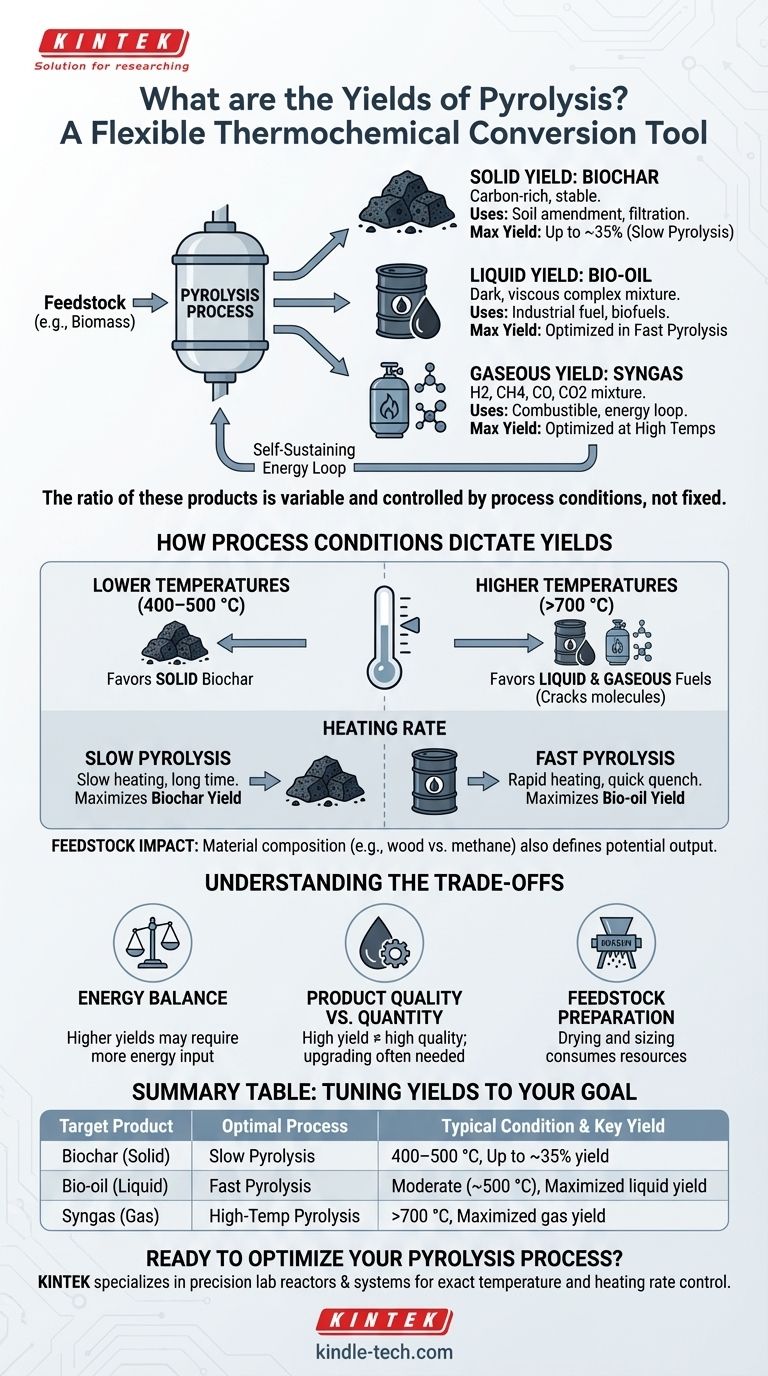
The yields of pyrolysis are not a single, fixed value; they are a variable ratio of solid, liquid, and gaseous products. The process is intentionally manipulated to favor one type of output over others. The three core products are a solid carbon-rich material called biochar, a liquid known as bio-oil, and a combustible syngas.
The central concept to grasp is that pyrolysis is a flexible thermochemical conversion tool. By precisely controlling the process conditions—primarily temperature and heating rate—you can deliberately steer the reaction to maximize the yield of either the solid, liquid, or gas product to fit a specific industrial or agricultural goal.

The Three Primary Products of Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis breaks down an input material (feedstock) in the absence of oxygen, ensuring it doesn't combust. This thermal decomposition results in three distinct product streams.
Solid Yield: Biochar (or Coke)
Biochar is the stable, carbon-rich solid that remains after the volatile components have been driven off.
Its uses are diverse, ranging from a soil amendment in agriculture to a component in briquetting for fuel or as a sorbent for filtration.
Under slow pyrolysis conditions, biochar yields can be as high as 30% of the initial dry feedstock weight.
Liquid Yield: Bio-oil (or Pyrolysis Oil)
When the hot gases produced during pyrolysis are rapidly cooled, they condense into a dark, viscous liquid known as bio-oil.
This complex mixture, which includes components like tar and wood vinegar, can be used as an industrial fuel oil or further refined into higher-grade biofuels and chemicals.
Gaseous Yield: Syngas (or Pyrolysis Gas)
This product is the non-condensable fraction of gases that remain after the bio-oil has been separated.
It is a mixture of hydrogen (H2), methane (CH4), carbon monoxide (CO), and carbon dioxide (CO2). This syngas is combustible and is very often recycled to provide the heat required to run the pyrolysis plant itself, creating a self-sustaining energy loop.
How Process Conditions Dictate Yields
You cannot ask about yield without also considering the process. The feedstock and the "how" of the pyrolysis process are the dominant factors controlling the final product ratios.
The Critical Role of Temperature
Temperature is the primary lever for controlling the output.
Lower temperatures, typically between 400–500 °C, favor the production of solid biochar. The heat is sufficient to drive off volatiles but not intense enough to break down the carbon backbone.
Higher temperatures, above 700 °C, crack the complex hydrocarbon molecules into smaller, lighter ones, significantly favoring the production of liquid and gaseous fuels.
The Influence of Heating Rate
The speed at which the feedstock is heated (the pyrolysis "type") fundamentally alters the product distribution.
Slow pyrolysis involves heating the material slowly over a long period. This gives molecules time to polymerize and rearrange into stable carbon structures, maximizing the biochar yield.
Fast pyrolysis, in contrast, heats the material extremely quickly. This process vaporizes the organic compounds before they can form char, maximizing the bio-oil yield when the vapors are rapidly quenched.
The Impact of Feedstock
The input material defines the potential output. Pyrolyzing biomass like wood or agricultural waste yields the three products discussed above.
However, pyrolyzing a different feedstock, like methane gas, yields only two products: solid carbon and gaseous hydrogen. This demonstrates how the chemical makeup of the starting material is fundamental to the final product composition.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Optimizing for one yield often comes at the expense of another and introduces practical complexities.
Energy Balance
Achieving higher yields of bio-oil and syngas requires higher temperatures, which demands a greater energy input. While the syngas can be used to power the reactor, there is always an energy balance to consider to ensure the process is efficient.
Product Quality vs. Quantity
A high yield of bio-oil does not automatically mean it is a high-quality fuel. Raw bio-oil is often acidic, unstable, and has a high water content, requiring significant and costly upgrading before it can be used as a transportation fuel.
Feedstock Preparation
The stated yields are typically based on a prepared feedstock. In reality, raw materials like wood or waste must be dried and sized correctly before being fed into a reactor. This pre-processing step consumes energy and resources, affecting the overall net efficiency of the system.
Tuning Pyrolysis Yields to Your Goal
Your target product dictates the process conditions you should employ.
- If your primary focus is soil amendment or carbon sequestration: Maximize biochar yield by using slow pyrolysis at lower temperatures (400–500 °C).
- If your primary focus is producing a liquid biofuel: Maximize bio-oil yield by using fast pyrolysis with moderate temperatures and rapid cooling of the product vapors.
- If your primary focus is generating energy or synthesis gas: Maximize syngas yield by using high temperatures (above 700 °C) to crack all heavier molecules.
By understanding these principles, you can view pyrolysis not as a fixed process, but as a precise tool for chemical conversion.
Summary Table:
| Target Product | Optimal Process | Typical Temperature | Key Yield |
|---|---|---|---|
| Biochar (Solid) | Slow Pyrolysis | 400–500 °C | Up to 35% of feedstock |
| Bio-oil (Liquid) | Fast Pyrolysis | Moderate (~500 °C) | Maximized liquid yield |
| Syngas (Gas) | High-Temp Pyrolysis | >700 °C | Maximized gas yield |
Ready to Optimize Your Pyrolysis Process?
Whether your goal is to produce biochar for soil enhancement, bio-oil for fuel, or syngas for energy, the right lab equipment is crucial for R&D and process scaling. KINTEK specializes in precision lab reactors, furnaces, and pyrolysis systems that provide the exact temperature control and heating rates needed to achieve your target yields.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can help you tune your pyrolysis process for maximum efficiency and product quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable Laboratory High Temperature High Pressure Reactors for Diverse Scientific Applications
- Wall Mounted Water Distillation Unit
- High Temperature Constant Temperature Heating Circulator Water Bath Chiller Circulator for Reaction Bath
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the alternative to brazing? Compare Welding, Soldering & Mechanical Fastening
- What factors should be considered when selecting a material for high temperature applications? A Guide to Long-Term Performance
- What is the effect of residence time on pyrolysis? Control Product Yields from Bio-oil to Biochar
- Can you reheat a brazed joint? A guide to repair, disassembly, and post-braze processes
- What are the types of filter press in chemical industry? Choose the Right One for Your Process
- How can you control temperature inside a resistance furnace? Master Precise Thermal Management
- Why is a laboratory ultrasonic homogenizer necessary? Ensure Accurate Silver-Silica Nanocomposite Analysis
- What are the catalysts for catalytic pyrolysis? Unlock the Key to Optimizing Biofuel and Chemical Yields



















