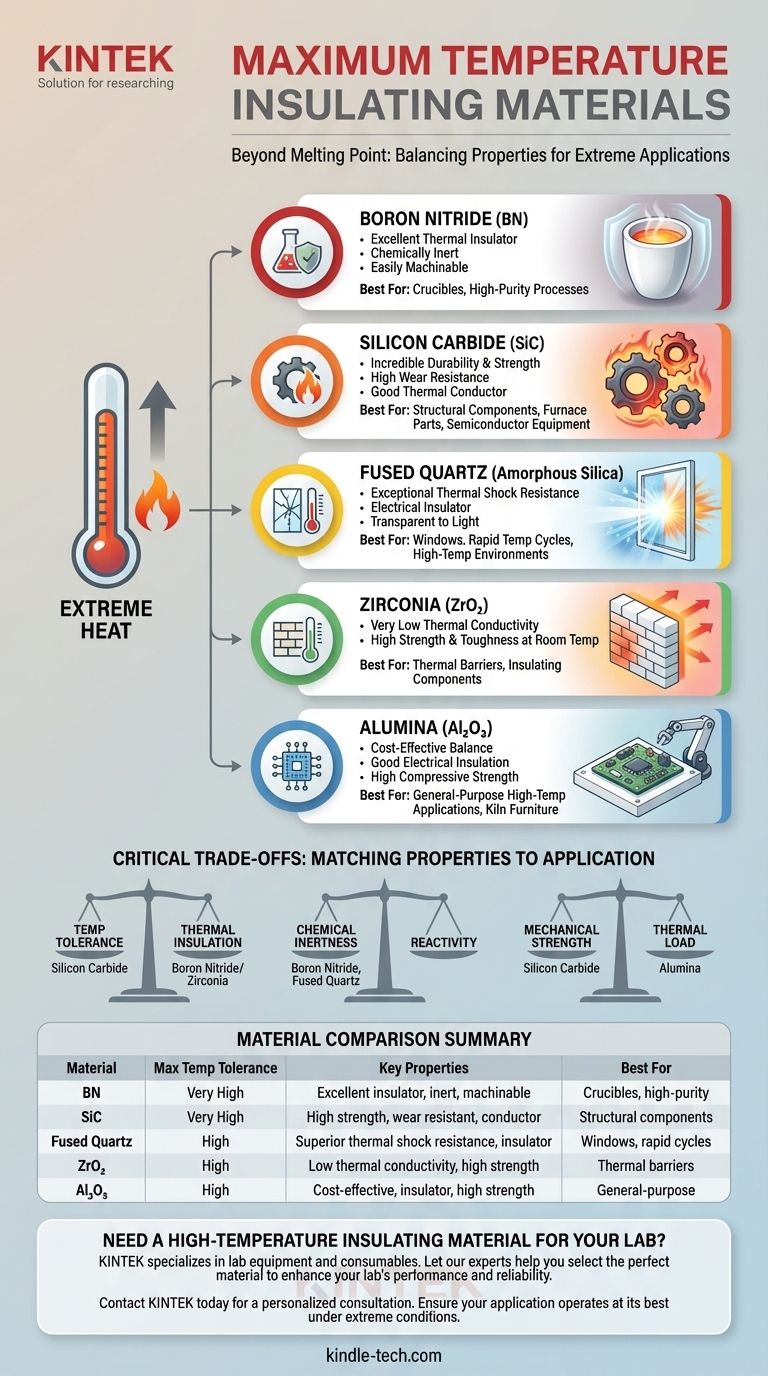
For the highest temperature applications, you must look to advanced refractory materials and technical ceramics. Key examples include Boron Nitride, Silicon Carbide, and Fused Quartz, each engineered to withstand extreme heat while offering unique properties for specific industrial and scientific uses.
The most critical insight is that "maximum temperature tolerance" is only one part of the equation. The ideal material depends on a balance of its thermal conductivity, chemical inertness, and mechanical strength under the specific conditions of your application.

A Closer Look at High-Temperature Materials
Choosing the right material requires understanding the distinct characteristics of each leading option. They are not interchangeable, and their performance is dictated by more than just a melting point.
Fused Quartz (Amorphous Silica)
Fused Quartz is a high-purity glass known for its exceptional resistance to thermal shock. This means it can endure rapid and extreme temperature changes without cracking.
It is also an excellent electrical insulator and is transparent to a wide range of light wavelengths, making it useful for windows in high-temperature environments.
Silicon Carbide (SiC)
Silicon Carbide is a ceramic prized for its incredible durability and strength at very high temperatures. It maintains its structural integrity well above 1000°C.
It is often used in applications requiring high wear resistance, such as in semiconductor production equipment and as a structural component in furnaces. Note that it has relatively high thermal conductivity, making it less of a pure insulator and more of a durable, heat-tolerant structural material.
Boron Nitride (BN)
Boron Nitride is an outstanding thermal insulator that is also easily machinable, a rare combination for a technical ceramic. This allows it to be shaped into complex components.
It is extremely chemically inert and is not wetted by most molten metals, making it an ideal choice for crucibles and containers in high-purity metallurgical processes.
Other Key Refractory Ceramics
Beyond the initial examples, two other materials are workhorses in high-temperature applications.
Alumina (Aluminum Oxide) is one of the most cost-effective and widely used technical ceramics. It offers a great balance of high-temperature stability, good electrical insulation, and high compressive strength.
Zirconia (Zirconium Dioxide) offers one of the highest strength and toughness ratings at room temperature among all advanced ceramics. Critically, it has very low thermal conductivity, making it a superb thermal barrier or insulator.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
Selecting a material based on a single property is a common mistake. The operational environment dictates which trade-offs are acceptable.
Temperature Tolerance vs. Thermal Insulation
A material that can withstand extreme heat is not necessarily a good material to block heat.
Silicon Carbide, for example, can operate at very high temperatures but conducts heat relatively well. In contrast, Zirconia and Boron Nitride can also tolerate high heat but are far more effective at preventing its transfer.
Chemical Inertness
At high temperatures, chemical reactions accelerate. The material you choose must not react with its contents or the surrounding atmosphere.
Boron Nitride and Fused Quartz offer superior chemical resistance, making them suitable for working with molten metals and corrosive substances where contamination is a concern.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Heat can soften and weaken materials. If your application involves physical stress, abrasion, or pressure, a material's strength at its operating temperature is a critical factor.
Silicon Carbide and Alumina are known for their excellent mechanical properties under thermal load, making them ideal for structural components like kiln furniture and heating element supports.
Cost and Machinability
Finally, practical considerations often guide the decision. High-performance materials come with significant cost implications.
Boron Nitride is highly effective but expensive. Alumina offers a much more economical balance of properties for a wider range of applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final selection must be driven by your primary engineering goal.
- If your primary focus is maximum thermal insulation: Zirconia and Boron Nitride are superior choices due to their very low thermal conductivity.
- If your primary focus is mechanical strength and wear resistance: Silicon Carbide and Alumina provide the durability needed for structural components.
- If your primary focus is resistance to thermal shock and chemical purity: Fused Quartz and Boron Nitride are excellent for applications with rapid temperature cycles or contact with reactive materials.
Ultimately, choosing the right material is about matching its unique combination of properties to the demands of your specific environment.
Summary Table:
| Material | Max Temp Tolerance | Key Properties | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Boron Nitride (BN) | Very High | Excellent thermal insulator, chemically inert, machinable | Crucibles, high-purity processes |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Very High | High strength, wear resistance, good thermal conductor | Structural components, furnace parts |
| Fused Quartz | High | Superior thermal shock resistance, electrical insulator | Windows, rapid temperature cycles |
| Zirconia (ZrO₂) | High | Low thermal conductivity, high strength at room temperature | Thermal barriers, insulating components |
| Alumina (Al₂O₃) | High | Cost-effective, good electrical insulation, high strength | General-purpose high-temperature applications |
Need a High-Temperature Insulating Material for Your Lab?
Choosing the right material is critical for the safety and efficiency of your high-temperature processes. The wrong choice can lead to equipment failure, contamination, or wasted resources.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing expert guidance and high-quality materials like Boron Nitride, Silicon Carbide, and Zirconia to meet your specific laboratory needs. We help you navigate the trade-offs between thermal insulation, mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and cost.
Let our experts help you select the perfect material to enhance your lab's performance and reliability.
Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation and ensure your application operates at its best under extreme conditions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Parts
- Zirconia Ceramic Gasket Insulating Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Hexagonal Boron Nitride HBN Ceramic Ring
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Sheet Wear-Resistant Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- High Temperature Wear-Resistant Alumina Al2O3 Plate for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- Why is Boron Nitride used in RRDE? Enhance Precision with Superior Insulating and Protective Material
- What is the function of a BN inner liner in a graphite mold during Flash Sintering? Master Precise Current Control
- What is the insulating material used in furnace? Achieve Peak Thermal Efficiency & Stability
- What are alloys in simple words? Unlock the Power of Engineered Materials
- What are the disadvantages of brazing? Understanding the key limitations and trade-offs.



















