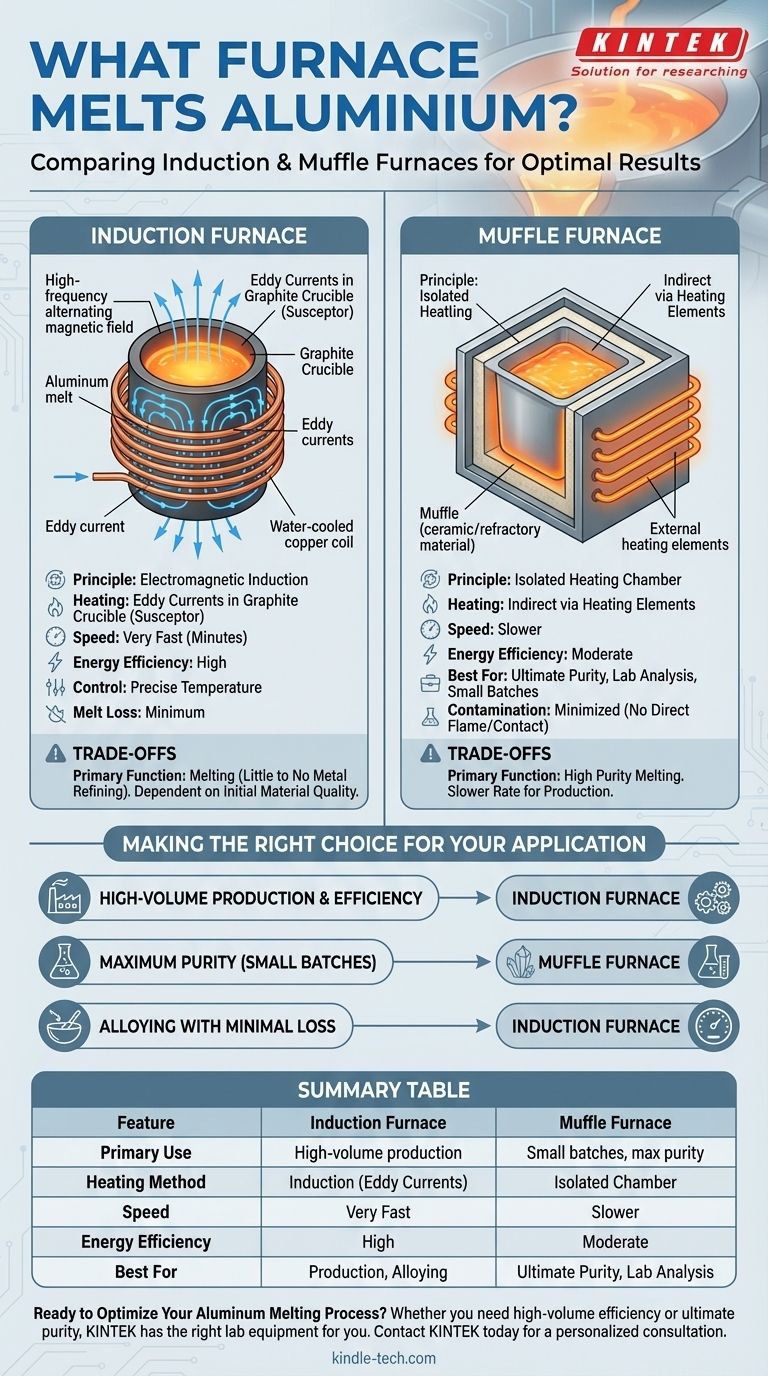
For melting aluminum, the most common and effective choice is an induction furnace. These furnaces are favored for their high energy efficiency, precise temperature control, and clean melting process, which minimizes metal loss and contamination. They are highly scalable, making them suitable for both small-scale operations and large industrial production.
The optimal furnace for melting aluminum depends on your specific goals. While induction furnaces offer the best balance of efficiency, speed, and control for most applications, specialized furnaces like muffle furnaces are superior when absolute purity is the primary concern.

How Induction Furnaces Melt Aluminum
An induction furnace does not use direct flame or external heating elements to melt the metal. Instead, it leverages the principles of electromagnetism.
The Principle of Induction Heating
The furnace generates a powerful, high-frequency alternating magnetic field. This field surrounds a crucible, typically made of graphite, which holds the aluminum charge.
Graphite is an ideal material because it acts as a susceptor, meaning it readily absorbs the electromagnetic energy and converts it into heat.
Inducing Eddy Currents
The rapidly changing magnetic field induces powerful electrical currents, known as eddy currents, within the graphite crucible itself. The resistance within the graphite causes it to heat up rapidly and uniformly, melting the aluminum inside through conduction and radiation.
This method is exceptionally clean, as the heat is generated directly within the crucible system, not from an external flame that could introduce impurities.
Key Benefits of Induction Furnaces
The design of an induction furnace offers several distinct advantages for processing aluminum.
Energy Efficiency and Speed
By generating heat directly where it's needed, induction furnaces minimize thermal loss. This makes them significantly more energy-efficient than traditional fuel-fired furnaces. High-power units can melt metals in a matter of minutes, drastically increasing production throughput.
Precise Temperature Control
The power supplied to the induction coil can be regulated with extreme precision. This allows for stable, uniform heating and prevents overheating, which is critical for maintaining the quality and properties of aluminum alloys.
Clean Melting and Minimal Loss
Because there is no combustion, the process is inherently clean, with no byproducts from fuel contaminating the melt. This, combined with precise temperature control, results in minimum melt losses from oxidation or vaporization.
Scalability and Versatility
Induction furnaces are available in a vast range of sizes, from small tabletop units for workshops to massive systems for industrial foundries. This allows businesses to invest in a system that fits their current needs and easily scale up as production demands grow.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, induction furnaces have one key limitation that must be considered.
Little to No Metal Refining
An induction furnace is primarily a melting device, not a refining one. It will efficiently melt the aluminum you put into it, but it will not remove existing impurities from the source material.
The quality of the final product is therefore highly dependent on the quality of the initial aluminum scrap or ingot. If refining is required, a separate process or a different type of furnace system would be necessary.
Considering a Muffle Furnace
For applications demanding the absolute highest purity, a muffle furnace is a viable alternative. This design separates the material being heated from any direct contact with flames or heating elements.
This isolation prevents contamination and issues like spatter, making it ideal for laboratory analysis or producing small batches of exceptionally pure material, though typically at a slower rate than induction melting.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the correct furnace, you must first define your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production and energy efficiency: An induction furnace is the superior choice due to its speed, control, and low operational cost.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum purity in smaller batches: A muffle furnace is better suited, as it isolates the aluminum from all potential contaminants.
- If your primary focus is creating alloys with minimal material loss: The precise control and clean nature of an induction furnace make it ideal for alloying with predictable, repeatable results.
Ultimately, understanding the capabilities and limitations of each furnace type empowers you to select the tool that best aligns with your specific operational goal.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Induction Furnace | Muffle Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | High-volume production melting | Small batches, maximum purity |
| Heating Method | Electromagnetic induction (eddy currents) | Isolated heating chamber |
| Speed | Very Fast (minutes) | Slower |
| Energy Efficiency | High | Moderate |
| Best For | Production efficiency, alloying | Ultimate purity, lab analysis |
Ready to Optimize Your Aluminum Melting Process?
Whether you need the high-volume efficiency of an induction furnace or the ultimate purity of a muffle furnace, KINTEK has the right lab equipment for you. Our experts will help you select the perfect solution to enhance your productivity and material quality.
Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation and discover how our specialized furnaces can meet your specific laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Multi-zone Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between induction melting and vacuum induction melting? Choosing the Right Process for Purity
- What is vacuum arc melting technique? Discover the Precision of Vacuum Induction Melting
- What principle is used to generate heat in a vacuum induction melting furnace? Achieve Clean, Efficient Metal Melting
- What is the vacuum induction method? Master High-Purity Metal Melting for Advanced Alloys
- How does induction work in a vacuum? Achieve Ultra-Pure Metal Melting with VIM



















