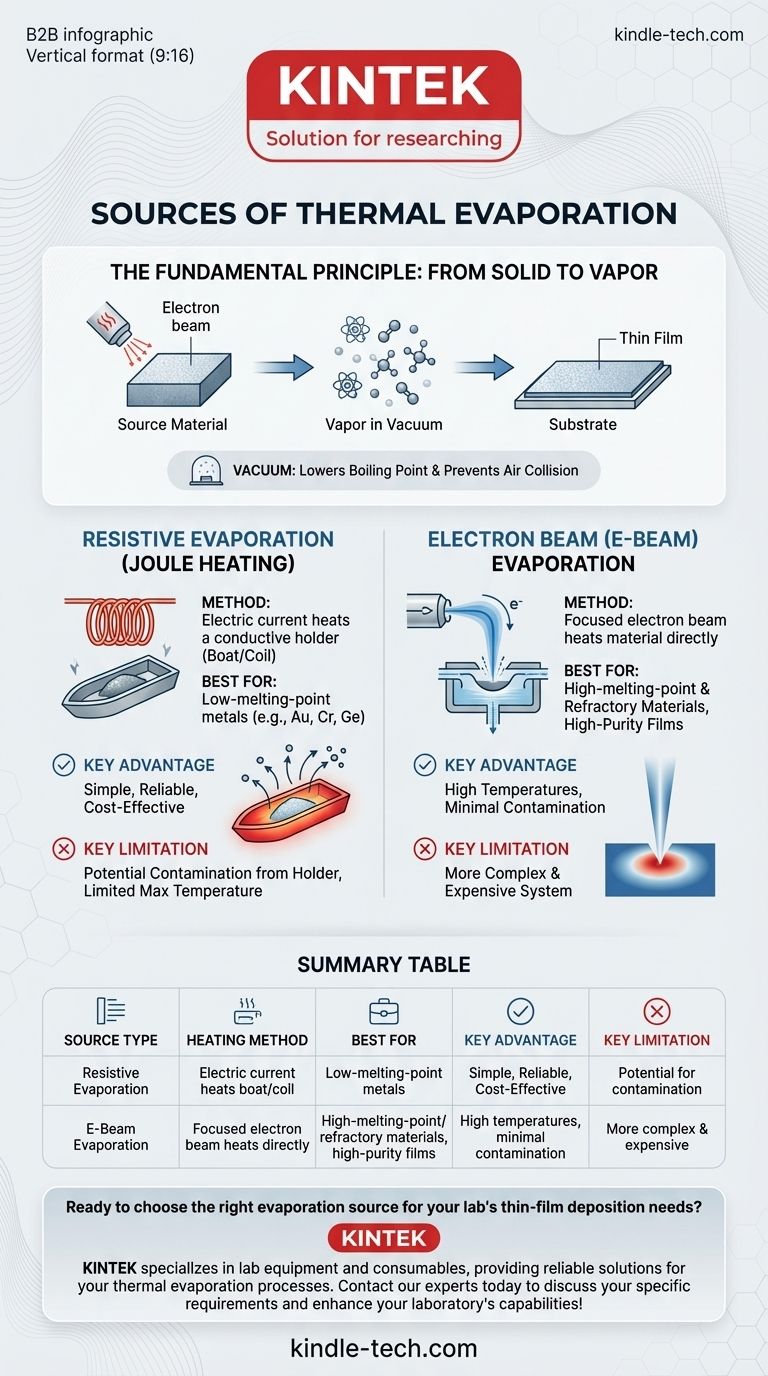
In thermal evaporation, the heat required to vaporize a source material is generated through two primary methods: resistive heating and electron beam heating. Resistive evaporation, the more common and simpler method, uses an electric current to heat a boat or coil holding the material. Electron beam (e-beam) evaporation uses a focused beam of high-energy electrons to directly heat the source material, allowing for much higher temperatures.
The core challenge in thermal evaporation is delivering enough energy to a source material to make it vaporize in a vacuum. The choice of heat source—either a resistively heated element or a focused electron beam—is determined by the material's melting point and the required purity of the final film.

The Fundamental Principle: From Solid to Vapor
Before comparing sources, it's crucial to understand the shared process they enable. All thermal evaporation techniques operate on the same fundamental principle.
Heating to the Point of Vaporization
The goal is to heat a source material until its atoms or molecules gain enough thermal energy to break free from the solid or liquid state. This transforms the material into a vapor within a vacuum chamber.
The Critical Role of Vacuum
The entire process occurs under high vacuum. This serves two purposes: it lowers the boiling point of the material and, more importantly, it ensures the vaporized atoms can travel to the target without colliding with air molecules.
Condensation and Film Growth
These vaporized atoms travel in a straight line until they strike a cooler surface, known as the substrate. Upon impact, they lose energy, condense back into a solid state, and gradually build up to form a thin film.
A Closer Look at Evaporation Sources
The key differentiator between thermal evaporation techniques is how the heat is generated and applied to the source material.
Resistive Evaporation (Joule Heating)
This is the most direct and widely used method. An electric current is passed through a conductive, heat-resistant holder, often called a boat, basket, or coil.
The holder is typically made from a refractory metal like tungsten or molybdenum. The source material, often in pellet or powder form, is placed directly into this holder. As the current flows, the holder's electrical resistance generates intense heat (Joule heating), which is then transferred to the source material, causing it to melt and evaporate.
Electron Beam (E-Beam) Evaporation
This is a more advanced and powerful technique. Instead of heating a container, a high-energy beam of electrons is generated and magnetically steered to strike the surface of the source material directly.
This focused energy transfer is extremely efficient, heating only a small portion of the material to a very high temperature. The surrounding material stays cool, acting as its own crucible and minimizing contamination.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Each method presents a distinct set of advantages and limitations. The choice is not about which is "better" but which is appropriate for the task.
The Simplicity and Limits of Resistive Evaporation
Resistive evaporation is valued for its simplicity, lower cost, and robust nature. It is the workhorse for depositing many common metals with relatively low melting points, such as gold (Au), chromium (Cr), and germanium (Ge).
However, its primary drawback is the potential for contamination. Since the heated boat is in direct contact with the molten source material, atoms from the boat itself can co-evaporate and become incorporated into the thin film, reducing its purity. This method is also unsuitable for materials that require extremely high temperatures, such as refractory metals.
The Power and Purity of E-Beam Evaporation
E-beam evaporation's main advantage is its ability to reach temperatures far beyond what resistive heating can achieve. This makes it essential for depositing high-melting-point and refractory materials.
Because the electron beam heats the source material directly, the cooler, un-melted portion of the material acts as the crucible. This significantly reduces contamination, leading to higher-purity films. The trade-off is a much more complex and expensive system.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct evaporation source is a critical decision based on your material requirements and desired film quality.
- If your primary focus is depositing common metals with low melting points (e.g., gold, aluminum, chromium): Resistive evaporation offers a straightforward, reliable, and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is depositing refractory metals, ceramics, or materials requiring the highest purity: E-beam evaporation is the necessary choice to achieve the required temperatures and minimize contamination from a holder.
Ultimately, your choice depends on a clear understanding of your material's properties and the performance demands of your application.
Summary Table:
| Source Type | Heating Method | Best For | Key Advantage | Key Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resistive Evaporation | Electric current heats a metal boat/coil | Low-melting-point metals (e.g., Gold, Aluminum) | Simple, reliable, and cost-effective | Potential for contamination from the holder |
| E-Beam Evaporation | Focused electron beam heats material directly | High-melting-point/refractory materials, high-purity films | High temperatures, minimal contamination | More complex and expensive system |
Ready to choose the right evaporation source for your lab's thin-film deposition needs?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing reliable solutions for your thermal evaporation processes. Whether you require the simplicity of resistive sources or the high-purity capabilities of e-beam systems, our expertise ensures you get the right equipment for your materials and application goals.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and enhance your laboratory's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Conductive Boron Nitride Crucible BN Crucible
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition PECVD equipment? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings


















