In short, the key sputtering parameters you can control are the sputtering power, working gas pressure, gas flow rate, substrate temperature, and the total deposition time. These variables are not independent; they work together as a system to govern the energy and arrival rate of atoms onto your substrate, which ultimately determines the final properties of your thin film.
The central challenge in sputtering is not merely knowing what the parameters are, but understanding how they interact. Your goal is to precisely manage the plasma environment and particle energy to control the film's thickness, density, stress, and microstructure.

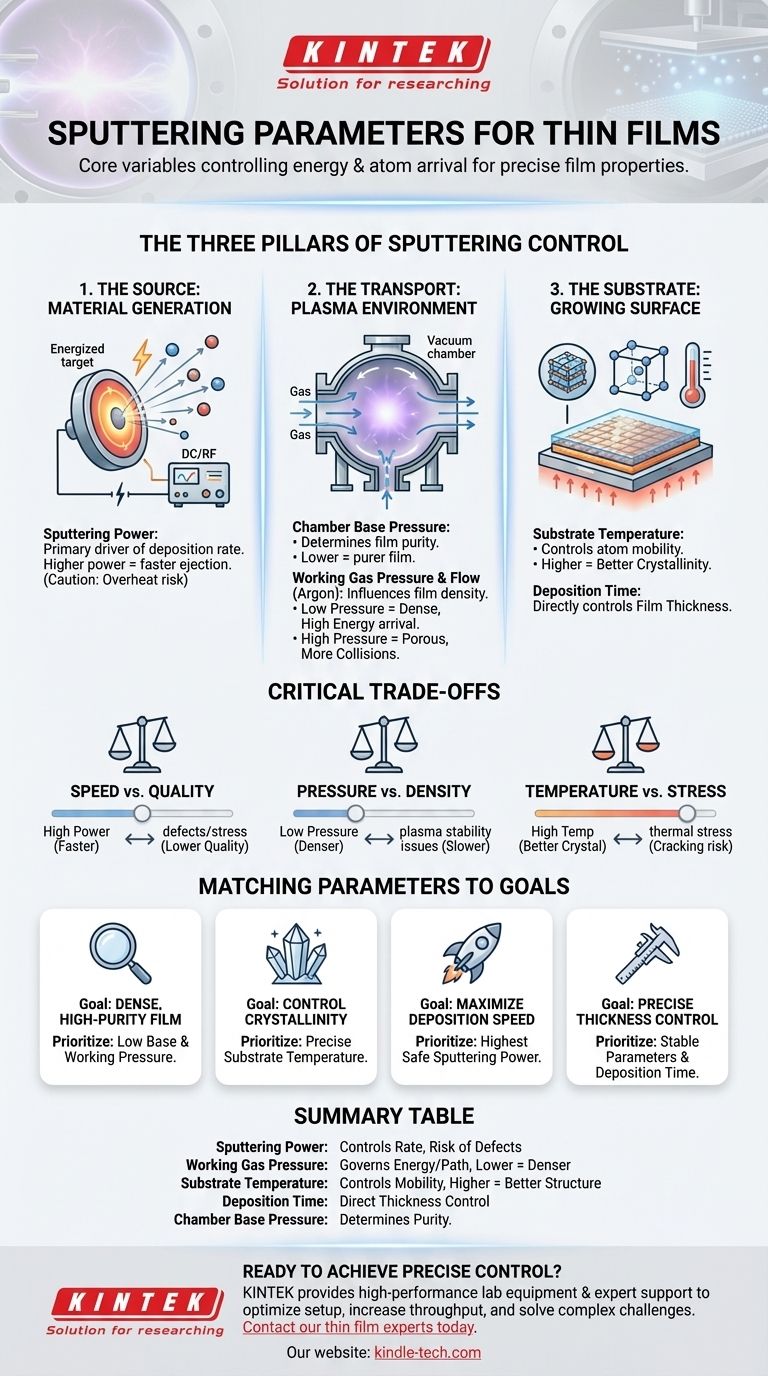
The Three Pillars of Sputtering Control
The sputtering process can be broken down into three fundamental stages: generating material from the source, transporting it through a plasma environment, and depositing it onto the substrate. Each stage has its own set of critical control parameters.
1. The Source: Generating the Material
This is where the deposition process begins. By energizing a target, you eject atoms that will become your film.
Sputtering Power (DC or RF)
The power applied to the sputtering target is the primary driver of the deposition rate. Higher power results in more energetic ions striking the target, ejecting more material.
This is your main control for deposition speed. However, excessive power can overheat and damage the target or the substrate.
2. The Transport: The Plasma Environment
Once atoms are ejected from the target, they travel through a low-pressure gas environment to reach the substrate. The nature of this environment is critical.
Chamber Base Pressure
Before introducing the sputtering gas, the chamber is evacuated to a very low pressure (the base pressure). This removes contaminants like water vapor and oxygen that could otherwise be incorporated into your film, creating impurities.
A lower base pressure leads to a purer film.
Working Gas Pressure and Flow
An inert gas, typically Argon, is introduced to create the plasma. The pressure of this "working gas" directly influences the deposition.
- Low Pressure: Fewer gas atoms mean ejected particles travel in a straight line to the substrate, arriving with high energy. This creates a dense, solid film.
- High Pressure: More gas atoms cause more collisions. Particles lose energy and arrive at the substrate from many angles, which can create a more porous, less dense film.
3. The Substrate: The Growing Surface
This is where the film is formed. The condition of the substrate surface dictates the final structure and properties of the film.
Substrate Temperature
Heating the substrate gives the arriving atoms more surface mobility. This allows them to settle into more ordered, crystalline structures.
Room temperature deposition often results in an amorphous or poorly crystallized film, while higher temperatures can improve crystallinity and adhesion.
Deposition Time
For a stable process, the thickness of the deposited film is directly proportional to the deposition time. This is the most straightforward parameter for controlling the final film thickness.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
Optimizing one parameter often forces a compromise on another. Understanding these relationships is key to achieving consistent, high-quality results.
Speed vs. Quality
Increasing sputtering power will deposit your film faster, increasing throughput. However, the high-energy particle bombardment can introduce defects and stress into the film, reducing its quality and performance.
Pressure vs. Film Density
Operating at a lower working gas pressure creates denser, higher-quality films. However, it can be more difficult to sustain a stable plasma at very low pressures, and the deposition rate might decrease.
Temperature vs. Stress
While substrate heating is excellent for improving a film's crystal structure, it can introduce thermal stress. This occurs when the thin film and the substrate have different coefficients of thermal expansion, causing the film to crack or delaminate upon cooling.
Matching Parameters to Your Deposition Goal
Your specific objective determines how you should balance these parameters.
- If your primary focus is achieving a dense, high-purity film: Prioritize a low chamber base pressure and a low working gas pressure, even if it means a slower deposition rate.
- If your primary focus is controlling film crystallinity: Precise substrate temperature control is your most important lever.
- If your primary focus is maximizing deposition speed: Use the highest sputtering power that your target and substrate can tolerate without causing damage.
- If your primary focus is precise thickness control: Ensure all other parameters (power, pressure) are highly stable and use deposition time as your final control variable.
Mastering these parameters transforms sputtering from a procedure into a predictable engineering tool for creating high-performance thin films.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Primary Role | Key Impact on Film |
|---|---|---|
| Sputtering Power | Controls deposition rate | Higher power = faster deposition, risk of defects |
| Working Gas Pressure | Governs particle energy & path | Lower pressure = denser, higher-quality films |
| Substrate Temperature | Controls atom mobility & structure | Higher temperature = better crystallinity |
| Deposition Time | Directly controls film thickness | Proportional to final thickness |
| Chamber Base Pressure | Determines film purity | Lower pressure = purer film, fewer impurities |
Ready to achieve precise control over your thin film deposition process?
The right sputtering parameters are critical for developing films with the exact properties you need. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the high-performance lab equipment and expert support that researchers and engineers rely on to master their sputtering processes.
We help you:
- Optimize your setup for superior film density, purity, and crystallinity.
- Increase throughput without sacrificing film quality.
- Solve complex challenges like stress management and defect reduction.
Let's discuss your specific application. Contact our thin film experts today to find the ideal sputtering solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Glassy Carbon Electrochemical Electrode
People Also Ask
- What is plasma enhanced? A Guide to Low-Temperature, High-Precision Manufacturing
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- How does plasma vapor deposition work? A Low-Temperature Coating Solution for Sensitive Materials
- What is plasma CVD? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for Sensitive Materials
- What are the advantages of plasma enhanced CVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition



















