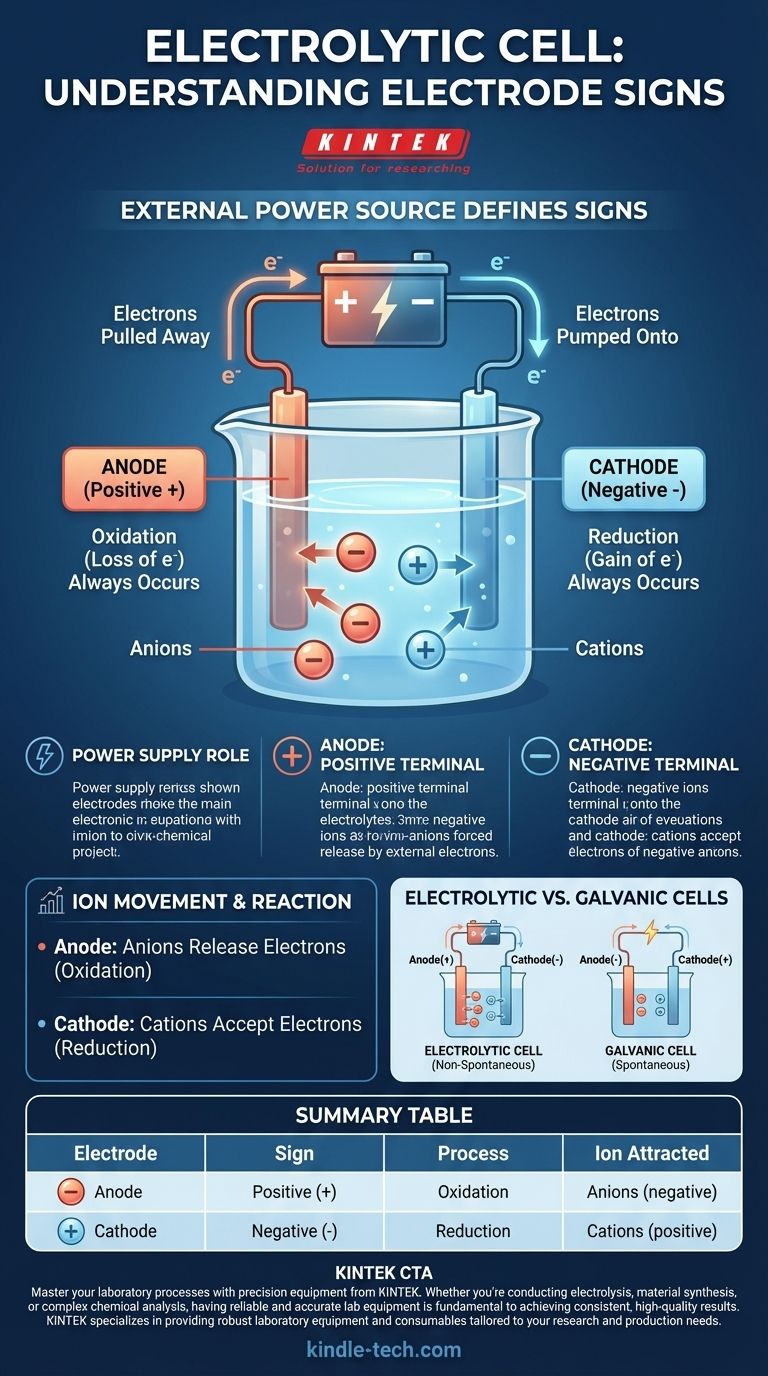
In an electrolytic cell, the sign convention is defined by the external power source. The anode is assigned a positive (+) sign, and the cathode is assigned a negative (-) sign. This is because an external voltage is applied to drive a chemical reaction that would not occur spontaneously.
The key to understanding an electrolytic cell is to recognize that it is not a self-contained system. The signs of its electrodes are dictated entirely by the external power supply to which it is connected, forcing a non-spontaneous chemical change to occur.
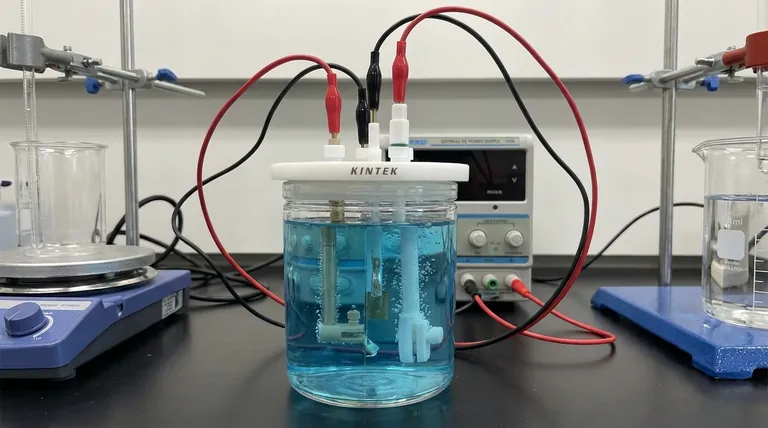

Why an External Power Source Defines the Signs
An electrolytic cell uses electrical energy to create chemical energy. This process, known as electrolysis, requires an outside force—a battery or DC power supply—to initiate and sustain the reaction.
The Role of the Power Supply
The power supply acts as an "electron pump." It pulls electrons from one electrode and pushes them to the other, creating a charge imbalance that forces ions in the electrolyte solution to react.
The Anode is Connected to the Positive Terminal
The positive terminal of the external power supply is connected to the anode. This terminal actively pulls electrons away from the anode, leaving it with a net positive charge.
The Cathode is Connected to the Negative Terminal
Conversely, the negative terminal of the power supply is connected to the cathode. This terminal actively pumps electrons onto the cathode, giving it an excess of electrons and a net negative charge.
How Ion Movement Creates the Reaction
The forced charges on the electrodes are what attract the ions dissolved in the electrolyte, compelling them to move and react. The fundamental definitions of oxidation and reduction remain constant.
Anode: The Site of Oxidation (Always)
Regardless of the cell type, oxidation (the loss of electrons) always occurs at the anode. In an electrolytic cell, negatively charged ions (anions) are attracted to the positive anode, where they release their excess electrons and are oxidized.
Cathode: The Site of Reduction (Always)
Similarly, reduction (the gain of electrons) always occurs at the cathode. Positively charged ions (cations) in the solution are attracted to the negative cathode, where they accept the excess electrons and are reduced.
A Critical Distinction: Electrolytic vs. Galvanic Cells
A primary source of confusion arises when comparing electrolytic cells to galvanic (or voltaic) cells, such as a standard battery. Their sign conventions are opposite for a very specific reason.
Spontaneous vs. Non-Spontaneous Reactions
A galvanic cell runs on a spontaneous chemical reaction that produces electrical energy. Here, the anode is the natural source of electrons, making it negative, and the cathode is where they are consumed, making it positive.
An electrolytic cell runs a non-spontaneous reaction that consumes electrical energy. The external power source reverses the natural polarity to force the reaction to proceed.
The Universal Constant
Despite the difference in signs, the core processes are the same in both cell types:
- Anode is always the site of Oxidation.
- Cathode is always the site of Reduction.
How to Remember the Signs
Use these principles to keep the conventions clear based on your goal.
- If your primary focus is identifying the terminals: Remember that in an electrolytic cell, the signs match the external power supply: the Anode is Positive and the Cathode is Negative.
- If your primary focus is tracking the ions: Follow the simple rule of opposite charges: negative anions move to the positive anode, and positive cations move to the negative cathode.
- If your primary focus is distinguishing cell types: Associate "electrolytic" with an external power source that forces a positive charge on the anode and a negative charge on the cathode to drive the reaction.
Ultimately, the signs of an electrolytic cell are a direct consequence of an external power source overriding the natural flow of a chemical reaction.
Summary Table:
| Electrode | Sign | Process | Ion Attracted |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anode | Positive (+) | Oxidation | Anions (negative) |
| Cathode | Negative (-) | Reduction | Cations (positive) |
Master your laboratory processes with precision equipment from KINTEK.
Whether you're conducting electrolysis, material synthesis, or complex chemical analysis, having reliable and accurate lab equipment is fundamental to achieving consistent, high-quality results. KINTEK specializes in providing robust laboratory equipment and consumables tailored to your research and production needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can power your innovations and enhance the efficiency of your laboratory workflows.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Five-Port
- Double Layer Five-Port Water Bath Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
- Double-Layer Water Bath Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
- Quartz Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Electrochemical Experiments
- Optical Water Bath Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
People Also Ask
- What are the standard components of the five-port water bath electrolytic cell? Master the Precision Instrument for Electrochemical Analysis
- What is the proper way to handle a five-port water bath electrolytic cell? Ensure Accurate and Safe Electrochemical Experiments
- What general precaution should be taken when handling the electrolytic cell? Ensure Safe and Accurate Lab Results
- What material is the five-port water bath electrolytic cell made of? High Borosilicate Glass & PTFE Explained
- How should the five-port water bath electrolytic cell be cleaned for maintenance? A Step-by-Step Guide to Reliable Results



















