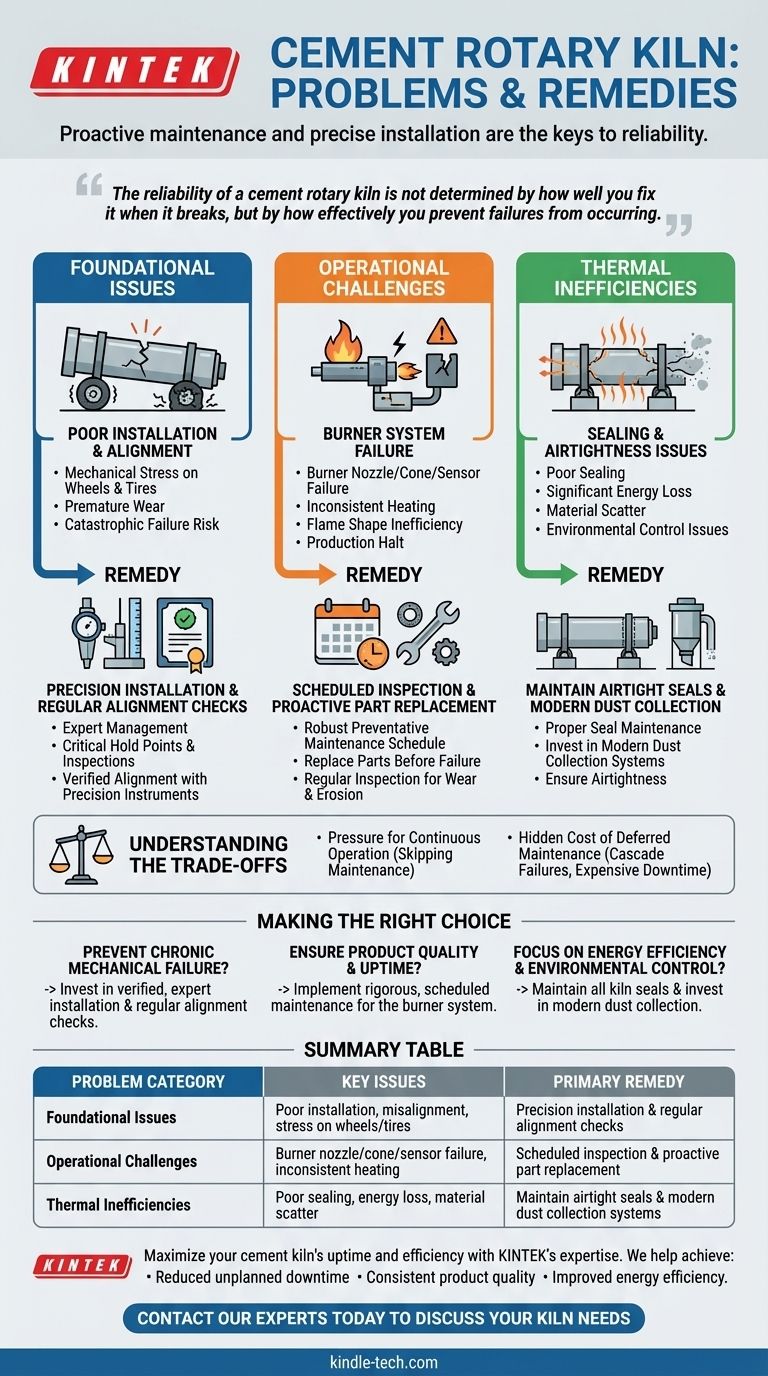
At its core, a rotary kiln's problems fall into three categories: foundational mechanical issues, operational component failure, and thermal inefficiencies. The most common challenges stem from poor installation causing mechanical stress on wheels and tires, failures within the burner system requiring part replacements, and issues with sealing that lead to energy loss and material scatter.
The reliability of a cement rotary kiln is not determined by how well you fix it when it breaks, but by how effectively you prevent failures from occurring. Proactive, systematic maintenance and a precise initial installation are the most effective remedies for nearly every common kiln problem.

Foundational Issues: Installation and Alignment
The long-term health of a rotary kiln is decided before it ever processes its first batch of material. Errors made during installation create chronic problems that are difficult and expensive to correct later.
The High Cost of a Flawed Start
A poorly executed installation can cause immediate and lasting damage. Improper handling may compromise the structural integrity of the drum shell itself, while missing critical inspection points during assembly can lead to voided warranties.
This initial phase is the single most important moment in the kiln's lifecycle. Rushing the process or using an inexperienced team creates a foundation of mechanical deficiencies.
Misalignment and Mechanical Stress
The most frequent consequence of a poor installation is misalignment. When the kiln is not perfectly aligned, it places immense, uneven stress on critical support components like the wheels (rollers) and tires (riding rings).
This constant stress leads to premature and excessive wear, increasing maintenance costs and creating the risk of catastrophic failure. It is a persistent problem that degrades the entire mechanical system over time.
The Remedy: Precision and Verification
The only effective remedy for installation-related issues is prevention. This requires a meticulous installation process managed by experts who adhere to a strict protocol of critical hold points and inspections.
Proper alignment must be verified with precision instruments before the kiln is commissioned. Investing heavily in getting the installation right from day one eliminates the single largest source of chronic mechanical failure.
Operational Challenges: The Burner System
The burner is the heart of the calcination process, responsible for generating and shaping the heat required to produce clinker. Its failure directly impacts production and product quality.
Critical Burner Component Failures
The burner is a complex assembly, and several of its parts are subject to intense heat and wear. The most common failure points include the burner nozzle, the burner cone, and various burner sensors.
When any of these components degrade or fail, the kiln cannot operate as designed. The flame shape may become inefficient, temperature control may be lost, or the system may shut down entirely.
The Remedy: Scheduled Inspection and Replacement
The solution to burner-related issues is a robust preventative maintenance schedule. These critical components should be regularly inspected for wear, erosion, and malfunction.
Rather than waiting for a failure to halt production, parts should be replaced based on a known operational lifespan. This proactive approach ensures the kiln's thermal system remains reliable and efficient.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Managing a rotary kiln involves a constant balance between maximizing production output and ensuring long-term mechanical integrity. Short-term decisions often have significant long-term consequences.
The Pressure for Continuous Operation
The primary business driver is to keep the kiln running to maximize clinker production. This often creates pressure to shorten or skip scheduled maintenance shutdowns.
The Hidden Cost of Deferred Maintenance
Delaying critical maintenance, such as alignment checks or burner component replacement, is a high-risk gamble. A minor issue that could be fixed during a planned stop can easily cascade into a major failure, causing an unplanned shutdown that is far longer and more expensive.
The cost of a catastrophic failure in terms of lost production and emergency repairs almost always outweighs the perceived benefit of pushing the kiln past its maintenance limits.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
A proactive approach is the most effective strategy for ensuring the long-term reliability and efficiency of your rotary kiln. Your maintenance priorities should align with your primary operational goals.
- If your primary focus is preventing chronic mechanical failure: Invest in a verified, expert installation and conduct regular, precise alignment checks.
- If your primary focus is consistent product quality and uptime: Implement a rigorous, scheduled maintenance program for the burner system, proactively replacing nozzles, cones, and sensors.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency and environmental control: Ensure all kiln seals are properly maintained to ensure airtightness and invest in modern dust collection systems.
Viewing the kiln as an integrated system, where the health of one component affects all others, is the key to achieving sustained and predictable performance.
Summary Table:
| Problem Category | Key Issues | Primary Remedy |
|---|---|---|
| Foundational Issues | Poor installation, misalignment, stress on wheels/tires | Precision installation & regular alignment checks |
| Operational Challenges | Burner nozzle/cone/sensor failure, inconsistent heating | Scheduled inspection & proactive part replacement |
| Thermal Inefficiencies | Poor sealing, energy loss, material scatter | Maintain airtight seals & modern dust collection systems |
Maximize your cement kiln's uptime and efficiency with KINTEK's expertise.
Don't let preventable issues like misalignment or burner failure disrupt your production schedule and impact your bottom line. KINTEK specializes in providing the high-quality lab equipment, consumables, and technical support needed for proactive maintenance and precise operation.
We help our customers in the cement industry achieve:
- Reduced unplanned downtime through reliable components and expert guidance.
- Consistent product quality with precise thermal control solutions.
- Improved energy efficiency by addressing sealing and heat loss issues.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific rotary kiln maintenance and operational goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a rotary calciner work? Achieve Uniform Thermal Processing for Bulk Solids
- What does calcination do? Purify and Transform Materials with Controlled Heat
- What role does a rotary kiln play in the incineration treatment of waste composite materials? Energy & Volume Solutions
- What is the thermal regeneration process of activated carbon? Restore Performance and Cut Costs
- What is the use of catalyst in plastic pyrolysis? Boost Efficiency and Fuel Quality
- What is pyrolysis rate? Mastering Control for Optimal Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas Production
- How is calcination process performed? Master Thermal Decomposition for Industrial Applications
- What is the sintering process in kilns? Transform Powder into Dense, High-Strength Components



















