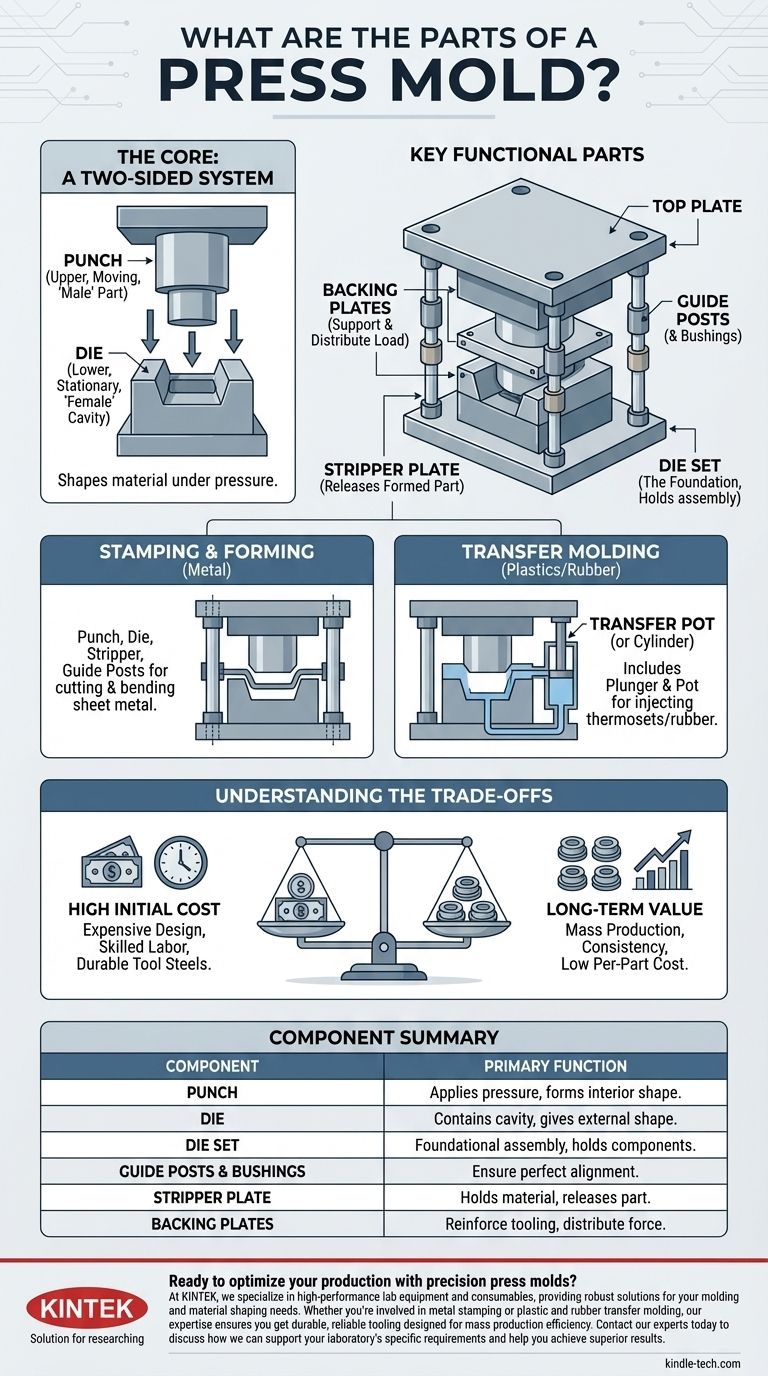
At its core, a press mold is a specialized tool comprised of two primary halves—the punch and the die—that work together under pressure to shape material. The specific components, however, vary based on the molding process, but they generally include a foundational die set, guide posts for alignment, and plates that hold, strip, and support the tooling.
A press mold is not a single entity but a system of components designed for a specific task. While the "punch" and "die" form the heart of the tool, understanding the supporting parts—like the die set, guide posts, and stripper plates—is essential to grasping how precision and repeatability are achieved in mass production.
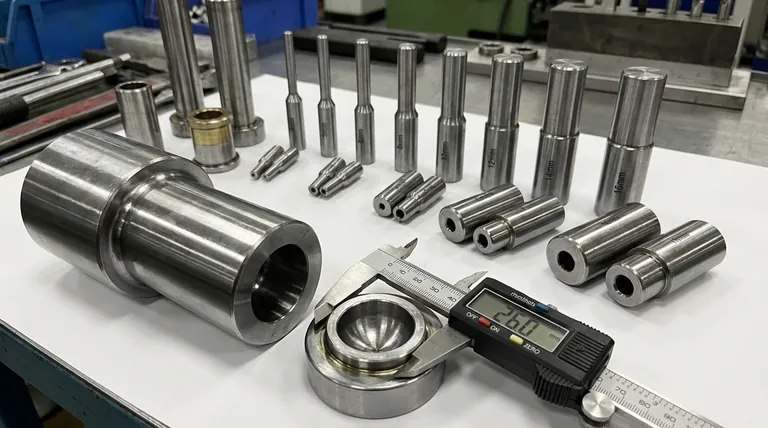

The Core Components: A Two-Sided System
Every press mold operates on the fundamental principle of a top and bottom half coming together to exert force. These two sides contain the primary shaping components.
The Punch (Upper Half)
The punch is typically the moving, upper portion of the mold. It is the "male" part of the tool that descends to apply pressure, often forming the interior shape of a component.
The Die (Lower Half)
The die is the stationary, lower half of the mold. It contains the "female" cavity that gives the part its final external shape. The raw material is placed on or in the die before the press cycle begins.
Key Supporting and Functional Parts
Beyond the two main shaping components, a series of critical parts ensure the mold functions with precision, safety, and efficiency.
The Die Set: The Foundation
The die set is the assembly that holds everything together. It consists of a top plate (for the punch) and a bottom plate (for the die), providing a solid foundation for mounting the mold into the press machine.
Guide Posts & Bushings: Ensuring Precision
Guide posts are hardened steel pins on one half of the die set that slide into bushings on the other half. Their sole purpose is to ensure the punch and die align perfectly every single time, which is critical for part quality and preventing tool damage.
The Stripper Plate: Releasing the Part
After a part is formed, it can stick to the punch. The stripper plate is a component designed to hold the stock material down during the process or to mechanically strip the finished part off the punch as it retracts.
Backing Plates: Providing Support
The immense forces involved in press molding can deform the primary tooling. Backing plates are thick, hardened steel plates placed behind the punch and die components to provide reinforcement and distribute the load.
Adapting the Mold for Different Processes
The term "press mold" can refer to tools used for stamping metal or for molding plastics and rubber. While the core principles are the same, the components are adapted for the material.
For Stamping & Forming (Metal)
This is the classic configuration described above. It uses a punch, die, die set, and stripper plates to cut, bend, or form sheet metal into a desired shape.
For Transfer Molding (Plastics/Rubber)
When working with materials like thermoset plastics or rubber, the mold requires additional parts. A plunger pushes raw material from a separate chamber, called a pot or cylinder, through channels and into the closed mold cavity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
It is crucial to recognize the economic and operational realities of using press molds.
High Initial Cost
Press dies are very expensive to design and manufacture. They require highly skilled labor and are machined from specialized, durable tool steels to withstand repeated high-pressure cycles.
Long-Term Value
The high upfront investment is justified by the mold's performance in mass production. Once built, a press mold can produce thousands or millions of parts with extremely high consistency and little variation in quality, leading to a very low cost per part.
Key Components by Molding Goal
To select the right design, you must first define your objective.
- If your primary focus is stamping or forming sheet metal: The key components are the punch, die, stripper plate, and guide posts for precise alignment.
- If your primary focus is transfer molding rubber or thermosets: In addition to the core components, you will need a transfer pot (or cylinder) and a plunger to inject the material into the mold cavity.
Understanding how these individual parts function as a system is the first step toward mastering the press molding process.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Function |
|---|---|
| Punch | The moving, upper 'male' part that applies pressure and forms the interior shape. |
| Die | The stationary, lower 'female' cavity that gives the part its external shape. |
| Die Set | The foundational assembly (top and bottom plates) that holds the mold components. |
| Guide Posts & Bushings | Ensure perfect alignment between the punch and die for consistent part quality. |
| Stripper Plate | Holds material down or strips the finished part off the punch after forming. |
| Backing Plates | Reinforce the tooling by distributing the immense forces involved in the process. |
Ready to optimize your production with precision press molds? At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, providing robust solutions for your molding and material shaping needs. Whether you're involved in metal stamping or plastic and rubber transfer molding, our expertise ensures you get durable, reliable tooling designed for mass production efficiency. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific requirements and help you achieve superior results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Multi-Punch Rotary Tablet Press Mold Ring for Rotating Oval and Square Molds
- Special Heat Press Mold for Lab Use
- Assemble Square Lab Press Mold for Laboratory Applications
- Cylindrical Press Mold for Lab Applications
- Polygon Press Mold for Lab
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of tablet press machine? Achieve High-Speed, Consistent Production
- What does a mould maker do? The Precision Engineer Behind Mass Production
- What is the use of tablet press? Transforming Powder into Precise, Uniform Tablets
- What is the impact factor of powder metallurgy progress? A 2022 Analysis & Context
- Which type of tablet press is more suitable for large scale production? Rotary Presses for High-Volume Efficiency









