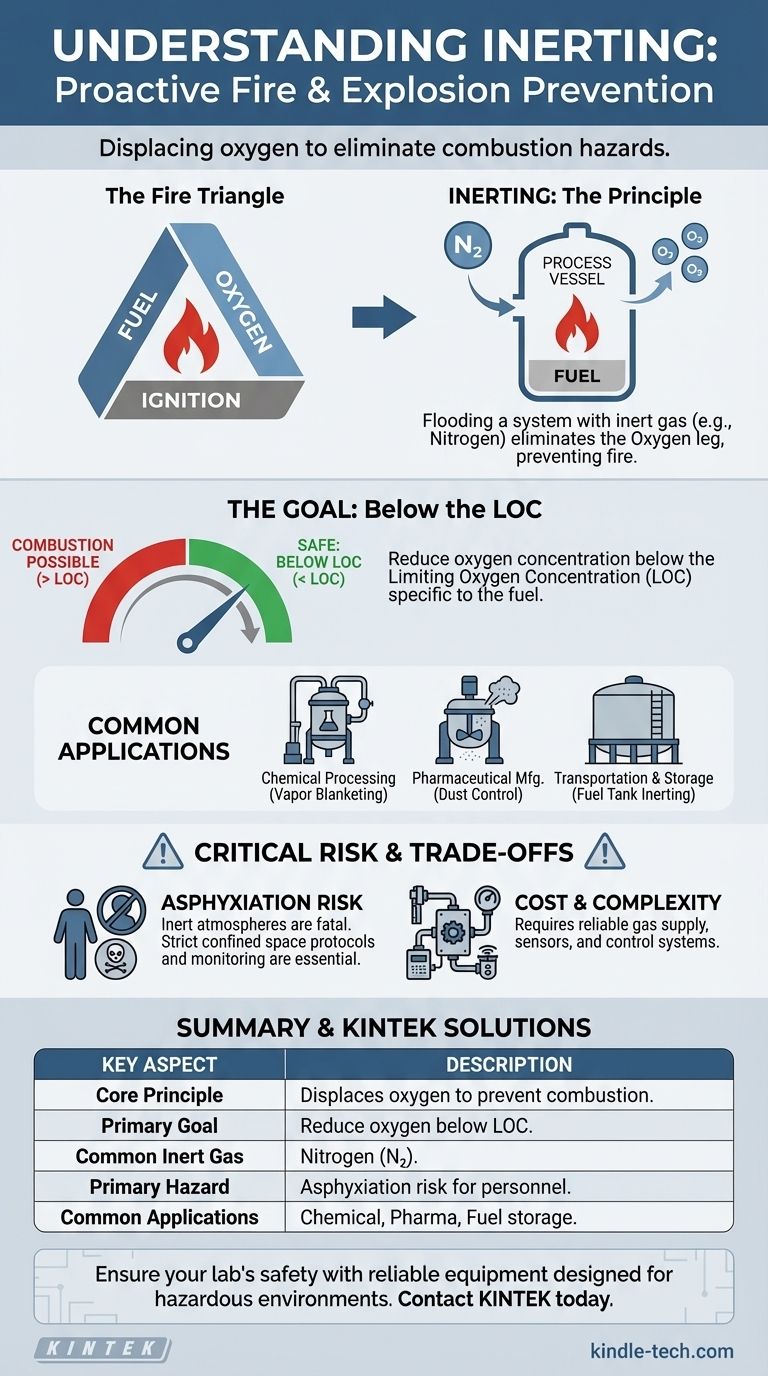
In fire and explosion prevention, inerting is the process of displacing the oxygen in a hazardous atmosphere with a non-combustible gas. By deliberately making the atmosphere oxygen-deficient, it becomes impossible for a fire or explosion to start, even if flammable fuel and an ignition source are present.
The core principle of inerting is to proactively eliminate one essential leg of the "fire triangle"—oxygen. This removes the possibility of combustion before it can ever begin, serving as a critical engineering control in high-risk industrial environments.

The Principle: How Inerting Prevents Combustion
To understand inerting, you must first understand the basic requirements for a fire or explosion. This is often visualized as the "fire triangle," which consists of three essential components.
Fuel, Oxygen, and Ignition
For combustion to occur, three elements must be present at the same time:
- Fuel: A flammable substance, such as a solvent vapor, combustible dust, or gas.
- Oxygen: Typically from the ambient air, which is about 21% oxygen.
- Ignition Source: A spark, flame, or sufficient heat to initiate the reaction.
Removing any one of these three elements prevents a fire. While controlling ignition sources and fuel is important, it is not always possible.
Eliminating Oxygen from the Equation
Inerting focuses exclusively on eliminating the oxygen element. This is achieved by flooding a closed system—like a process vessel, reactor, or storage tank—with an inert gas.
The inert gas, most commonly nitrogen, dilutes the concentration of oxygen in the vessel's atmosphere. This process continues until the oxygen level drops below a critical threshold known as the Limiting Oxygen Concentration (LOC).
The Limiting Oxygen Concentration (LOC)
The LOC is the minimum oxygen concentration required to support combustion for a specific fuel. Each flammable substance has its own unique LOC.
For example, the LOC for methane is around 12%, while for hydrogen it is much lower, at 5%. Safety standards typically require that inerting processes reduce the oxygen level to well below the LOC, often to 5% or less, to provide a margin of safety.
Common Applications and Scenarios
Inerting is not a theoretical concept; it is a fundamental safety practice applied across numerous industries where flammable materials are handled.
Chemical and Petrochemical Processing
In reactors and storage tanks, flammable vapors can easily accumulate in the headspace above a liquid. Inerting this vapor space, often called "blanketing," prevents an explosion if an ignition source like a static discharge were to occur.
Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
Many pharmaceutical products are fine powders that can create a combustible dust cloud during processing or transfer. Inerting mixers, dryers, and conveyance systems prevents devastating dust explosions.
Transportation and Storage
The fuel tanks of large oil tankers and cargo aircraft are often inerted to prevent ignition of fuel vapors. This is also common practice for storing highly volatile liquids in tank farms.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
While highly effective, inerting is an engineered system that comes with its own set of critical considerations and inherent risks that must be managed.
The Foremost Risk: Asphyxiation
An inerted atmosphere is, by design, incapable of supporting life. The primary hazard associated with inerting is the risk of asphyxiation for personnel.
Any vessel or area that has been inerted is an immediate danger to life. Strict safety protocols, including confined space entry permits, air monitoring, and lockout/tagout procedures, are absolutely essential before any human entry.
Cost and Complexity
Implementing an inerting system requires a reliable source of inert gas, such as a nitrogen generator or a bulk liquid nitrogen tank. It also involves the cost of piping, valves, oxygen sensors, and control systems to ensure the process operates correctly and safely.
Applying This to Your Goal
The specific strategy for inerting depends entirely on the material being handled and the nature of the industrial process.
- If your primary focus is storing volatile liquids: Your goal is to use a low-pressure "nitrogen blanket" to continuously protect the vapor space in your tanks.
- If your primary focus is preventing dust explosions: You must inert the entire volume of the process equipment, such as mills or dryers, where a combustible dust cloud can form.
- If your primary focus is operational safety for personnel: Your procedures must prioritize verifying the vessel has been thoroughly purged with breathable air and tested for safe oxygen levels before any maintenance work begins.
Ultimately, inerting is a powerful and proactive safety measure that chemically prevents a hazardous atmosphere from ever becoming ignitable.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Displaces oxygen in an atmosphere to prevent combustion, removing one element of the "fire triangle." |
| Primary Goal | Reduce oxygen concentration below the Limiting Oxygen Concentration (LOC) for a specific fuel. |
| Common Inert Gas | Nitrogen is most frequently used. |
| Primary Hazard | Asphyxiation risk for personnel due to oxygen-deficient atmosphere. |
| Common Applications | Chemical processing, pharmaceutical manufacturing, fuel tank blanketing, and combustible dust handling. |
Ensure your lab's safety with reliable equipment designed for hazardous environments.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Whether your processes involve volatile solvents or combustible dust, having the right, safe equipment is the first step in risk mitigation.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can support your safety protocols and operational goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- RRDE rotating disk (ring disk) electrode / compatible with PINE, Japanese ALS, Swiss Metrohm glassy carbon platinum
- Customizable PEM Electrolysis Cells for Diverse Research Applications
People Also Ask
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is the vapor phase deposition technique? A Guide to PVD & CVD Thin-Film Coating Methods
- What are the methods of deposition? A Guide to PVD and CVD Thin-Film Techniques
- What is the difference between PECVD and CVD? Unlock the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- What are the different types of thin films? A Guide to Optical, Electrical, and Functional Coatings



















