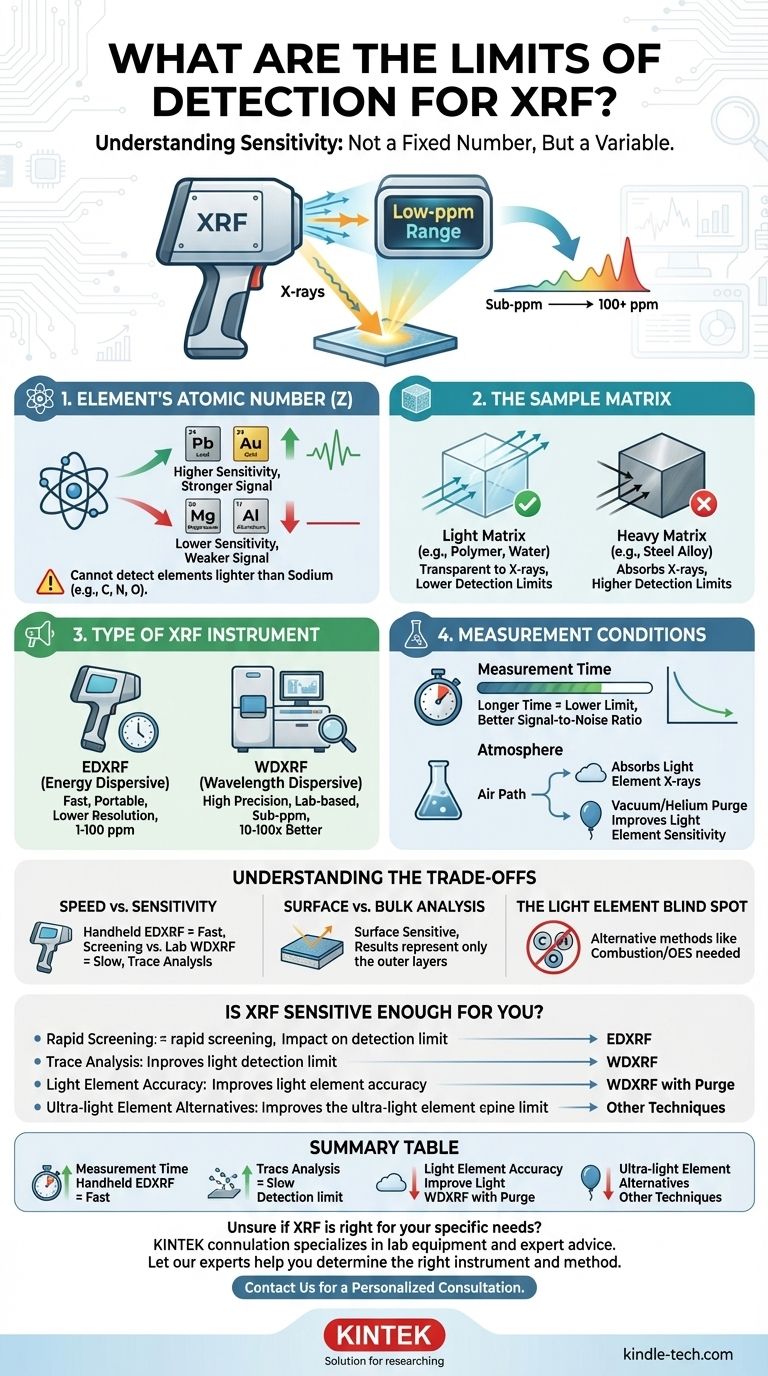
For most elements, the limit of detection for X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF) is typically in the low parts-per-million (ppm) range. However, this is not a single, fixed number. The true detection limit for any given analysis can vary by orders of magnitude, depending on the specific element being measured, the sample it's in, and the type of XRF instrument being used.
The sensitivity of XRF is not an inherent constant of the technique itself, but rather a variable outcome of your specific analytical problem. The central challenge is understanding how the element of interest, its surrounding material (the matrix), and your choice of instrument interact to determine the ultimate detection limit.

What Determines an XRF Detection Limit?
The performance of an XRF analysis is governed by a few fundamental factors. Understanding these principles is key to determining if the technique is suitable for your needs.
The Element's Atomic Number (Z)
XRF is generally more sensitive to heavier elements than lighter ones.
Heavier elements (like lead or gold) emit higher-energy fluorescent X-rays when excited. These energetic X-rays are less likely to be absorbed by the surrounding sample or the air, making them easier for the instrument's detector to count.
Conversely, light elements (like aluminum or magnesium) emit low-energy X-rays that are easily absorbed. This results in a weaker signal and, therefore, a higher (worse) limit of detection. XRF cannot detect elements lighter than sodium (e.g., carbon, nitrogen, oxygen).
The Sample Matrix
The "matrix" refers to all the other material in your sample besides the specific element you are trying to measure.
A light matrix, such as a polymer or water, is more transparent to X-rays. It allows both the initial X-rays and the fluorescent X-rays to pass through easily, leading to strong signals and low detection limits.
A heavy matrix, such as a steel alloy, is dense and absorbs X-rays more readily. This "matrix effect" can suppress the signal from your target element, making it harder to detect and raising the detection limit.
The Type of XRF Instrument
There are two primary types of XRF analyzers, and their capabilities differ significantly.
Energy Dispersive XRF (EDXRF) instruments are common, often available as portable handheld units. They are fast and excellent for screening, but they have lower resolution, which can lead to higher background noise and detection limits typically in the 1-100 ppm range.
Wavelength Dispersive XRF (WDXRF) instruments are larger, more complex lab-based systems. They use crystals to separate the X-ray wavelengths with very high precision. This results in much lower background noise and significantly better detection limits, often 10 to 100 times lower than EDXRF, reaching sub-ppm levels for many elements.
The Measurement Conditions
Two operational parameters directly influence your result.
First, measurement time is critical. A longer analysis time allows the detector to collect more X-ray signals, improving the signal-to-noise ratio and lowering the detection limit. This is a statistical process; quadrupling the time will roughly halve the detection limit.
Second, for light elements, the atmosphere between the sample and detector matters. Their low-energy X-rays are easily absorbed by air. Using a vacuum or a helium purge removes this interference, dramatically improving sensitivity for elements like magnesium, aluminum, and silicon.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing to use XRF involves balancing its strengths and weaknesses. Being aware of these trade-offs is crucial for interpreting your results correctly.
Speed vs. Sensitivity
The primary trade-off is between rapid field analysis and high-precision laboratory results. A handheld EDXRF provides answers in seconds, making it ideal for scrap metal sorting or consumer product screening. However, if you need to verify if lead content is below a 5 ppm regulatory threshold, you need the slower, more sensitive capabilities of a WDXRF.
Surface vs. Bulk Analysis
XRF is fundamentally a surface-sensitive technique. The X-rays only penetrate a short distance into the material, from a few micrometers to several millimeters, depending on the sample's density and the X-ray energy. The results you get represent the composition of the surface, which may not be representative of the bulk material if the sample is coated, corroded, or inhomogeneous.
The Light Element Blind Spot
It is critical to remember that XRF has a fundamental limitation. It cannot be used for elements like carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine. If your analysis depends on quantifying these elements, you must use a different technique, such as combustion analysis or Optical Emission Spectrometry (OES).
Is XRF Sensitive Enough for Your Application?
To determine if XRF is the right tool, match its capabilities to your specific goal.
- If your primary focus is rapid screening or alloy identification: A handheld EDXRF is almost certainly sufficient, as its ppm-level sensitivity is well-suited for confirming major and minor elemental constituents.
- If your primary focus is trace element analysis for regulatory compliance (e.g., RoHS, CPSIA): A high-performance benchtop EDXRF or a WDXRF is necessary to achieve the required low-ppm detection limits with high confidence.
- If your primary focus is analyzing light elements (e.g., Mg, Al, Si) with high accuracy: A WDXRF system with a vacuum or helium purge is essential, as standard air-path XRF performs poorly for these elements.
- If your primary focus is analyzing elements lighter than sodium (e.g., carbon): XRF is the wrong technique, and you should consider alternatives like combustion analysis or OES.
By understanding what controls its sensitivity, you can effectively decide if XRF provides the analytical power required to solve your problem.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Detection Limit | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Element Atomic Number | Lower for heavier elements | Excellent for Lead (Pb), Poor for Magnesium (Mg) |
| Sample Matrix | Lower in light matrices (e.g., plastic) | Higher in heavy matrices (e.g., steel) |
| Instrument Type | WDXRF: Sub-ppm to low ppm | EDXRF: ~1-100 ppm |
| Measurement Time | Longer time = Lower detection limit | Quadrupling time roughly halves the limit |
Unsure if XRF is sensitive enough for your specific materials and requirements?
The detection limits outlined are general guidelines. The true sensitivity for your analysis depends on your unique sample composition and goals. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with expert advice on XRF and other analytical techniques.
Let our experts help you determine the right instrument and method to achieve the precision you need. Contact us today for a personalized consultation to discuss your application and ensure accurate, reliable results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab Plastic PVC Calender Stretch Film Casting Machine for Film Testing
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Lab Blown Film Extrusion Three Layer Co-Extrusion Film Blowing Machine
- Single Punch Tablet Press Machine and Mass Production Rotary Tablet Punching Machine for TDP
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
People Also Ask
- What is the meaning of blowing film? A Guide to Biaxial Orientation and Stronger Plastic Films
- What products are blown film extrusion? From Grocery Bags to Industrial Sheeting
- What is the process of calendering? A Guide to High-Volume Plastic Film Production
- What is the cost of blown film extrusion? From $20K to High-End Systems
- What is the difference between calendaring and calendering? Master the Key Spelling and Context



















