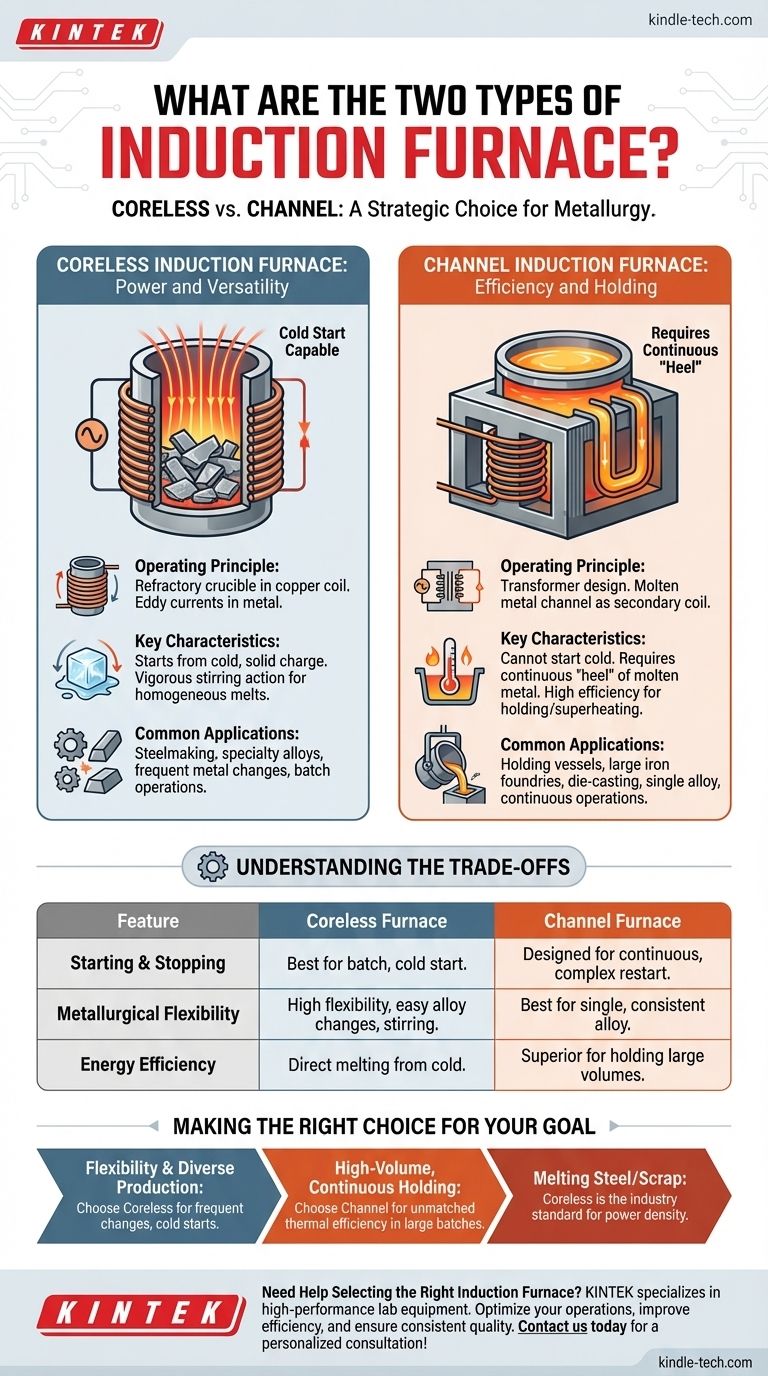
At a fundamental level, the two principal types of induction furnaces are the coreless induction furnace and the channel induction furnace. These designs are not interchangeable; they are distinguished by their core operating principles, which in turn dictate their ideal applications in the world of metallurgy and metal processing.
The choice between a furnace type is a strategic decision based on a trade-off between operational flexibility and thermal efficiency. Coreless furnaces provide the versatility to melt various metals from a cold start, while channel furnaces excel at efficiently holding and superheating large, continuous volumes of a single alloy.

The Coreless Induction Furnace: Power and Versatility
A coreless induction furnace is the more common and flexible of the two designs, especially in foundries that handle a variety of metals.
Operating Principle
In this design, a refractory-lined crucible containing the metal charge is placed directly inside a large, water-cooled copper coil. When a powerful alternating current is passed through the coil, it generates a strong magnetic field that induces intense eddy currents within the metal itself, rapidly heating and melting it.
Key Characteristics
The primary advantage of the coreless furnace is its ability to start from a cold, solid charge. The electromagnetic forces also create a vigorous stirring action, which is excellent for mixing alloys and ensuring a homogeneous melt.
Common Applications
Due to their flexibility, coreless furnaces are used for a wide range of applications, including steelmaking, specialty alloy production, and in foundries that require frequent changes between different types of metals.
The Channel Induction Furnace: Efficiency and Holding
The channel furnace operates on a different principle, functioning much like a transformer. It is a specialized tool designed for high-efficiency, continuous operations.
Operating Principle
This furnace features an iron core with a primary coil. A small, closed loop or "channel" of molten metal passes through this core, acting as a single-turn secondary coil. The current induced in this loop heats the metal, which then circulates into the main bath of the furnace, transferring heat.
Key Characteristics
A channel furnace cannot start from a cold charge. It requires a continuous "heel" of molten metal to maintain the secondary circuit. This makes it exceptionally efficient for holding metal at temperature or for superheating large volumes with minimal energy loss.
Common Applications
These furnaces are ideal for use as holding vessels in large iron foundries or die-casting operations. They are also used for melting lower-melting-point non-ferrous alloys like copper and aluminum in high-volume, single-alloy environments.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the wrong furnace type for an application leads to significant inefficiency and operational challenges. The fundamental differences create clear trade-offs.
Starting and Stopping
The coreless furnace's ability to melt from solid scrap makes it perfect for batch operations or facilities that don't run 24/7. In contrast, the channel furnace is designed for continuous work, as emptying it and restarting is a complex and energy-intensive process.
Metallurgical Flexibility
The vigorous stirring and simple crucible design of a coreless furnace make it easy to switch between different alloys. The channel furnace is best suited to a single, consistent alloy to avoid contamination and maximize its efficiency.
Energy Efficiency
For holding large amounts of molten metal at a constant temperature, the channel furnace is significantly more energy-efficient. However, for the initial task of melting solid metal from cold, the coreless furnace is more direct and effective.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your operational needs will point directly to the correct furnace technology.
- If your primary focus is flexibility and diverse alloy production: The coreless induction furnace is the clear choice for its ability to start from cold and handle frequent metal changes.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, continuous holding of a single alloy: The channel induction furnace provides unmatched thermal efficiency for maintaining temperature in large batches.
- If you are melting steel or high-temperature alloys from scrap: The power density and direct melting capability of the coreless furnace make it the industry standard.
Understanding these core designs and their inherent trade-offs empowers you to select the most effective tool for your specific metallurgical goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Coreless Induction Furnace | Channel Induction Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Principle | Crucible inside a copper coil; melts via induced eddy currents | Transformer-like; uses a molten metal loop as a secondary coil |
| Starting Capability | Can start from a cold, solid charge | Requires a continuous "heel" of molten metal |
| Primary Use | Melting from cold, batch operations, diverse alloys | Holding, superheating, continuous operations, single alloy |
| Key Advantage | High flexibility and alloy versatility | Superior energy efficiency for holding large volumes |
| Ideal For | Steelmaking, specialty alloys, foundries with frequent metal changes | High-volume iron foundries, die-casting, non-ferrous metals |
Need Help Selecting the Right Induction Furnace?
Choosing between a coreless and channel furnace is a critical decision that impacts your operational efficiency and product quality. KINTEK specializes in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including induction furnaces tailored to your specific metallurgical processes.
We can help you:
- Optimize your melting operations with the right furnace technology.
- Improve energy efficiency and reduce operational costs.
- Ensure consistent, high-quality melts for your specific alloys.
Let's discuss your application. Our experts are ready to guide you to the ideal solution for your laboratory or production needs.
Contact us today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does induction heating work on a stove? A Guide to Faster, Safer Cooking
- Which furnace is most commonly used for melting non ferrous metals? Induction Furnaces for Purity & Efficiency
- What is the structure of an induction furnace? A Guide to Its Core Components and Design
- What is the function of a vacuum induction melting furnace? Essential Guide for High-Purity FeCrAl Alloy Production
- How accurate is vacuum casting? Achieve High-Fidelity Prototypes and Low-Volume Production
- How hot does a magnetic induction heater get? Achieve Precise Temperatures from 100°C to 3000°C
- Why and when high frequency can be needed in the furnace? Achieve Precise Surface Heating for Your Materials
- What are the hazards of an induction furnace? A Guide to Preventing Catastrophic Failures



















