In essence, pyrolysis methods are distinguished by their heating rate and reaction time. The three primary types are slow, fast, and flash pyrolysis, each engineered to maximize a different primary product: biochar (a solid), bio-oil (a liquid), or syngas (a gas). The method you choose is a direct function of the end product you want to create.
The core principle to understand is that the speed at which you heat organic material in an oxygen-free environment fundamentally dictates its final chemical state. Slower processes create stable solids, while extremely rapid processes "freeze" the intermediate liquid and gas products before they can break down further.

The Core Principle: What is Pyrolysis?
A Foundation in Thermal Decomposition
Pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of materials at elevated temperatures in an inert atmosphere. It involves a change of chemical composition and is irreversible.
Crucially, this process occurs in the absence of oxygen. This prevents combustion and instead breaks down complex organic materials like biomass, plastics, or waste into a mixture of solid, liquid, and gas products.
The Three Key Products
Regardless of the method, pyrolysis yields three core products in varying proportions:
- Biochar: A stable, carbon-rich solid.
- Bio-oil (Pyrolysis Oil): A dense, acidic liquid mixture of oxygenated organic compounds.
- Syngas: A mixture of non-condensable, combustible gases like hydrogen (H₂), carbon monoxide (CO), carbon dioxide (CO₂), and methane (CH₄).
The Three Primary Pyrolysis Methods
The fundamental difference between pyrolysis methods lies in controlling the reaction conditions—temperature, heating rate, and residence time—to favor the formation of one product over the others.
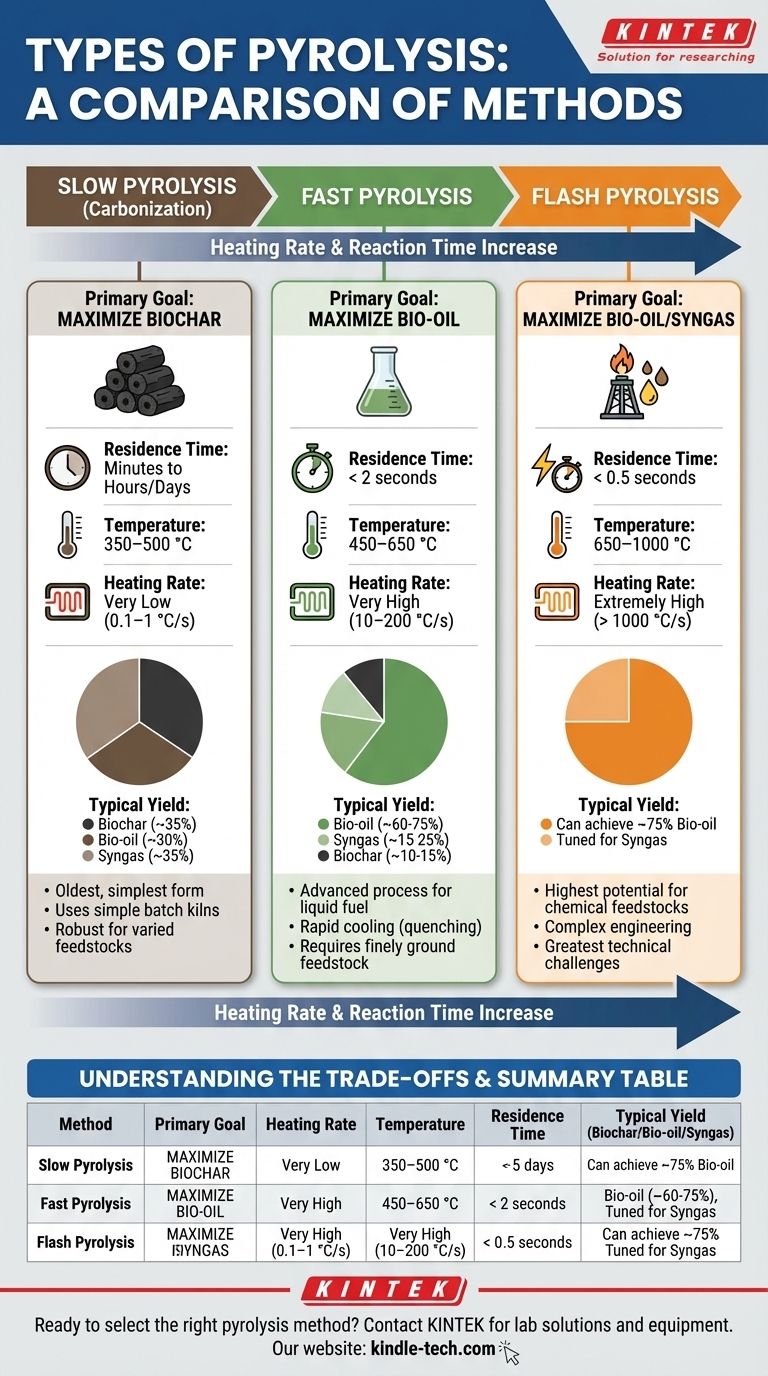
Slow Pyrolysis (Carbonization)
This is the oldest and simplest form of pyrolysis, often called carbonization.
Its primary goal is to maximize the yield of biochar. The process uses slow heating rates over a long period, allowing volatile components to escape while the solid carbon structure forms and stabilizes.
- Heating Rate: Very low (0.1–1 °C/s)
- Temperature: Moderate (350–500 °C)
- Residence Time: Long (minutes to hours, or even days)
- Typical Yield: High biochar (~35%), moderate bio-oil (~30%) and syngas (~35%).
Think of this as the industrial equivalent of how charcoal has been made for centuries.
Fast Pyrolysis
This is a more advanced process designed to convert biomass into a liquid fuel.
Its primary goal is to maximize the yield of bio-oil. This is achieved by heating the feedstock extremely quickly to decomposition temperature and then rapidly cooling—or "quenching"—the vapors to prevent them from breaking down further into gases.
- Heating Rate: Very high (10–200 °C/s)
- Temperature: Moderate to high (450–650 °C)
- Residence Time: Very short (< 2 seconds)
- Typical Yield: High bio-oil (~60-75%), moderate syngas (~15-25%), low biochar (~10-15%).
Success in fast pyrolysis depends on using finely ground feedstock for rapid heat transfer.
Flash Pyrolysis
Flash pyrolysis represents the extreme end of the speed spectrum, pushing conditions to maximize liquid and gas production.
Its primary goal is to maximize bio-oil and syngas, often to target specific high-value chemicals. The engineering is more complex, requiring specialized reactors that can achieve near-instantaneous heat transfer.
- Heating Rate: Extremely high (> 1000 °C/s)
- Temperature: High (650–1000 °C)
- Residence Time: Extremely short (< 0.5 seconds)
- Typical Yield: Can achieve very high bio-oil yields (~75%) or be tuned to favor syngas production depending on the temperature.
This method offers the highest potential for producing chemical feedstocks but also presents the greatest technical challenges.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a pyrolysis method is an exercise in balancing project goals with operational complexity and cost.
Biochar vs. Bio-oil: A Fundamental Choice
The most significant trade-off is between the primary product. Slow pyrolysis yields a stable solid (biochar) that is easy to handle and has applications in agriculture (soil amendment) and metallurgy.
Fast and flash pyrolysis produce a liquid (bio-oil) that is energy-dense and transportable but is also acidic, unstable, and requires significant upgrading to be used as a conventional fuel.
The Engineering Challenge of Speed
As the heating rate and speed of the process increase, so does the technical complexity.
Slow pyrolysis can be done in relatively simple batch kilns or reactors. Fast and flash pyrolysis require advanced systems like fluidized bed or ablative reactors, precise feedstock preparation (drying and grinding), and robust quenching systems. This directly translates to higher capital and operational costs.
Feedstock Sensitivity
Faster pyrolysis methods are far more sensitive to feedstock properties. For rapid heat transfer, the biomass must have low moisture content and a very small particle size.
Slow pyrolysis is more forgiving and can handle larger, more varied, and wetter feedstocks, making it a more robust choice for unprocessed waste streams.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your selection should be dictated entirely by your desired output and your operational capabilities.
- If your primary focus is producing a stable solid for soil amendment, carbon sequestration, or solid fuel: Slow pyrolysis is the most direct, robust, and cost-effective method.
- If your primary focus is generating a liquid fuel or a chemical intermediate from biomass: Fast pyrolysis is the established technology for maximizing bio-oil yields.
- If your primary focus is maximizing the recovery of high-value chemicals or syngas with advanced technology: Flash pyrolysis offers the highest potential yields but comes with the greatest engineering complexity.
Ultimately, the choice of pyrolysis method is a strategic decision that aligns reaction physics with your final product's market.
Summary Table:
| Method | Primary Goal | Heating Rate | Temperature | Residence Time | Typical Yield (Biochar/Bio-oil/Syngas) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slow Pyrolysis | Maximize Biochar | 0.1–1 °C/s | 350–500 °C | Minutes to Hours | ~35% / ~30% / ~35% |
| Fast Pyrolysis | Maximize Bio-oil | 10–200 °C/s | 450–650 °C | < 2 seconds | ~10-15% / ~60-75% / ~15-25% |
| Flash Pyrolysis | Maximize Bio-oil/Syngas | > 1000 °C/s | 650–1000 °C | < 0.5 seconds | Can achieve ~75% bio-oil |
Ready to select the right pyrolysis method for your lab's goals? The experts at KINTEK can help you navigate the trade-offs between biochar, bio-oil, and syngas production. We specialize in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables you need to implement your chosen pyrolysis process efficiently and reliably. Contact our team today to discuss your project requirements and optimize your thermal decomposition outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time



















