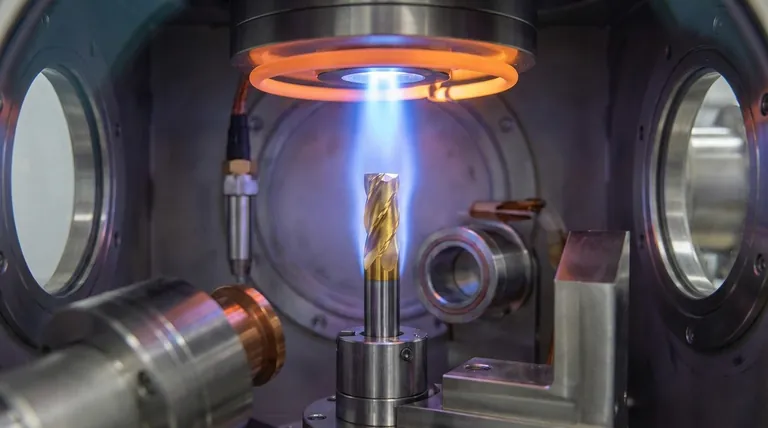
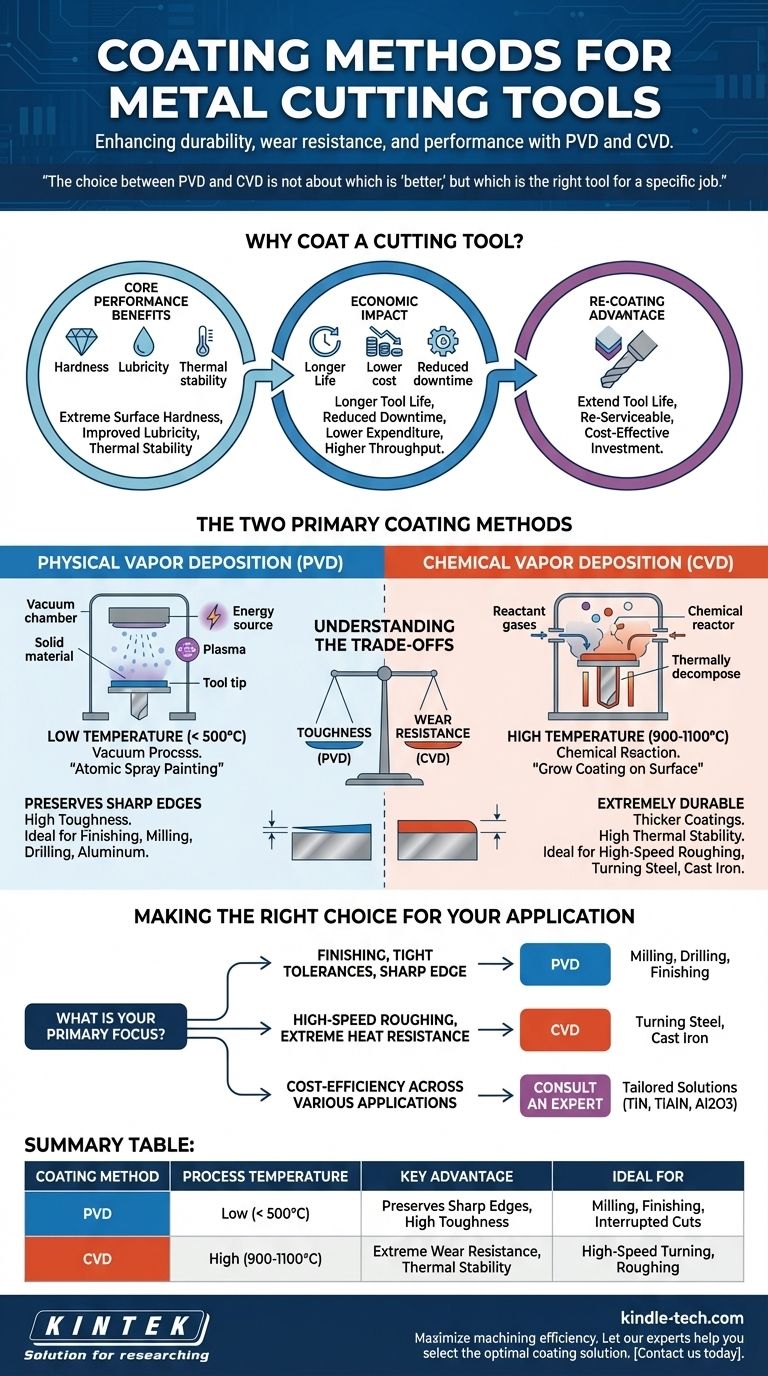
The two primary methods for coating metal cutting tools are Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). These processes apply a micro-thin layer of extremely hard material to a tool's surface, significantly increasing its durability and wear resistance. This enhancement results in longer tool life, better performance, and a notable reduction in overall production costs.
The choice between PVD and CVD is not about which is "better," but which is the right tool for a specific job. PVD is defined by its lower temperature process, ideal for maintaining sharp edges, while CVD uses high heat to create exceptionally durable coatings for high-wear applications.

Why Coat a Cutting Tool in the First Place?
Applying a coating is a standard, high-value step in modern tool manufacturing. A layer often just a few microns thick can fundamentally change a tool's performance characteristics and economic viability.
The Core Performance Benefits
The primary goal of a coating is to introduce properties the base tool material (like carbide or high-speed steel) lacks. This includes extreme surface hardness for wear resistance, improved lubricity to reduce friction and heat, and thermal stability to prevent breakdown at high cutting speeds.
The Economic Impact
A more durable tool lasts longer, which directly translates to cost savings. Longer tool life means fewer tool changes, reduced machine downtime, and lower overall tooling expenditure. This allows for higher cutting speeds and feeds, increasing throughput.
The Re-coating Advantage
High-performance tools are an investment. Many coated tools can be re-serviced by carefully re-grinding the cutting edge and then re-applying a fresh coating. This cycle can be repeated multiple times, dramatically extending the useful life of the tool body.
The Two Primary Coating Methods Explained
While both PVD and CVD create a protective layer, the way they do so creates distinct advantages and disadvantages for different cutting scenarios.
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD)
PVD is a lower-temperature process (typically below 500°C) conducted in a vacuum. Think of it as a highly controlled "atomic spray painting," where a solid coating material is vaporized and then deposited onto the tool.
Because it operates at lower temperatures, PVD does not alter the core properties of the tool's substrate material. This preserves the toughness and fatigue resistance of carbide, making it ideal for applications involving interrupted cuts, like milling.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
CVD is a high-temperature process (often 900-1100°C) where chemical gases react in a chamber to "grow" a coating directly on the tool's surface. This process results in an exceptionally strong molecular bond between the coating and the tool.
The primary benefit of CVD is its ability to create thicker, incredibly wear-resistant coatings with excellent thermal stability. This makes it the go-to choice for high-heat, continuous cutting operations like turning steel or cast iron at high speeds.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice between these methods comes down to balancing the demands of the material being cut and the type of machining operation.
Impact of Process Temperature
The high heat of the CVD process is its greatest strength and biggest limitation. While it creates a very durable coating, it can reduce the toughness of the underlying carbide substrate. PVD's low-temperature application avoids this, making PVD-coated tools inherently tougher.
Coating Thickness and Edge Sharpness
PVD coatings are thinner and smoother, which allows for the preservation of a very sharp, precise cutting edge. This is critical for finishing operations, drilling, and milling aluminum.
CVD coatings are generally thicker, which can slightly round the cutting edge. While this is a disadvantage for precision work, it adds strength to the edge, making it perfect for heavy roughing operations where brute-force wear resistance is paramount.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct coating is essential for optimizing a machining process. Base your decision on the primary demand of your specific application.
- If your primary focus is finishing, tight tolerances, or maintaining a sharp edge (e.g., milling, drilling): PVD is typically the superior choice due to its lower process temperature and ability to create a thin, smooth coating.
- If your primary focus is high-speed roughing, extreme heat resistance, and maximum wear life (e.g., turning steel): CVD is the standard due to its thick, thermally stable layers that excel in high-heat, abrasive environments.
- If your primary focus is cost-efficiency across various applications: Consider a tooling supplier that offers both options and can advise on specific coatings (like TiN, TiAlN, or Al2O3) tailored to the material you are cutting.
Understanding the fundamental differences between these technologies empowers you to select the right tool for the job, maximizing both performance and profitability.
Summary Table:
| Coating Method | Process Temperature | Key Advantage | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| PVD | Low (< 500°C) | Preserves sharp edges, high toughness | Milling, finishing, interrupted cuts |
| CVD | High (900-1100°C) | Extreme wear resistance, thermal stability | High-speed turning, roughing |
Maximize your machining efficiency with the right tool coating. The choice between PVD and CVD coatings is critical for tool life, performance, and cost savings. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for coating analysis and development, serving the precise needs of laboratories and manufacturers. Let our experts help you select the optimal coating solution for your specific application. Contact us today to discuss your requirements and enhance your tooling performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the CVD process reaction? A Guide to Chemical Vapor Deposition Mechanisms
- What are the steps of MOCVD process? A Guide to High-Quality Semiconductor Film Growth
- What role do heating filaments play in HWCVD systems? Master Low-Temp nanocrystalline SiC:H Film Deposition
- What are the benefits and characteristics of coatings produced by Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)? | High-Purity Solutions
- What is a thin film technology? The Atomic-Scale Process Powering Modern Electronics
- What is low pressure chemical vapor deposition LPCVD? Achieving Superior Uniform Thin Films
- What is Photochemical CVD? Discover Its Key Advantages in Advanced CMOS Technology
- What is the principle of CVD process? Growing High-Performance Materials from Gas



















