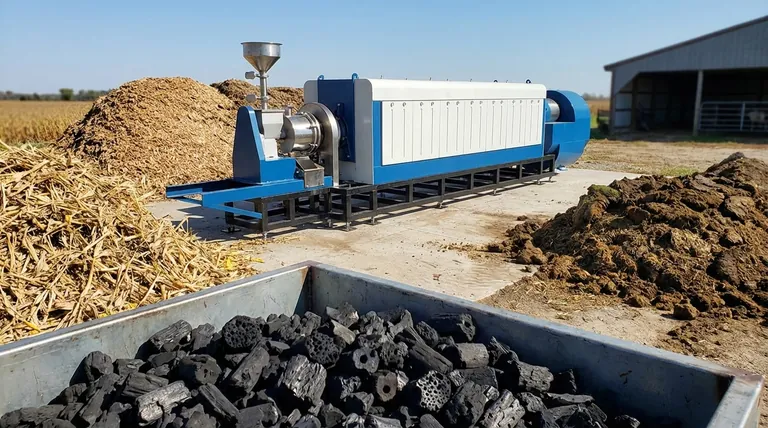
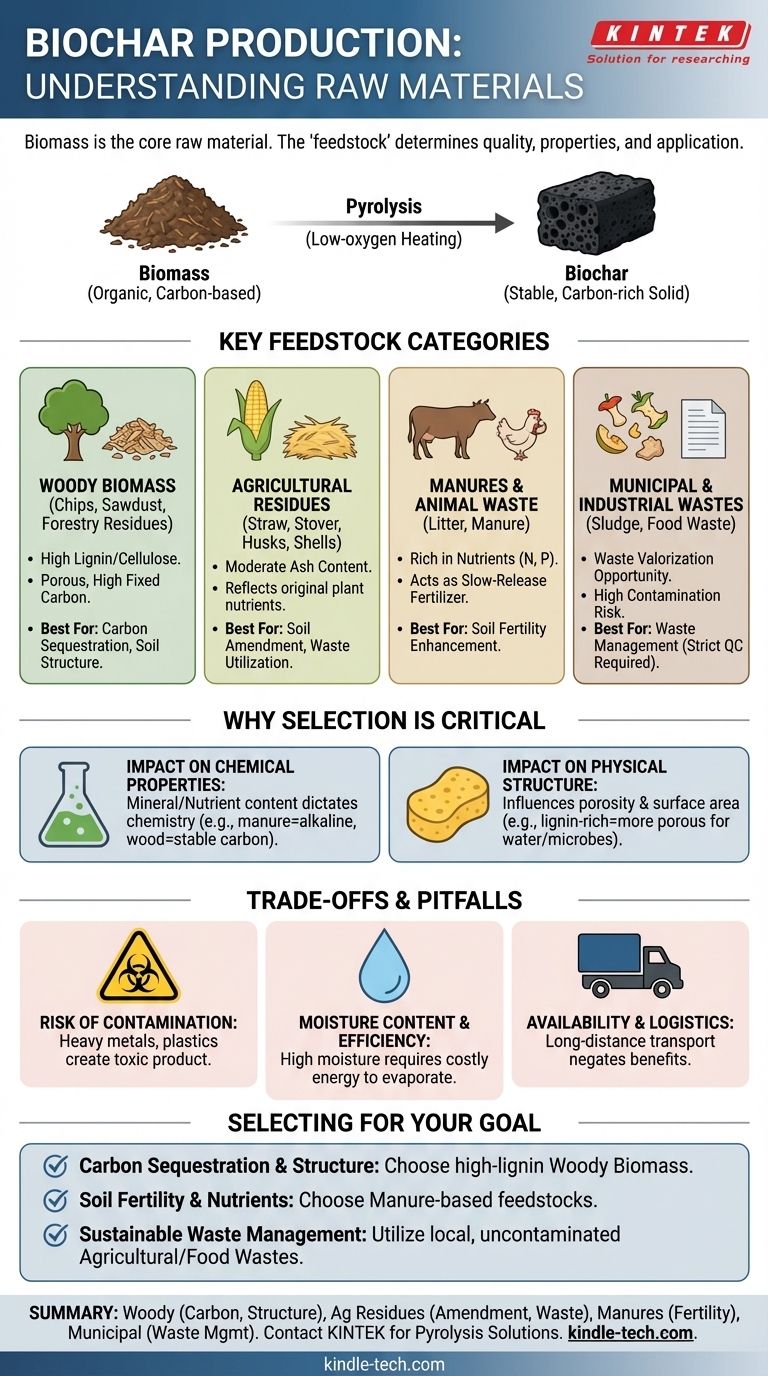
In short, the raw material for biochar is biomass. This includes a vast range of organic, carbon-based materials, from agricultural crop residues and wood waste to animal manures. The specific type of biomass used, known as the "feedstock," is the single most important factor determining the final properties and quality of the biochar.
The fundamental principle is that almost any organic material can be converted into biochar through a process called pyrolysis. However, the choice of feedstock is not arbitrary; it is a critical decision that dictates the biochar's chemical composition, physical structure, and ultimate suitability for its intended purpose.

What Qualifies as a Biochar Feedstock?
A suitable feedstock is any raw organic material that can be heated in a low-oxygen environment to create a stable, carbon-rich solid. These materials are broadly categorized based on their origin.
Woody Biomass
This category includes materials like wood chips, sawdust, forestry residues, and dedicated energy crops like willow.
Woody feedstocks are high in lignin and cellulose. This structure results in biochar that is typically high in fixed carbon, structurally robust, and highly porous, making it excellent for long-term carbon sequestration and improving soil aeration.
Agricultural Residues
This is one of the most common and abundant feedstock sources, including materials like corn stover, wheat straw, rice husks, and nut shells.
These materials often produce biochar with a higher ash content compared to woody biomass. The specific nutrient profile of the resulting biochar will directly reflect the nutrients present in the original plant material.
Manures and Animal Waste
This category includes poultry litter, cattle manure, and other animal bedding materials.
Biochar produced from manure is significantly richer in nutrients like phosphorus and nitrogen. This makes it function more like a slow-release fertilizer, though it often has a lower fixed carbon content and is less stable over geological timescales.
Municipal and Industrial Wastes
Feedstocks can also include sources like paper sludge, food processing waste, and biosolids.
While this presents an excellent opportunity for waste valorization, it requires the most stringent quality control. The risk of contamination from heavy metals, plastics, or other unwanted chemicals is highest in this category.
Why Feedstock Selection is Critical
The initial composition of the raw material directly translates into the final characteristics of the biochar. Understanding this link is essential for producing a product fit for a specific application.
The Impact on Chemical Properties
A feedstock's inherent mineral and nutrient content dictates the final biochar's chemistry. For example, manure-based feedstocks lead to nutrient-rich, alkaline biochar ideal for fertilizing acidic soils. In contrast, wood-based biochar is lower in nutrients but higher in stable carbon.
The Impact on Physical Structure
The physical makeup of the feedstock influences the biochar's resulting porosity and surface area. Lignin-rich woody biomass tends to create a more porous, high-surface-area biochar, which is superior for improving soil water retention and providing a habitat for beneficial microbes.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
Choosing a feedstock is not just about the ideal final product; it involves practical and environmental considerations.
The Risk of Contamination
This is the most significant pitfall. Using feedstocks contaminated with heavy metals, herbicides, plastics, or construction waste (e.g., treated or painted wood) will create a toxic product. These contaminants become concentrated during pyrolysis and can permanently damage soil and water systems.
Moisture Content and Efficiency
Feedstocks must be relatively dry for pyrolysis to be energy-efficient. A high moisture content requires a large amount of energy simply to evaporate water before the carbonization process can even begin, making the entire operation inefficient and costly.
Availability and Logistics
The most sustainable and cost-effective approach is to use locally abundant waste streams. Transporting bulky biomass over long distances can negate the environmental and economic benefits of producing biochar.
Selecting the Right Feedstock for Your Goal
Your intended application should guide your choice of raw material.
- If your primary focus is long-term carbon sequestration and improving soil structure: Choose high-lignin woody biomass like wood chips or forestry residues for a stable, porous, and high-carbon product.
- If your primary focus is enhancing soil fertility and nutrient content: Choose manure-based feedstocks or nutrient-accumulating crop residues to create a biochar that acts as a slow-release organic fertilizer.
- If your primary focus is sustainable waste management: Utilize locally available, uncontaminated agricultural or food processing wastes, turning a potential liability into a valuable soil amendment.
Ultimately, the selection of the raw material is the foundational decision that defines the value, function, and safety of the final biochar.
Summary Table:
| Feedstock Category | Common Examples | Key Characteristics | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Woody Biomass | Wood chips, sawdust, forestry residues | High in lignin/cellulose, porous, high fixed carbon | Carbon sequestration, soil structure |
| Agricultural Residues | Straw, corn stover, rice husks, nut shells | Moderate ash content, reflects original plant nutrients | Soil amendment, waste utilization |
| Manures & Animal Waste | Poultry litter, cattle manure | High in nutrients (N, P), acts as slow-release fertilizer | Soil fertility enhancement |
| Municipal/Industrial Waste | Paper sludge, food waste, biosolids | Opportunity for waste valorization | Waste management (requires strict quality control) |
Ready to produce high-quality biochar for your specific application?
The right feedstock is critical, but so is the right equipment. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and pyrolysis systems tailored for biomass conversion. Whether you're researching feedstock properties or scaling up production, our solutions ensure efficiency, safety, and consistent results.
Let KINTEK empower your biochar project. Contact our experts today to discuss your needs and find the perfect equipment for your laboratory or production facility.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- High Performance Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Research and Development
People Also Ask
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions

















