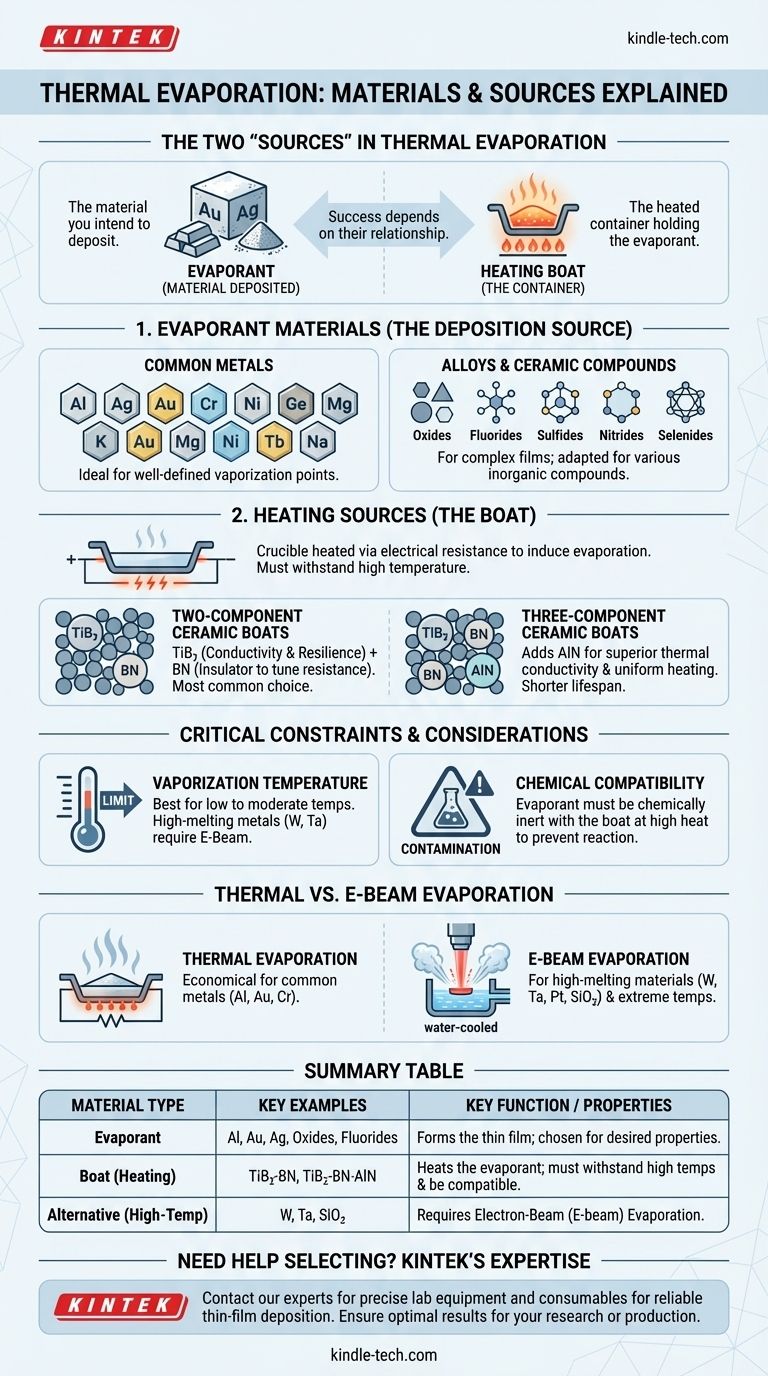
In thermal evaporation, the term "source" can refer to two distinct things: the material you intend to deposit (the evaporant) and the heated container that holds it (the boat). A vast range of materials, including pure metals like gold and aluminum, alloys, and various ceramic compounds, can be used as the evaporant. The heating sources themselves are typically specialized ceramic boats engineered for high temperatures and specific electrical properties.
The success of thermal evaporation depends entirely on the relationship between the material being deposited and the heating source. While the technique is versatile, the choice of materials is fundamentally constrained by vaporization temperatures and the chemical compatibility between the evaporant and the heated boat.

What Materials Can Be Evaporated? (The Evaporant)
Thermal evaporation is a highly flexible deposition technique capable of handling a wide variety of source materials to create thin films.
Common Metals
Many pure metals are ideal candidates for thermal evaporation due to their well-defined vaporization points.
Common examples include Aluminum (Al), Silver (Ag), Gold (Au), Chromium (Cr), Nickel (Ni), Germanium (Ge), and Magnesium (Mg).
Alloys and Ceramic Compounds
Beyond pure metals, the process can be adapted for more complex materials.
The technique is used for various alloys and a broad spectrum of inorganic compounds, including oxides, fluorides, sulfides, nitrides, and selenides.
What Are the Heating Sources Made Of? (The Boat)
The "source" also refers to the crucible, or boat, that holds the evaporant. This component is actively heated via electrical resistance to induce evaporation. Its material composition is critical for performance and reliability.
The Role of the Evaporation Boat
The boat must achieve a temperature high enough to vaporize the source material without melting, breaking, or chemically reacting with it.
These boats are typically constructed from advanced, mixed ceramics designed to balance electrical conductivity and heat resistance.
Two-Component Ceramic Boats
The most common evaporation boats are made from a ceramic composite of Titanium Diboride (TiB₂) and Boron Nitride (BN).
Titanium Diboride provides excellent electrical conductivity and high-temperature resilience. Boron Nitride is an electrical insulator used to tune the boat's overall resistance to match the system's power supply.
Three-Component Ceramic Boats
For applications requiring more uniform heating, a third material is added: Aluminum Nitride (AlN).
This three-component boat (TiB₂-BN-AlN) offers superior thermal conductivity, which helps heat the evaporant more evenly. However, this comes at the cost of a shorter operational lifespan and lower corrosion resistance.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While versatile, thermal evaporation is not a universal solution. Its effectiveness is governed by clear physical and chemical constraints.
The Vaporization Temperature Constraint
Thermal evaporation works best for materials with relatively low to moderate vaporization temperatures.
High-melting-point refractory metals like Tungsten (W) and Tantalum (Ta) are extremely difficult to deposit with standard thermal evaporation because the required temperatures can destroy the heating boat.
Chemical Compatibility is Crucial
At high temperatures, the evaporant can chemically react with the boat material. This can contaminate the resulting thin film and damage the source.
Choosing a boat material that is chemically inert with respect to your evaporant at deposition temperatures is essential for a clean and repeatable process.
Thermal vs. E-Beam Evaporation
When thermal evaporation is not suitable, electron-beam (e-beam) evaporation is often the alternative.
E-beam uses a focused beam of electrons to heat the source material directly, allowing it to reach much higher temperatures. It is the preferred method for depositing high-melting-point metals (W, Ta, Pt) and certain dielectric materials like **silicone dioxide (SiO₂) **.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right combination of evaporant and source boat is the key to a successful deposition. Base your decision on the properties of your desired film and the capabilities of your system.
- If your primary focus is depositing common metals like Aluminum, Gold, or Chrome: Standard thermal evaporation with a two-component ceramic boat is a highly effective and economical choice.
- If your primary focus is depositing high-melting-point materials like Tungsten or certain ceramics: You should plan to use an e-beam evaporation system, as it is designed to handle the extreme temperatures required.
- If your primary focus is achieving highly uniform heating for sensitive materials: A three-component (TiB₂-BN-AlN) boat may improve your results, but be prepared for its shorter operational lifespan.
- If your primary focus is process reliability: Always ensure the voltage and current ratings of your chosen boat are a perfect match for your system's power supply network.
By understanding the interplay between the evaporant, the source boat, and the system's power, you can reliably control your thin-film deposition process.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Key Examples | Key Function/Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Evaporant (Material Deposited) | Aluminum (Al), Gold (Au), Silver (Ag), Oxides, Fluorides | Forms the thin film; chosen based on desired film properties. |
| Boat (Heating Source) | TiB₂-BN composite, TiB₂-BN-AlN composite | Heats the evaporant; must withstand high temperatures and be chemically compatible. |
| Alternative for High-Temp Materials | Tungsten (W), Tantalum (Ta), Silicone Dioxide (SiO₂) | Requires Electron-Beam (E-beam) Evaporation instead of thermal evaporation. |
Need help selecting the right materials for your thermal evaporation process?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving the precise needs of laboratories. Our expertise ensures you get the correct evaporant materials and compatible, high-performance evaporation boats for reliable thin-film deposition.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and ensure optimal results for your research or production.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Multi-zone Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Tube
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages disadvantages and uses of sheet metal? The Ultimate Guide to Material Selection
- How does hardness change with temperature? Understand the Inverse Relationship to Prevent Failure
- What is the difference between metallic and non-metallic coating? A Guide to Sacrificial vs. Barrier Protection
- How can you improve corrosion resistance? Extend Equipment Life with Proven Strategies
- What are the disadvantages of using metal? Understanding Corrosion, Weight, and Cost Challenges



















