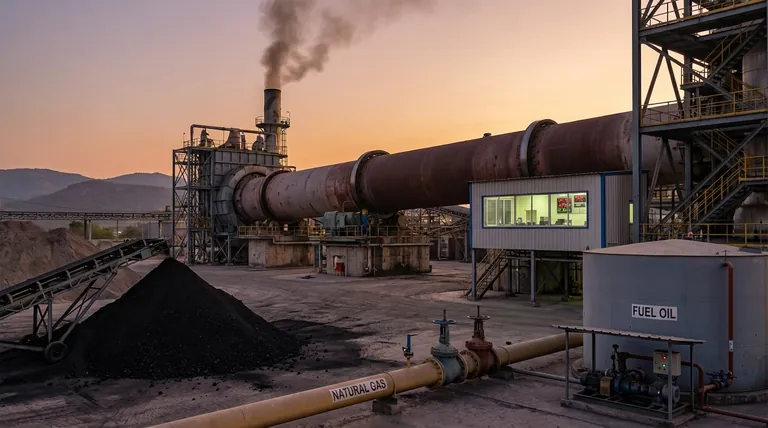
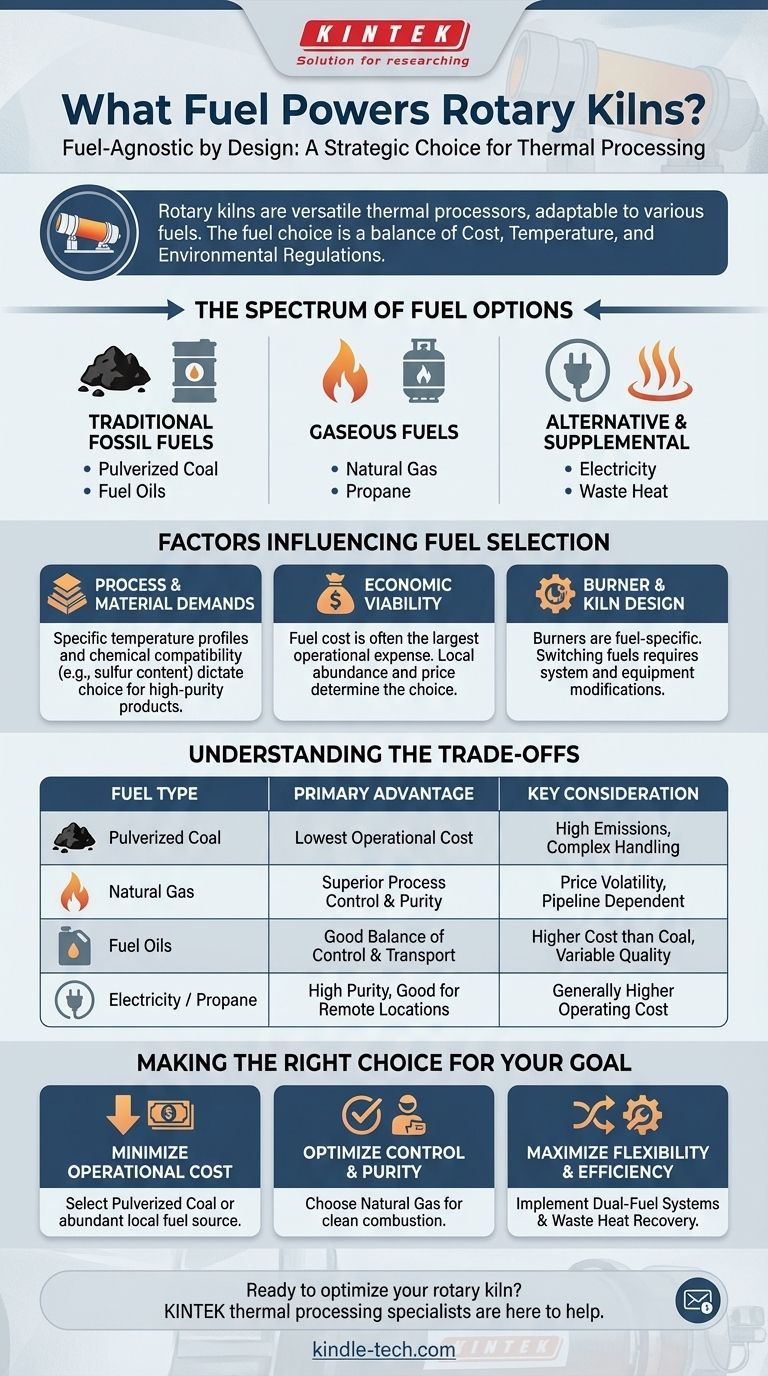
At their core, rotary kilns are highly versatile thermal processors that can be fueled by a wide range of sources. The most common fuels include pulverized coal, natural gas, and various fuel oils, but they can also be adapted to use propane, synthetic gases, or even electricity depending on the specific application and economic factors.
The fundamental takeaway is that rotary kilns are fuel-agnostic by design. The final choice of fuel is almost always a strategic decision driven by a balance of three factors: local fuel cost, the required processing temperature, and environmental regulations.

The Spectrum of Fuel Options
A rotary kiln's primary function is to heat materials to a very high temperature to cause a chemical or physical change. The fuel is simply the means to generate that heat, and many options are available.
Traditional Fossil Fuels
The workhorses of kiln firing are traditional fossil fuels. Pulverized coal, first used in 1895, remains a dominant choice in many industries, particularly cement manufacturing, due to its high energy density and cost-effectiveness.
Heavy and light fuel oils are also common, offering easier transport and storage than solid coal.
Gaseous Fuels
Natural gas is a premier fuel for rotary kilns when available and affordable. It burns cleanly, offers exceptionally precise temperature control, and produces minimal ash.
For applications in more remote locations or as a backup, propane can serve a similar role to natural gas.
Alternative and Supplemental Sources
Modern kiln operations are increasingly integrating other energy sources. Some specialized processes may use electricity for direct heating, although this is generally less common due to high cost.
More importantly, many systems are designed to reuse waste heat. Exhaust gases from the hot end of the kiln are often ducted to a pre-heater to raise the temperature of the incoming material, significantly improving overall thermal efficiency.
Factors Influencing Fuel Selection
The decision of which fuel to use is never arbitrary. It is a calculated choice based on the interplay of process needs, economics, and logistics.
Process and Material Demands
The material being processed dictates the entire operation. Producing cement or lime requires specific and stable temperature profiles that some fuels can maintain more easily than others.
The chemistry of the fuel is also critical. For example, the sulfur content in coal or fuel oil can react with materials like lime, so a cleaner-burning fuel like natural gas may be necessary for high-purity products.
Economic Viability
In most heavy industries, fuel cost is the single largest operational expense. Therefore, the choice is often dictated by which energy source is most abundant and cheapest in a given region.
This is why coal remains prevalent in areas with large reserves, while natural gas is favored where extensive pipeline infrastructure exists.
Burner and Kiln Design
A kiln is not a simple furnace; it is an integrated system. The burner, which injects and ignites the fuel, is specifically designed for a particular fuel type—whether solid, liquid, or gas.
Switching from natural gas to pulverized coal, for instance, requires a completely different burner system, as well as equipment for milling, conveying, and storing the coal.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Each fuel source presents a distinct set of advantages and disadvantages. Recognizing these trade-offs is key to understanding why a particular fuel is chosen for a specific operation.
Coal: Cost-Effective but Complex
Coal offers unmatched energy for its cost in many regions. However, it requires extensive on-site handling, produces ash that must be managed, and releases higher levels of pollutants like SOx, NOx, and particulates unless expensive scrubbing technology is installed.
Natural Gas: Clean but Volatile
Gas provides superior process control and is the cleanest-burning fossil fuel, which simplifies environmental compliance and can improve product purity. Its primary downside is price volatility and dependence on pipeline availability, which can make it an uneconomical choice in some markets.
Fuel Oils: The Middle Ground
Fuel oils are easier to transport and store than coal and offer better combustion control. However, they are typically more expensive than coal and can have variable properties (like sulfur content) that affect emissions and product quality.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the optimal fuel, you must first define your primary objective for the kiln operation.
- If your primary focus is minimizing operational cost: Pulverized coal or the most abundant local fuel source is almost always the most economical path forward.
- If your primary focus is process control and product purity: Natural gas is the superior choice for its clean combustion and highly responsive temperature management.
- If your primary focus is operational flexibility and efficiency: A dual-fuel system combined with robust waste heat recovery provides resilience against price swings and maximizes thermal efficiency.
The remarkable adaptability of the rotary kiln to various fuel sources is a key reason it remains an indispensable tool across global industry.
Summary Table:
| Fuel Type | Primary Advantage | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Pulverized Coal | Lowest operational cost | High emissions, complex handling |
| Natural Gas | Superior process control & purity | Price volatility, pipeline dependent |
| Fuel Oils | Good balance of control & transport | Higher cost than coal, variable quality |
| Electricity / Propane | High purity, good for remote locations | Generally higher operating cost |
Ready to optimize your rotary kiln's performance? The choice of fuel is critical to your operational costs, product quality, and environmental compliance. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts can help you analyze your specific process requirements to select the ideal fuel and burner system for your goals. Contact our thermal processing specialists today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- At what temperature does wood pyrolysis begin? Control the Process for Biochar, Bio-Oil, or Syngas
- How are tube furnaces classified based on the orientation of the tube? Choose the Right Design for Your Process
- What is a rotary heat type furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Uniform Heating & Mixing
- What is the temperature of a rotary hearth furnace? Find the Right Heat for Your Process
- What is a rotary retort furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity in Continuous Heat Treatment



















