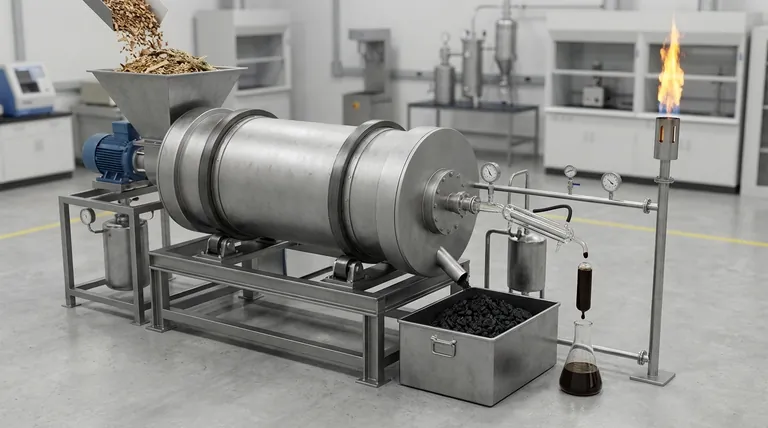
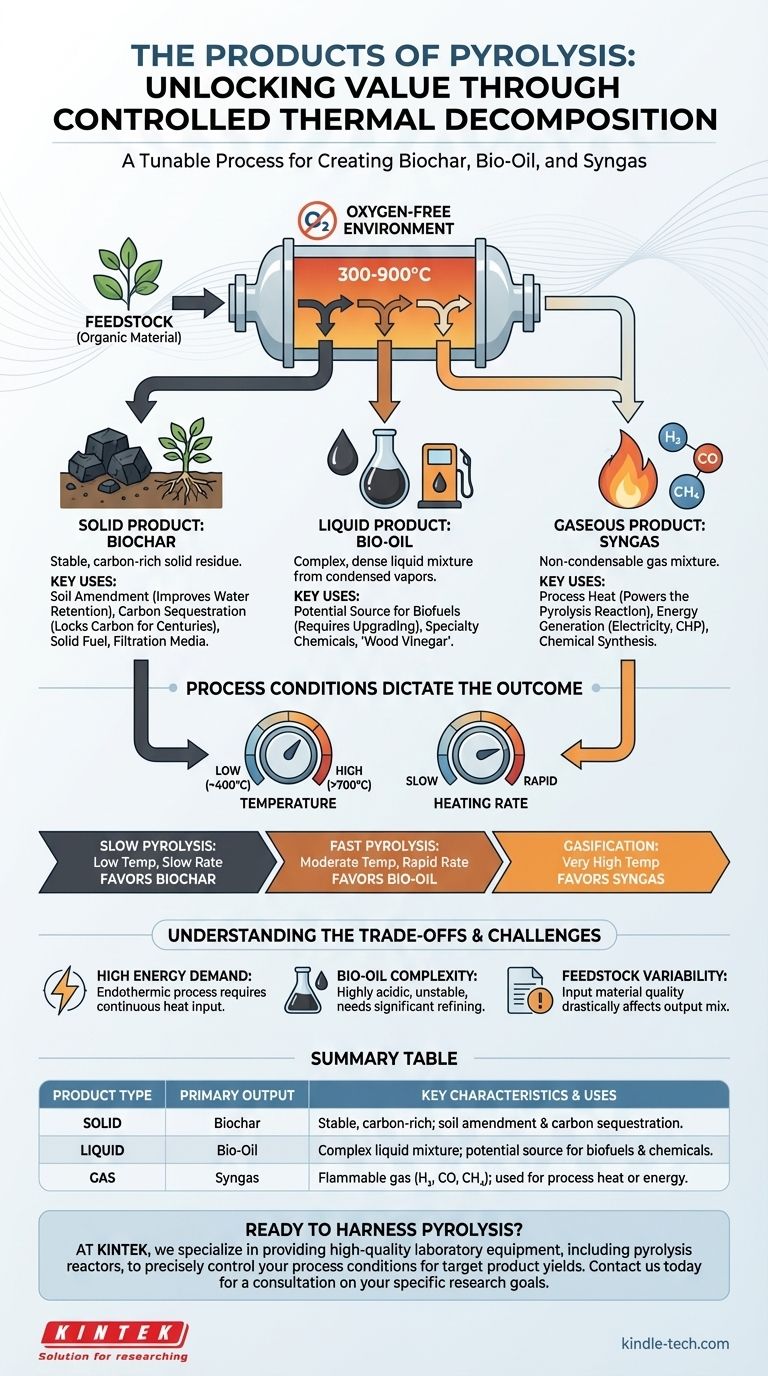
The products of pyrolysis fall into three distinct categories: a solid, a liquid, and a gas. When organic material is heated to high temperatures (typically 300-900°C) in an environment without oxygen, it doesn't burn; it thermally decomposes. This process breaks down complex molecules into a stable, carbon-rich solid known as biochar, a complex liquid mixture called bio-oil, and a collection of non-condensable gases referred to as syngas.
Pyrolysis is not a single reaction but a tunable process. The key takeaway is that you can control the conditions—primarily temperature and heating rate—to deliberately favor the production of either the solid (biochar), the liquid (bio-oil), or the gas (syngas), depending on your end goal.

The Pyrolysis Process: A Controlled Decomposition
What is Pyrolysis?
Pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of materials at elevated temperatures in an inert atmosphere. It involves a change in chemical composition and is an irreversible process.
Think of it as a high-temperature pressure cooker for organic matter. Instead of burning the material away into ash and smoke, the absence of oxygen forces it to break apart into its fundamental chemical components.
Why the Absence of Oxygen is Critical
Oxygen is the key ingredient for combustion (burning). By removing it from the reaction chamber, we prevent the feedstock from simply burning.
This ensures the energy put into the system is used to break chemical bonds within the material, yielding a set of valuable and often energy-dense products rather than just heat and ash.
A Breakdown of the Core Products
The distribution of products from pyrolysis is highly dependent on the process conditions and the feedstock used. However, they always fall into these three categories.
The Solid Product: Biochar
Biochar is a stable, charcoal-like solid that is rich in carbon. It is the solid residue left after the volatile components have been driven off as liquids and gases.
Its primary uses include soil amendment, where it can improve water retention and soil structure, and carbon sequestration, as it locks carbon into a stable form for hundreds or even thousands of years. It can also be used as a solid fuel or activated to create filtration media.
The Liquid Product: Bio-Oil
Also known as pyrolysis oil, tar, or wood vinegar, bio-oil is a dark, dense liquid mixture. It is formed by condensing the condensable portion of the pyrolysis vapors.
This complex liquid contains water, acids, alcohols, and hundreds of other organic compounds. While it can be a source for specialty chemicals, its main interest lies in its potential to be upgraded or refined into biofuels, similar to crude fossil oil.
The Gaseous Product: Syngas
Syngas (synthesis gas) is the non-condensable fraction of the pyrolysis output. It is a mixture of various gases.
This includes flammable components like hydrogen (H₂), carbon monoxide (CO), and methane (CH₄), as well as non-flammable components like carbon dioxide (CO₂) and nitrogen (N₂). This gas is often captured and used to provide the heat for the pyrolysis process itself, making the system more energy efficient.
How Process Conditions Dictate the Outcome
You cannot simply "do" pyrolysis and get a fixed result. The output is a direct function of the process parameters you choose.
The Role of Temperature and Heating Rate
The two most important levers you can pull are temperature and the rate at which the feedstock is heated. These variables determine which reaction pathways are favored.
-
Slow Pyrolysis: Lower temperatures (~400°C) and slow heating rates favor the production of biochar. The long processing time allows for the formation of stable carbon structures.
-
Fast Pyrolysis: Moderate to high temperatures (~500°C) with very rapid heating rates and short vapor residence times favor the production of bio-oil. This process vaporizes the organic matter quickly and condenses it before it can break down further into gas.
-
Gasification: Very high temperatures (>700°C) and longer residence times begin to favor the production of syngas. While technically a different process, it exists on the same spectrum as pyrolysis and is designed to break everything down into the simplest gaseous molecules.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While a powerful technology, pyrolysis is not a magic bullet. It comes with significant technical and economic challenges that must be understood.
High Energy Demand
Pyrolysis is an endothermic process, meaning it requires a continuous input of energy to maintain the high temperatures needed for decomposition. While the syngas produced can be used to offset this, the initial energy investment and process efficiency are critical concerns.
Bio-Oil Complexity
Bio-oil is not a "drop-in" replacement for crude oil. It is highly acidic, corrosive to standard pipes and engines, and chemically unstable over time. It requires significant and often costly secondary processing (upgrading) before it can be used as a transportation fuel.
Feedstock Variability
The type and quality of the input material—whether it's wood chips, agricultural waste, or plastic—dramatically affect the final product mix and quality. A consistent and well-prepared feedstock is crucial for achieving predictable and efficient operation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal pyrolysis strategy depends entirely on the product you value most.
- If your primary focus is carbon sequestration or soil improvement: Employ slow pyrolysis at lower temperatures to maximize the yield of stable, high-carbon biochar.
- If your primary focus is producing liquid biofuels or chemical precursors: Use fast pyrolysis with rapid heating and quenching to maximize the yield and quality of your bio-oil.
- If your primary focus is waste reduction and energy generation: Design the system to prioritize syngas production (or simply burn all products) to generate heat and electricity in a combined heat and power (CHP) configuration.
Ultimately, understanding that you can steer the output of pyrolysis is the first step toward effectively applying this technology to your specific goal.
Summary Table:
| Product Type | Primary Output | Key Characteristics & Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Solid | Biochar | Stable, carbon-rich solid; used for soil amendment & carbon sequestration. |
| Liquid | Bio-Oil | Complex liquid mixture; a potential source for biofuels and chemicals. |
| Gas | Syngas | Flammable gas mixture (H₂, CO, CH₄); used for process heat or energy. |
Ready to harness the power of pyrolysis in your lab?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality laboratory equipment, including pyrolysis reactors and ovens, to help you precisely control the process conditions needed to produce your target product—whether it's biochar, bio-oil, or syngas. Our experts can help you select the right equipment for your specific feedstock and research goals.
Contact us today using the form below to discuss your project and discover how KINTEK's solutions can advance your work in sustainable materials and energy research.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Mesh belt controlled atmosphere furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs



















