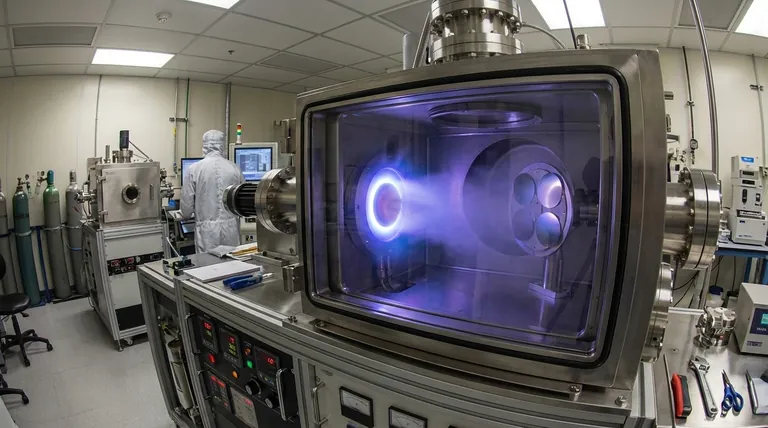
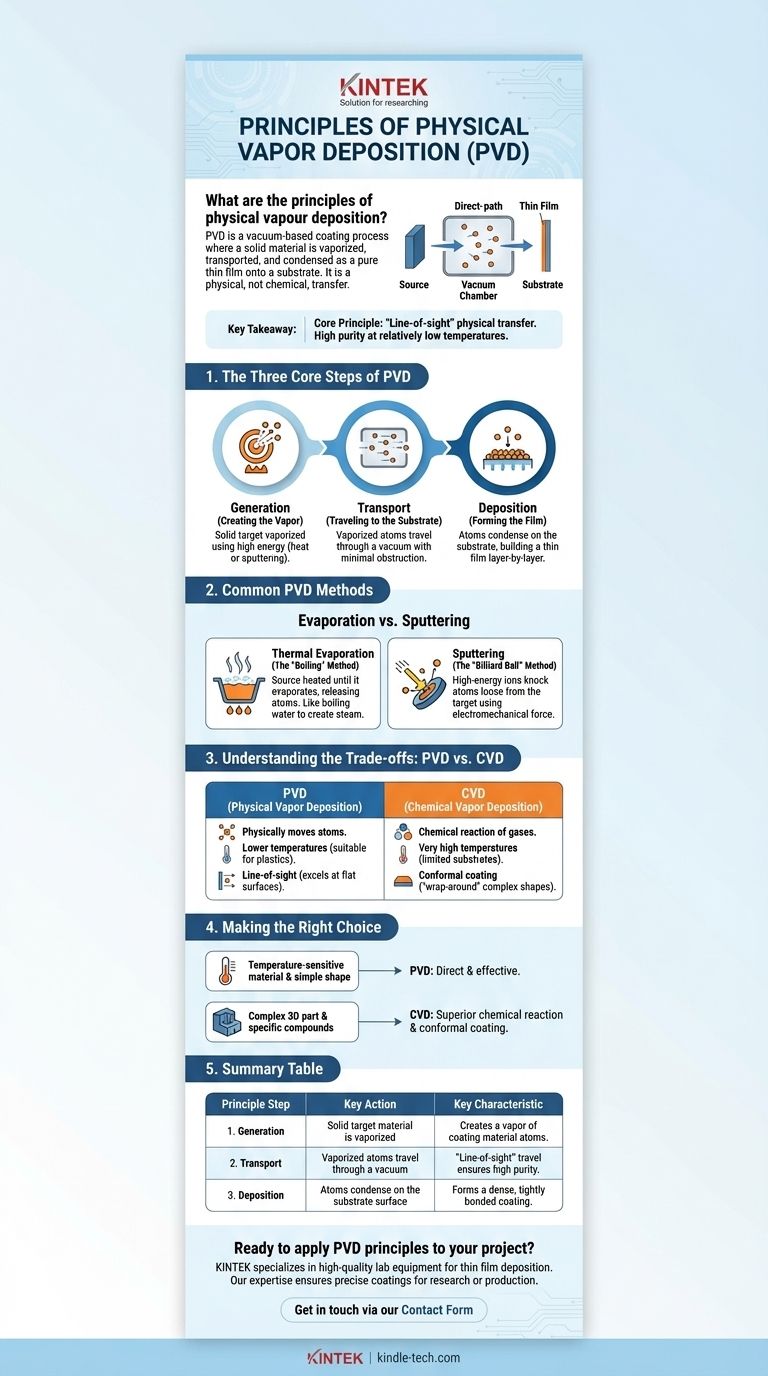
In essence, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a family of vacuum-based coating processes where a solid material is vaporized in a vacuum chamber, transported atom-by-atom across that chamber, and condensed onto a substrate's surface as a pure, high-performance thin film. This entire process is physical, not chemical, meaning the coating material is the same as the starting material, just in a different form.
The core principle distinguishing PVD is its "line-of-sight" physical transfer. Unlike chemical processes, PVD physically moves atoms from a source to a substrate without altering their chemical nature, offering high purity at relatively low temperatures.

The Three Core Steps of PVD
Every PVD process, regardless of the specific technique, follows a fundamental three-step sequence inside a vacuum chamber. The vacuum is critical because it allows atoms to travel from the source to the substrate without colliding with air molecules.
Step 1: Generation (Creating the Vapor)
The first step is to convert the solid source material, known as the "target," into a gaseous, vaporized state. This is achieved by supplying a high amount of energy to the target material.
The methods for generating this vapor are the primary differentiators between PVD techniques.
Step 2: Transport (Traveling to the Substrate)
Once atoms are freed from the source, they travel through the vacuum chamber. Because the chamber has very few gas molecules, the path from the source to the substrate is largely unobstructed.
This "line-of-sight" travel is a defining characteristic of PVD.
Step 3: Deposition (Forming the Film)
When the vaporized atoms arrive at the substrate—which is typically kept at a cooler temperature—they condense back into a solid state. They build up on the surface layer-by-layer, forming a thin, dense, and tightly bonded film.
Common PVD Methods: Evaporation vs. Sputtering
While there are many PVD variants, most fall into two main categories based on how they generate the vapor.
Thermal Evaporation: The "Boiling" Method
Thermal evaporation is the most straightforward PVD method. The source material is heated in the vacuum until it begins to boil and evaporate, releasing atoms.
This is analogous to boiling water to create steam, but it is done with solid materials like metals at extremely high temperatures and low pressures.
Sputtering: The "Billiard Ball" Method
Sputtering uses electromechanical force instead of just heat. First, a high-energy gas, typically Argon, is introduced into the chamber and ionized to create a plasma.
These high-energy ions are then accelerated into the target, striking it with such force that they knock atoms loose from the surface. These "sputtered" atoms then travel to the substrate and deposit as a film.
Understanding the Trade-offs: PVD vs. CVD
To fully grasp PVD, it's useful to contrast it with its counterpart, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
The Key Difference: Physical vs. Chemical
The fundamental distinction is in the name. PVD physically moves existing atoms from a source to a substrate. CVD uses a chemical reaction where precursor gases react near the substrate surface to form an entirely new solid material as the coating.
Temperature and Substrate Limitations
CVD typically requires very high temperatures (often 850-1100°C) to drive the necessary chemical reactions. This limits the types of materials that can be used as substrates.
PVD processes generally operate at much lower temperatures, making them suitable for coating heat-sensitive materials like plastics or certain alloys.
Conformal Coating ("Wrap-around")
Because CVD relies on a gas that can flow around an object, it offers excellent conformal coating, meaning it can uniformly coat complex shapes, sharp corners, and internal surfaces.
PVD, being a line-of-sight process, excels at coating flat surfaces but struggles to coat complex, three-dimensional geometries evenly.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The choice between PVD and a process like CVD depends entirely on the material properties, substrate sensitivity, and geometric complexity of your application.
- If your primary focus is coating a heat-sensitive material or achieving a high-purity metallic film on a simple geometry: PVD is the more direct and effective solution.
- If your primary focus is creating a uniform coating on a complex 3D part or depositing specific non-metal compounds like carbides or nitrides: CVD is often the superior technology due to its chemical reaction and gas-based nature.
Ultimately, understanding these core principles empowers you to select the process that aligns perfectly with your engineering requirements.
Summary Table:
| Principle Step | Key Action | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Generation | Solid target material is vaporized using high energy (heat or sputtering). | Creates a vapor of coating material atoms. |
| 2. Transport | Vaporized atoms travel through a vacuum chamber to the substrate. | "Line-of-sight" travel ensures high purity. |
| 3. Deposition | Atoms condense on the substrate surface, building a thin film layer-by-layer. | Forms a dense, tightly bonded coating. |
Ready to apply PVD principles to your project?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for all your thin film deposition needs. Whether you are researching new materials or scaling up production, our expertise ensures you have the right tools for precise, high-performance coatings.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities. Let's achieve your coating goals together.
Get in touch via our Contact Form
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
People Also Ask
- How do I choose a filter press? Match the Right Technology to Your Slurry for Optimal Results
- What is the mechanism of rapid cooling in FeCrAl alloy experiments? Validate Material Self-Healing & Safety.
- What is the use of oil sludge? Turn Hazardous Waste into Energy & Construction Materials
- What is a thin film circuit? Achieve Unmatched Miniaturization & High-Frequency Performance
- How do you prepare samples for SEM analysis? Achieve Clear, Accurate Imaging Every Time
- What is the process of slow heating and low temperature pyrolysis produces? Maximizing Biochar for Carbon Sequestration
- How does a larger area affect the pressure of the same force? Master the Physics of Force Distribution
- What are the properties of the sintering process? Achieve High-Strength, Complex Parts from Powder



















