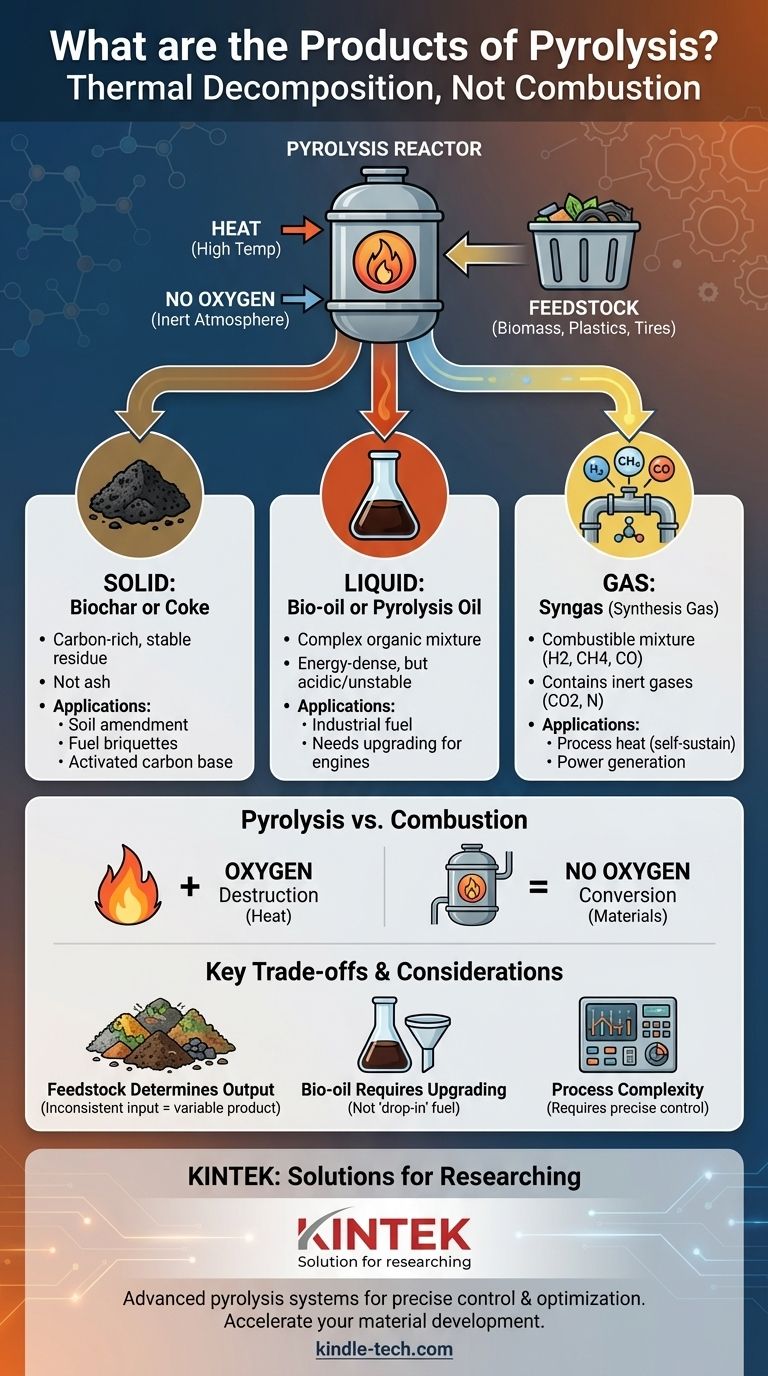
At its core, pyrolysis is not a form of combustion but rather a thermal decomposition process that occurs in the absence of oxygen. Instead of burning material, it breaks it down into three distinct categories of valuable products: a solid char, a liquid bio-oil, and a combustible gas mixture. The specific products depend heavily on the original material being processed and the precise conditions of the reaction.
Pyrolysis should be understood as a material conversion technology, not a simple waste destruction method. It transforms feedstock into a carbon-rich solid (biochar), a complex liquid fuel (bio-oil), and a combustible gas (syngas), each with its own potential applications.

A Critical Distinction: Pyrolysis vs. Combustion
To understand the products of pyrolysis, it's essential to first distinguish it from combustion (or incineration). This distinction is the key to grasping its purpose.
What is Combustion?
Combustion is a high-temperature chemical reaction between a fuel and an oxidant, almost always oxygen. It is an exothermic process that releases heat and light. Its primary goal is to completely destroy the fuel to generate heat.
What is Pyrolysis?
Pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of materials at high temperatures in an inert atmosphere, meaning an environment with little to no oxygen. Instead of burning the material, it breaks down its complex molecules into smaller, more stable ones, effectively deconstructing it into its core components.
The Three Primary Products of Pyrolysis
Regardless of the feedstock, the output of pyrolysis is almost always a combination of solids, liquids, and gases. The ratio and specific composition of these products are controlled by process parameters like temperature and heating rate.
The Solid Product: Biochar or Coke
Once the volatile components of the feedstock are driven off as liquids and gases, a stable, carbon-rich solid residue remains. This is often called biochar (when from biomass) or coke.
This solid product is not ash. It has significant uses as a fuel source in briquettes, an agricultural soil amendment to improve water retention, or as a base material for activated carbon used in filtration. When pyrolyzing tires, this solid stream also includes recovered steel wire.
The Liquid Product: Bio-oil or Tar
As the pyrolysis process cools its gaseous output, a significant portion condenses into a liquid. This is commonly known as pyrolysis oil (bio-oil), though it may also be referred to as tar or wood vinegar depending on the feedstock.
This liquid is a complex mixture of water, organic acids, alcohols, and hundreds of other organic compounds. It is energy-dense and can be used as an industrial fuel oil or, with significant refining, upgraded into transportation fuels like biodiesel.
The Gaseous Product: Syngas
The components that do not condense into a liquid are known as non-condensable gases, or syngas (synthesis gas). This is a mixture of combustible and non-combustible gases.
The typical components include hydrogen (H2), methane (CH4), carbon monoxide (CO), and various other hydrocarbons. It also contains inert gases like carbon dioxide (CO2) and nitrogen (N). This gas has a low-to-modest heating value and is very often redirected to provide the heat for the pyrolysis reactor, making the entire process more energy-efficient and self-sustaining.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, pyrolysis is not a perfect solution. Understanding its limitations is critical for proper application.
Feedstock Determines Output
The single greatest variable is the input material, or feedstock. The products from pyrolyzing wood biomass (biochar, wood vinegar) are very different from the products of pyrolyzing waste plastic or tires (carbon black, hydrocarbon-rich fuel oil). Inconsistent feedstock leads to inconsistent products.
Bio-oil Requires Upgrading
Pyrolysis oil is not a "drop-in" replacement for diesel or gasoline. It is typically acidic, corrosive, and chemically unstable over time. It almost always requires a secondary refining or upgrading process to be used in conventional engines or chemical supply chains.
Process Complexity
Pyrolysis plants are more technologically complex and capital-intensive than simple incinerators. They require precise control over temperature, pressure, and feedstock handling to produce a consistent and high-quality product slate.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Pyrolysis is best viewed as a flexible platform technology. The "best" application depends entirely on your end goal.
- If your primary focus is waste volume reduction and energy recovery: Pyrolysis is highly effective at converting the bulk of waste into energy-dense products (oil and gas) while creating a small volume of stable, manageable solid char.
- If your primary focus is creating valuable materials: Pyrolysis can be optimized to maximize the output of biochar for agriculture or high-grade carbon black for industrial use in pigments and manufacturing.
- If your primary focus is producing alternative liquid fuels: Pyrolysis is a direct pathway to creating a liquid fuel from solid waste, but you must account for the necessity and cost of post-processing and upgrading the raw bio-oil.
Ultimately, pyrolysis empowers us to see waste not as something to be destroyed, but as a resource to be converted into more valuable forms.
Summary Table:
| Product Type | Common Name(s) | Key Characteristics | Primary Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solid | Biochar, Coke | Carbon-rich, stable residue from biomass or other feedstocks. | Fuel briquettes, soil amendment, activated carbon base. |
| Liquid | Bio-oil, Pyrolysis Oil | Complex mixture of organic compounds; energy-dense but requires refining. | Industrial fuel, potential source for upgraded transportation fuels. |
| Gas | Syngas | Mixture of combustible gases (H2, CH4, CO) and inert gases. | On-site heat generation for the pyrolysis reactor, fuel source. |
Ready to transform your material conversion process?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced pyrolysis solutions for laboratories and research facilities. Our equipment is designed for precise control over temperature and atmosphere, enabling you to optimize product yields—whether your goal is maximizing biochar for agricultural research, producing bio-oil for fuel studies, or generating syngas for energy recovery.
Let our experts help you select the right pyrolysis system for your specific feedstock and research objectives. Contact us today to discuss how KINTEK's lab equipment can accelerate your development of sustainable materials and fuels.
Get in touch with our pyrolysis specialists now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Mesh belt controlled atmosphere furnace
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time



















