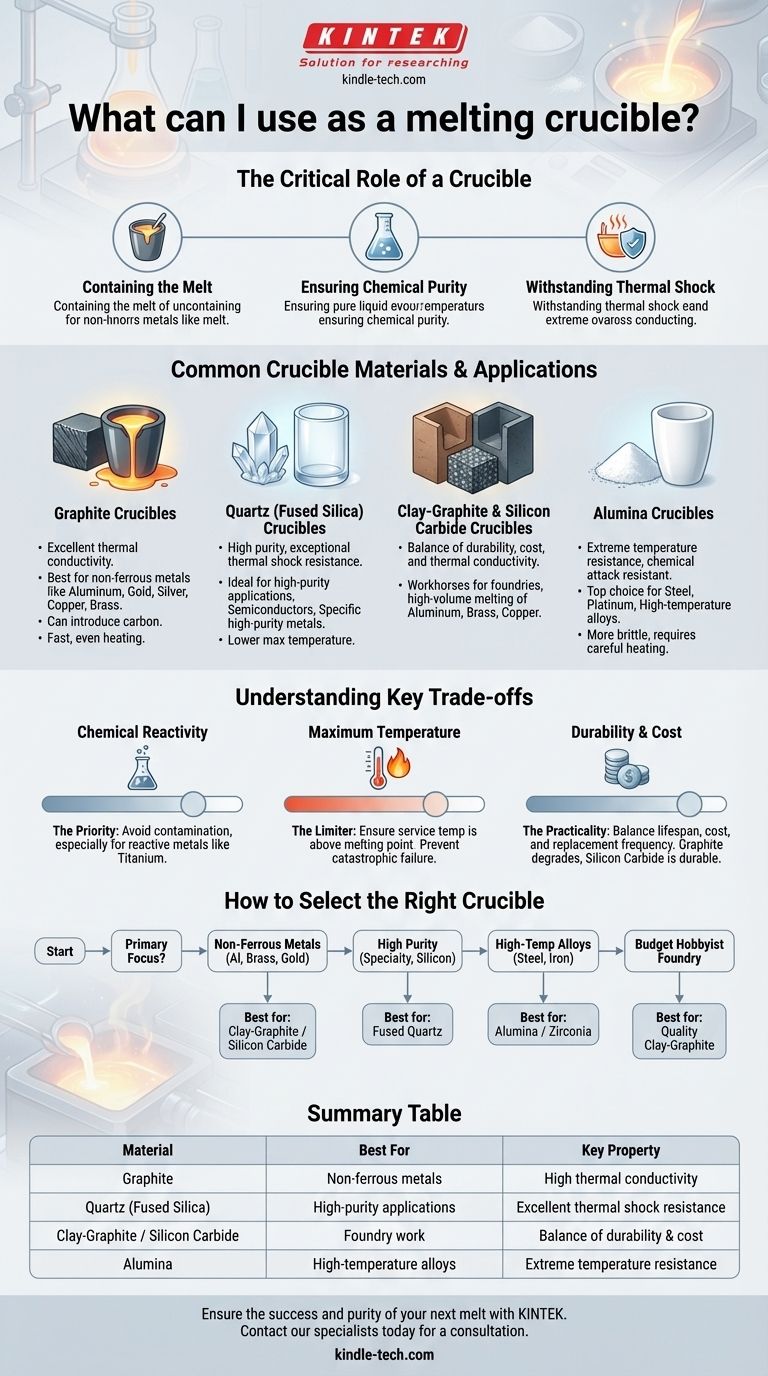
For melting materials at high temperatures, the most common and effective crucibles are made from graphite, quartz (fused silica), or a composite ceramic like clay-graphite or silicon carbide. The correct choice is not arbitrary; it is dictated by the maximum temperature required and, most importantly, the chemical properties of the material you intend to melt.
The central challenge is not finding a container that can withstand heat, but selecting one that will not chemically react with or contaminate the molten material at extreme temperatures. Your choice of crucible is a critical factor in the purity and success of your final product.
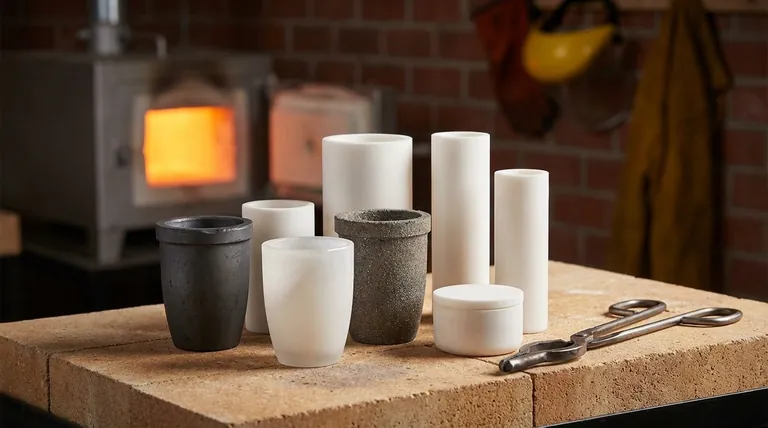

The Critical Role of a Crucible
A crucible is more than just a melting pot. It's a specialized container designed to function reliably at temperatures that would destroy ordinary vessels.
### Containing the Melt
The most basic function is to safely contain liquid metal or other materials. The crucible must have a melting point significantly higher than the substance it holds.
### Ensuring Chemical Purity
A crucible must remain chemically inert. Any reaction between the crucible and the molten charge can introduce impurities, altering the properties of the final material. This is a critical consideration in metallurgy and material science.
### Withstanding Thermal Shock
The process of heating and cooling a material places immense stress on its container. A good crucible must have excellent thermal shock resistance to avoid cracking or shattering during use.
Common Crucible Materials and Their Applications
The material of your crucible directly impacts its performance. Each type offers a unique profile of temperature resistance, chemical compatibility, and durability.
### Graphite Crucibles
Graphite crucibles are excellent for high thermal conductivity, allowing for fast and even heating of the charge.
They are a standard choice for melting non-ferrous metals like aluminum, gold, silver, copper, and brass. However, they can introduce carbon into the melt and will oxidize and degrade if used in an oxygen-rich atmosphere at very high temperatures without a protective glaze.
### Quartz (Fused Silica) Crucibles
As mentioned in your reference, quartz is a high-purity option. Fused silica, a type of glass made from silica, is known for its exceptional thermal shock resistance.
These crucibles are ideal for applications requiring high purity, such as melting silicon for the semiconductor industry or working with specific high-purity metals. Their primary limitation is a lower maximum operating temperature compared to some ceramics.
### Clay-Graphite & Silicon Carbide Crucibles
These are the workhorses of many foundries. By combining materials, they offer a balance of properties.
Clay-graphite crucibles blend the thermal conductivity of graphite with the durability and lower cost of clay. Silicon Carbide (SiC) crucibles offer even better durability and thermal conductivity, making them a premium choice for high-volume melting of aluminum, brass, and copper.
### Alumina Crucibles
For extremely high-temperature applications, alumina ceramic is a top choice.
Alumina crucibles can withstand temperatures high enough to melt steel, platinum, and other high-temperature alloys. They are very hard and resistant to chemical attack but can be more brittle and susceptible to thermal shock if not heated carefully.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
Selecting a crucible involves balancing three critical factors: chemical compatibility, temperature limits, and cost.
### The Priority: Chemical Reactivity
This is the most important consideration. For example, melting highly reactive metals like titanium requires a specialized, non-reactive crucible, as even graphite would contaminate it. Always verify that your intended crucible material will not react with your molten charge.
### The Limiter: Maximum Temperature
Ensure the crucible's maximum service temperature is well above the melting point of your material. Pushing a crucible beyond its rated temperature can lead to catastrophic failure. An alumina crucible for steel is appropriate; a quartz one is not.
### The Practicality: Durability and Cost
Graphite and clay-graphite crucibles are often considered consumable items that degrade over many uses. Silicon carbide is more durable but more expensive. Ceramic crucibles like alumina can last a very long time if handled properly but may have a higher initial cost and require careful heating protocols.
How to Select the Right Crucible for Your Application
Your choice should be guided entirely by your specific goal.
- If your primary focus is melting common non-ferrous metals (aluminum, brass, gold): A clay-graphite or silicon carbide crucible offers the best balance of performance and cost.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest purity for specialty materials or silicon: A fused quartz crucible is the correct choice due to its inert nature.
- If your primary focus is melting steel, iron, or other high-temperature alloys: You must use a high-temperature ceramic crucible, such as one made from alumina or zirconia.
- If your primary focus is general hobbyist foundry work on a budget: A quality clay-graphite crucible is the most versatile and cost-effective starting point.
Ultimately, matching the crucible material to the specific demands of your work is the foundation for a safe and successful melt.
Summary Table:
| Material | Best For | Key Property |
|---|---|---|
| Graphite | Non-ferrous metals (gold, aluminum) | High thermal conductivity |
| Quartz (Fused Silica) | High-purity applications (semiconductors) | Excellent thermal shock resistance |
| Clay-Graphite / Silicon Carbide | Foundry work (brass, copper) | Balance of durability and cost |
| Alumina | High-temperature alloys (steel, platinum) | Extreme temperature resistance |
Ensure the success and purity of your next melt. Selecting the perfect crucible is critical for achieving your desired results. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including a full range of crucibles for every application. Our experts can help you choose the right material for your specific needs, whether you're working with precious metals, high-purity materials, or industrial alloys. Contact our specialists today for a consultation and let us provide the reliable equipment you need for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
People Also Ask
- Why use high-purity alumina crucibles for RPPO calcination? Ensure Stoichiometric Purity at 1150°C
- What precautions should be taken when using a crucible? Essential Steps for Safety and Accuracy
- What temperature can alumina crucible withstand? A Guide to High-Temperature Stability and Safety
- Why are alumina crucibles selected for wood-plastic composite tests? Ensure Precision at 1000°C
- What is a crucible material for a furnace? A Guide to Choosing the Right High-Temperature Container



















