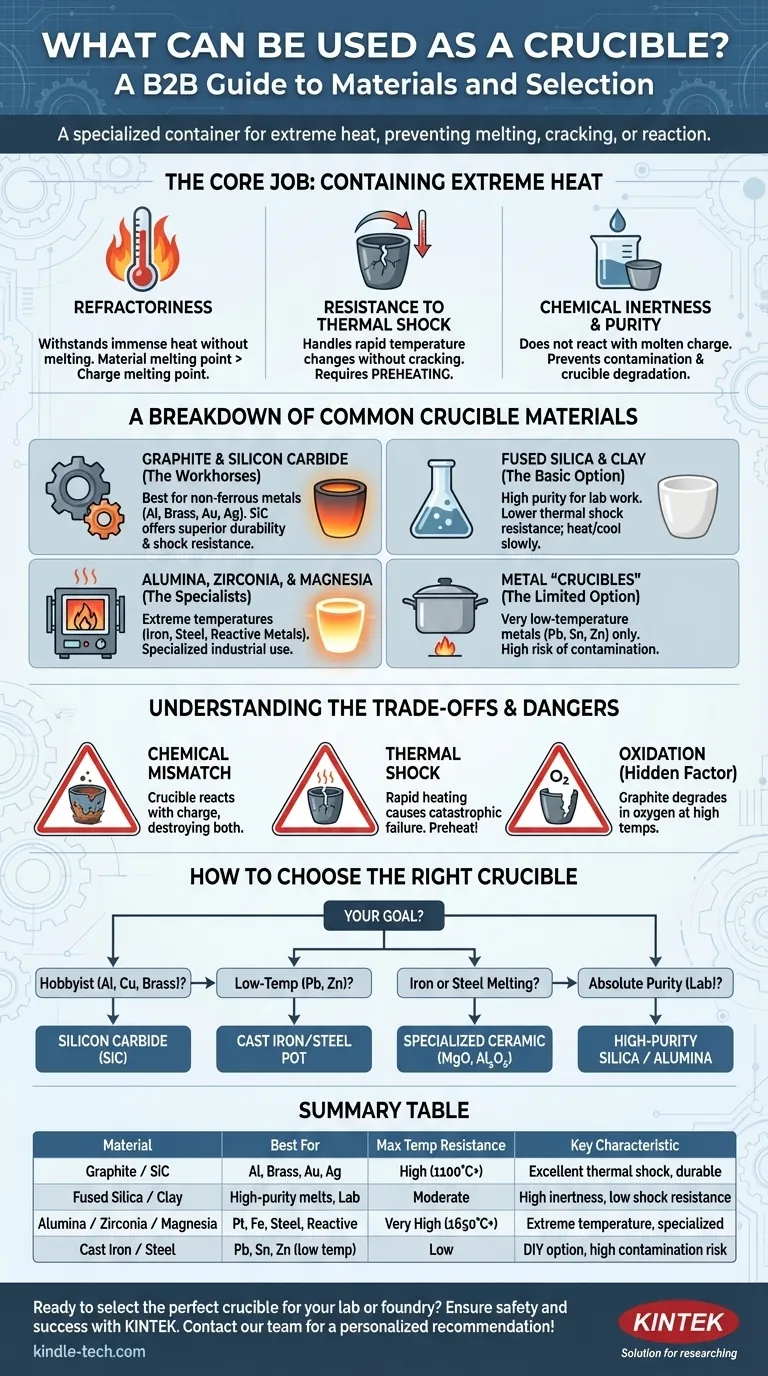
In essence, a crucible is a specialized container made from materials that can withstand extremely high temperatures without melting, cracking, or reacting with the substance inside. The most common and effective materials are graphite, silicon carbide, and various high-purity ceramics like alumina and zirconia. The specific material you choose is dictated by the temperature you need to reach and the chemical properties of the substance you are heating.
Choosing a crucible is not about finding one "best" material, but about matching the crucible's properties—specifically its temperature resistance and chemical inertness—to the exact metal or substance you intend to melt. This decision is critical for both the success of your work and your personal safety.

The Core Job of a Crucible: Containing Extreme Heat
A crucible is far more than a simple pot. It is a piece of technical equipment engineered to perform reliably under conditions that would destroy ordinary materials. Its performance depends on three key properties.
The Principle of Refractoriness
Refractoriness is the ability of a material to withstand immense heat without deforming or melting. This is a crucible's primary job.
The melting point of the crucible material must be significantly higher than the melting point of the substance you are heating, known as the charge. For example, to melt aluminum (melts at 1220°F / 660°C), you need a crucible rated for well over 2000°F / 1100°C.
Resistance to Thermal Shock
Thermal shock is the stress a material endures when its temperature changes rapidly. A crucible must be able to handle being heated to thousands of degrees and then cooling back down without cracking.
Materials with low thermal expansion and high thermal conductivity are more resistant to thermal shock. Even so, proper preheating of a crucible before introducing the charge is a critical step to prevent catastrophic failure.
Chemical Inertness and Purity
A crucible must be chemically inert, meaning it should not react with the molten charge. A chemical reaction can ruin the purity of your melt and will also degrade and destroy the crucible itself over time.
This is especially important in metallurgy, where the chemistry between the molten metal, the slag (impurities), and the crucible material can determine success or failure.
A Breakdown of Common Crucible Materials
Different materials are suited for different temperatures and applications. They range from all-purpose workhorses to highly specialized tools.
Graphite & Silicon Carbide (The Workhorses)
These are the most common crucibles for hobbyists and foundries melting non-ferrous metals like aluminum, brass, bronze, silver, and gold. They are typically composites, blending materials to optimize performance.
- Clay-Graphite: The traditional choice. Graphite provides high thermal conductivity for efficient melting, while clay acts as a binder.
- Silicon Carbide (SiC): Modern SiC crucibles, often mixed with graphite, offer superior strength, durability, and excellent resistance to thermal shock. They are a clear performance upgrade over basic clay-graphite.
Fused Silica & Clay (The Basic Option)
Made from high-purity quartz sand or fireclay, these ceramic crucibles are often white or tan. They are excellent for applications demanding high purity, as they are very inert.
However, their resistance to thermal shock is significantly lower than graphite composites. They must be heated and cooled very slowly and carefully to prevent cracking.
Alumina, Zirconia, & Magnesia (The Specialists)
These are high-performance ceramics used for industrial and laboratory work involving extremely high temperatures or specific chemical challenges.
- Alumina (Al₂O₃): With a very high melting point (~3700°F / 2040°C), it's used for melting high-purity materials and some platinum group metals.
- Zirconia (ZrO₂): Can withstand even higher temperatures than alumina and is used for melting specialty alloys and reactive metals.
- Magnesia (MgO): A "basic" refractory material excellent for melting iron and steel, as it resists the "basic" slags produced during the process.
Metal "Crucibles" (The Limited, Low-Temp Option)
For very low-temperature metals, a simple metal pot can sometimes be used. A thick-walled cast iron or steel pot can melt lead, tin, or zinc, whose melting points are far below that of steel.
This is a limited, DIY-level solution. There is always a risk of contaminating your melt with iron, and you must never use this method for metals like aluminum or copper, as their melting points are high enough to damage or melt the steel container.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Dangers
Making the wrong choice is not just inefficient; it can be extremely dangerous. A failed crucible can spill thousands of degrees of molten metal.
The Risk of Chemical Mismatch
Using a crucible that reacts with your charge will destroy it. For example, using a silica-based (acidic) crucible to melt steel that produces a basic slag will cause the slag to literally eat away the crucible walls.
The Danger of Thermal Shock
Never place a cold crucible into a roaring-hot furnace. The rapid expansion will crack it. Always preheat your crucible slowly and ensure it is free of any moisture, which can turn to steam and fracture the vessel.
The Hidden Factor of Oxidation
Some materials, most notably graphite, will degrade in an oxygen-rich atmosphere at high temperatures. The carbon will literally burn away, thinning the crucible walls and weakening it over time. This is why a properly tuned fuel/air mixture in a furnace is so important.
How to Choose the Right Crucible
Base your decision on your specific goal, prioritizing safety and material compatibility above all else.
- If you are a hobbyist melting aluminum, brass, or copper: A silicon carbide (SiC) crucible offers the best combination of performance, durability, and thermal shock resistance.
- If you are melting lead, zinc, or pewter at low temperatures: A thick-walled cast iron or steel pot can suffice, but be aware of the high risk of iron contamination.
- If you are melting iron or steel: You must use a specialized ceramic crucible, such as magnesia or alumina, designed to handle the extreme temperatures and slag chemistry involved.
- If your work demands absolute purity (lab analysis or precious metals): A high-purity fused silica, alumina, or zirconia crucible is necessary to prevent any chemical reaction with your sample.
Understanding these core principles transforms the crucible from a simple pot into a critical scientific instrument for your work.
Summary Table:
| Material | Best For | Max Temp Resistance | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Graphite / Silicon Carbide | Aluminum, Brass, Bronze, Silver, Gold | High (2000°F / 1100°C+) | Excellent thermal shock resistance, durable |
| Fused Silica / Clay | High-purity melts, lab work | Moderate | High chemical inertness, low thermal shock resistance |
| Alumina / Zirconia / Magnesia | Platinum, iron, steel, reactive metals | Very High (3000°F / 1650°C+) | Extreme temperature resistance, specialized use |
| Cast Iron / Steel | Lead, Tin, Zinc (low temp only) | Low | DIY option, high risk of contamination |
Ready to select the perfect crucible for your lab or foundry?
Choosing the wrong material can lead to failed experiments, contaminated melts, or even dangerous accidents. At KINTEK, we specialize in lab equipment and consumables, providing crucibles engineered for precision, safety, and performance. Our experts will help you match the ideal graphite, silicon carbide, or ceramic crucible to your specific temperature and chemical requirements.
Ensure your process is safe and successful—contact our team today for a personalized recommendation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- High Purity Pure Graphite Crucible for Evaporation
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of selecting an alumina crucible for TGA? Ensure High-Precision Thermal Analysis Data
- What are the advantages of high-purity alumina crucibles for molten ZnNaK//Cl salts? Ensure Experimental Purity
- What role do high-purity alumina crucibles play in high-temperature steam oxidation? Ensure Data Integrity up to 1350°C
- How does the use of corrosion-resistant ceramic crucibles ensure the chemical purity of materials? | KINTEK
- Why is the use of high-purity alumina crucibles necessary for NMC powders? Ensure Purity in Cathode Synthesis



















