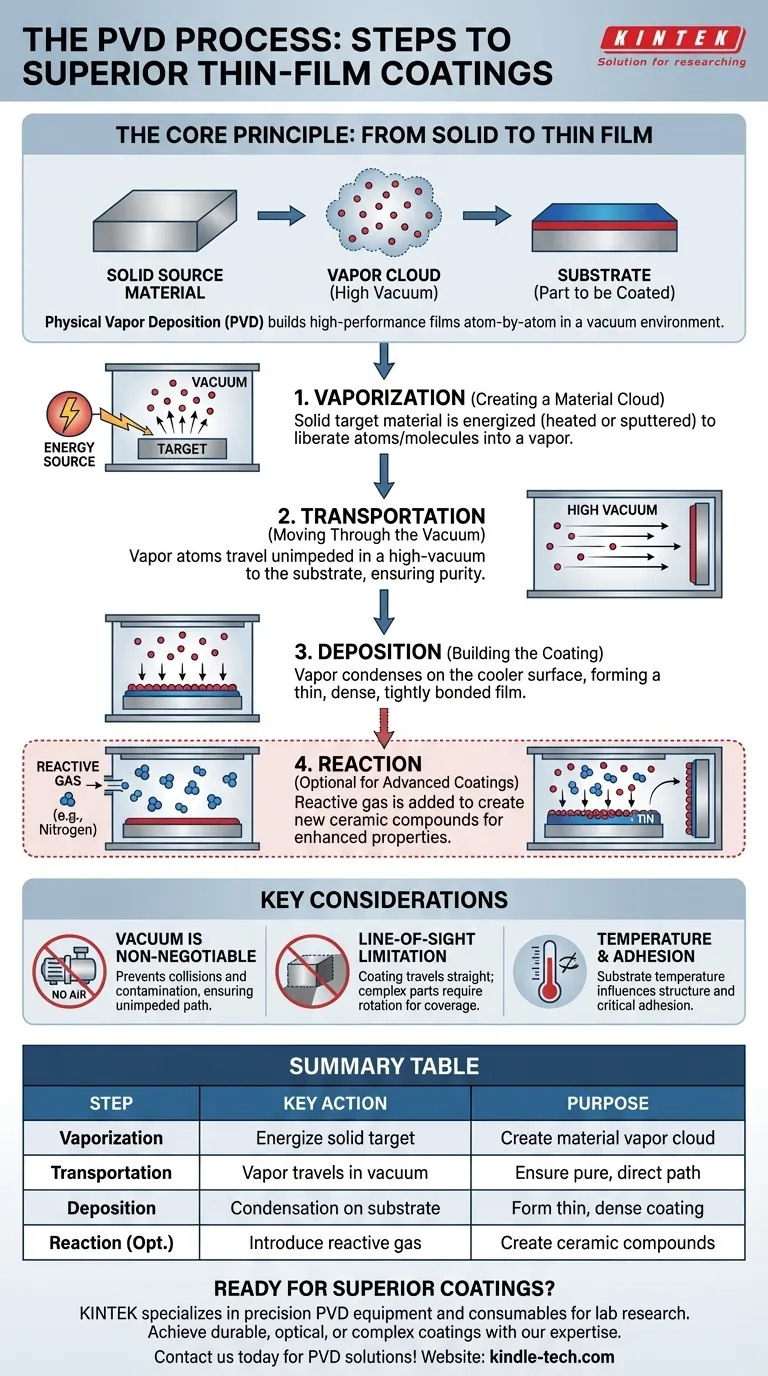
At its core, the Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) process consists of three fundamental stages. In a high-vacuum environment, a solid source material is converted into a vapor, this vapor travels across the chamber to the part being coated, and it then condenses on that part to form a thin, high-performance film. Some advanced PVD processes add a fourth stage involving a chemical reaction to create new coating compounds.
PVD is best understood not as a single method, but as a foundational principle: taking a solid material, turning it into a vapor within a vacuum, and re-condensing it atom-by-atom onto a surface to build a superior coating.
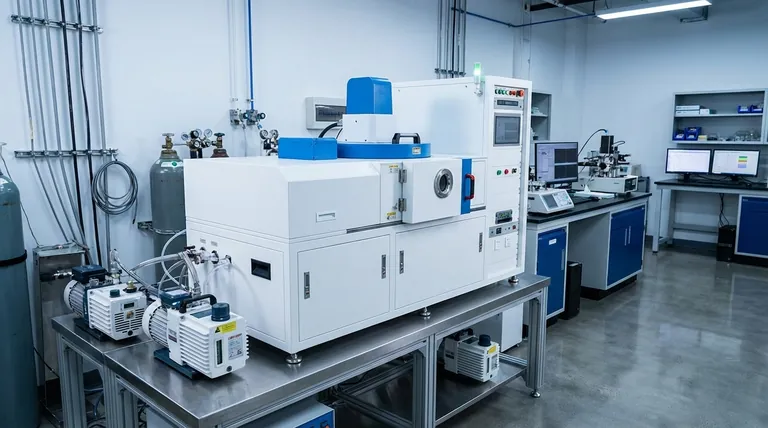

The Core Principle: From Solid to Thin Film
Physical Vapor Deposition is a vacuum-based coating technique designed to produce extremely thin yet durable films on a wide variety of materials, known as substrates.
The entire process occurs at very low pressure (a high vacuum), which is critical for ensuring the purity and quality of the final coating. The coating itself is built layer by layer, often atom by atom, resulting in a highly controlled and uniform finish.
The Foundational Stages of PVD
While there are many specific PVD techniques like sputtering or ion plating, they all follow the same essential sequence of events.
Step 1: Vaporization (Creating a Material Cloud)
The process begins with a solid source material, often called a target. This target is bombarded with energy inside the vacuum chamber to liberate individual atoms or molecules from its surface.
This energy can be supplied in several ways, such as heating the material until it evaporates or striking it with high-energy ions in a process called sputtering. The result is the creation of a vapor cloud of the source material.
Step 2: Transportation (Moving Through the Vacuum)
Once vaporized, the atoms and molecules travel in a relatively straight line from the source target toward the substrate.
The high-vacuum environment is non-negotiable for this step. It ensures there are virtually no air or gas molecules for the vaporized material to collide with, allowing for an unimpeded path to the substrate.
Step 3: Deposition (Building the Coating)
When the vaporized particles reach the surface of the cooler substrate, they condense back into a solid state. This condensation forms a thin, dense, and tightly bonded film.
Because this happens on an atomic scale, the process allows for precise control over the coating's thickness, structure, and final properties.
The Optional Fourth Step: Reaction
For certain types of advanced coatings, a fourth step is introduced. A carefully controlled amount of a reactive gas, such as nitrogen, oxygen, or acetylene, is added to the vacuum chamber.
This gas reacts with the metal vapor during transportation or upon deposition to form a new ceramic compound on the substrate's surface, such as Titanium Nitride (TiN), creating an even harder and more durable coating.
Understanding the Key Considerations
To truly grasp the PVD process, it's essential to understand the "why" behind its core requirements and limitations.
Why the Vacuum is Non-Negotiable
Without a high vacuum, the vaporized coating particles would collide with molecules of air. This would prevent them from reaching the substrate, contaminate the final film, and make the entire process fail.
The Line-of-Sight Limitation
PVD is fundamentally a line-of-sight process. The coating material travels in a straight path, meaning it will only deposit on surfaces that the vapor source can "see." To coat complex shapes, parts must be rotated on intricate fixtures to expose all surfaces to the vapor stream.
Temperature and Adhesion
While PVD is considered a "low temperature" process compared to other methods, the substrate's temperature is still a critical parameter. It influences the coating's structure and, most importantly, how well it adheres to the surface.
Applying This to Your Goal
Understanding these steps helps you select the right approach for your specific application.
- If your primary focus is a durable, wear-resistant metallic finish: A PVD process involving sputtering with a reactive gas (like nitrogen) is ideal for creating hard ceramic coatings like TiN.
- If your primary focus is a highly pure optical or electronic layer: Thermal evaporation PVD offers precise control to create very thin, pure films with specific properties without the high energy of sputtering.
- If your primary focus is coating a complex 3D object: You must account for the line-of-sight nature of PVD by designing proper part rotation and fixturing to ensure uniform coverage.
Ultimately, mastering the PVD process is about controlling these fundamental stages to build a microscopic layer with precisely engineered macroscopic properties.
Summary Table:
| PVD Process Step | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Vaporization | Solid target material is energized (heated or sputtered) | Creates a vapor cloud of coating material |
| 2. Transportation | Vaporized particles travel through high-vacuum chamber | Ensures pure, unimpeded path to substrate |
| 3. Deposition | Particles condense on cooler substrate surface | Forms thin, dense, tightly bonded coating |
| 4. Reaction (Optional) | Reactive gas (e.g., nitrogen) is introduced | Creates ceramic compounds like Titanium Nitride (TiN) |
Ready to achieve superior thin-film coatings for your laboratory? KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables for advanced PVD processes. Whether you need durable wear-resistant finishes, pure optical layers, or coatings for complex 3D objects, our expertise ensures optimal results. Contact us today to discuss how our PVD solutions can enhance your research and manufacturing capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
People Also Ask
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- What are the benefits of PECVD? Achieve Superior Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















