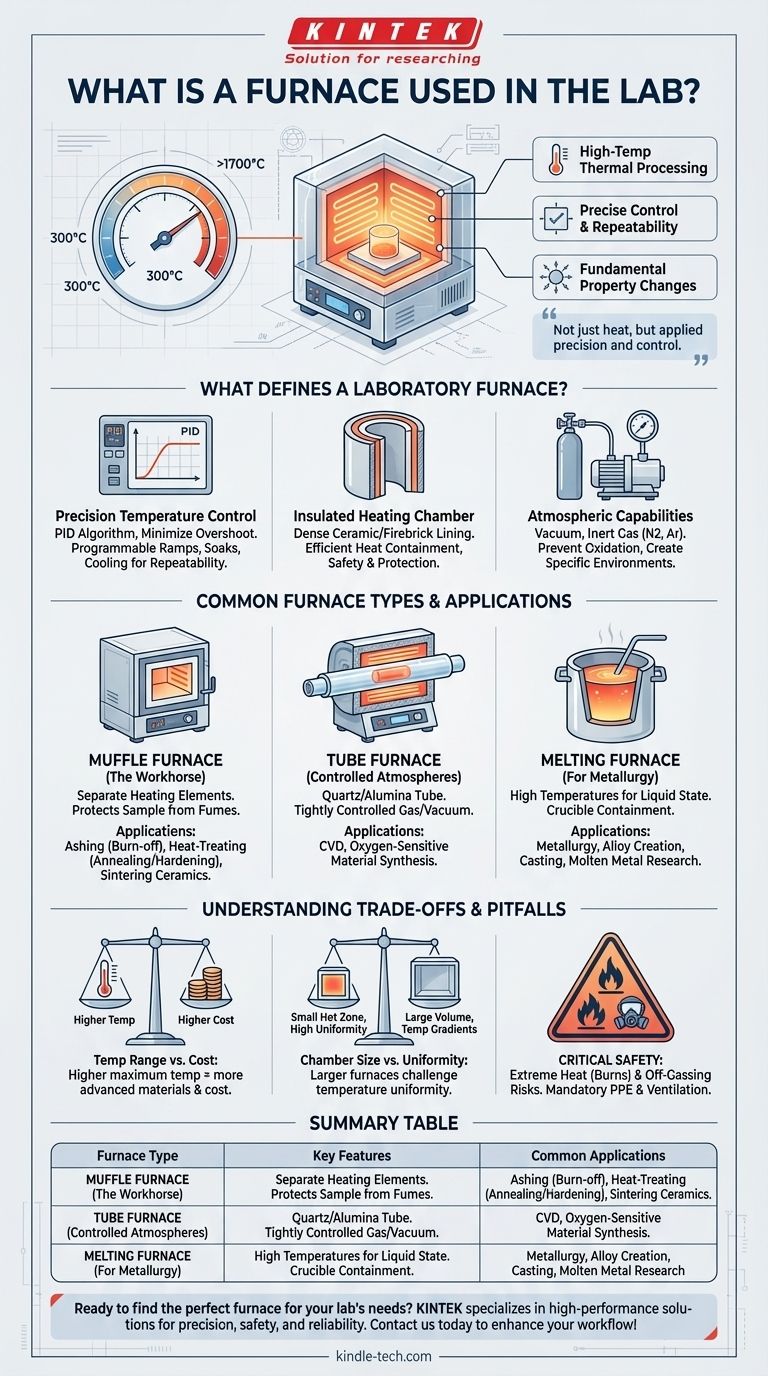
At its core, a laboratory furnace is a high-temperature thermal processing instrument used to subject materials to precisely controlled heat. Unlike a simple oven, it is designed to reach temperatures often ranging from 300°C to over 1700°C (572°F to 3092°F), enabling fundamental changes in a material's physical or chemical properties for research, testing, or sample preparation.
A lab furnace is not just about generating heat; it is about applying that heat with precision and control. The key is to understand that the specific task—be it melting metal, testing ceramics, or preparing a sample for analysis—dictates the type of furnace required.

What Defines a Laboratory Furnace?
While designs vary, all laboratory furnaces are built around a few core principles that separate them from standard heating equipment.
Precision Temperature Control
The defining feature of a lab furnace is its ability to execute a specific temperature profile. This is managed by a digital controller, often using a PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) algorithm to minimize temperature over- and undershooting.
This allows researchers to program precise heating rates (ramps), hold times (soaks), and cooling rates, which is critical for repeatable experiments.
Insulated Heating Chamber
The heart of the furnace is a highly insulated chamber. This chamber is typically lined with dense ceramic fiber or firebrick to contain the extreme heat efficiently and protect the user and surrounding equipment.
The heating elements themselves are often made of specialized materials like Kanthal (iron-chromium-aluminum alloy), silicon carbide (SiC), or molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2), chosen based on the furnace's maximum required temperature.
Atmospheric Capabilities
Many advanced furnaces offer the ability to control the atmosphere within the chamber. This can range from creating a vacuum to introducing a specific gas, such as nitrogen or argon, to create an inert environment that prevents oxidation during heating.
Common Furnace Types and Their Applications
The term "lab furnace" covers several distinct designs, each optimized for different tasks.
The Muffle Furnace (The Workhorse)
Think of a muffle furnace as the general-purpose tool for high-temperature work. The heating elements are separate from the main chamber (muffled), protecting them from any fumes or materials released from the sample.
These are ideal for applications like ashing (burning off organic material to determine inorganic content), heat-treating metals (annealing or hardening), and sintering ceramics.
The Tube Furnace (For Controlled Atmospheres)
A tube furnace features a cylindrical chamber, typically made of quartz, alumina, or mullite, that passes through the insulated heating zone. Its design is perfect for processes that require a tightly controlled atmosphere.
Samples are placed inside the tube, which can then be sealed and filled with a specific gas or have a vacuum pulled. This is essential for advanced material synthesis like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) or heat-treating oxygen-sensitive materials.
The Melting or Smelting Furnace (For Metallurgy)
As its name implies, this furnace is designed specifically to bring materials to their liquid state. They are engineered to handle the high temperatures needed to melt metals like aluminum, bronze, or even steel in laboratory settings.
These furnaces are heavily used in metallurgy to create new alloys, perform casting, and conduct research on the properties of molten metals. They are built to safely contain a crucible, the ceramic pot that holds the liquid material.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
Selecting a furnace involves balancing capability, safety, and cost. Misunderstanding these factors can lead to failed experiments or safety hazards.
Temperature Range vs. Cost
The single biggest cost driver is the maximum operating temperature. A furnace rated for 1200°C is significantly less expensive than one that can reach 1700°C, as the higher temperature requires more advanced (and expensive) heating elements and insulation materials.
Chamber Size vs. Temperature Uniformity
In any furnace, there is a central volume known as the "hot zone" where the temperature is most uniform. In larger furnaces, maintaining this uniformity across the entire chamber becomes more challenging and technically demanding.
For sensitive processes, a smaller, more uniform furnace is often better than a larger one with significant temperature gradients.
Critical Safety Considerations
Furnaces are powerful tools that command respect. The primary hazards are extreme heat, which can cause severe burns instantly, and potential off-gassing from the materials being heated.
Proper ventilation is non-negotiable. Always use appropriate Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), including heat-resistant gloves and safety glasses. Ensure the furnace's electrical supply meets its high power demands to prevent fire risk.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct furnace depends entirely on the material you are working with and the transformation you wish to achieve.
- If your primary focus is sample preparation like ashing or general-purpose heat treatment: A standard muffle furnace is your most versatile and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is melting metals or creating new alloys: You need a dedicated melting or smelting furnace built to safely contain crucibles of liquid material.
- If your primary focus is research requiring a controlled gas environment (inert, vacuum, or reactive): A tube furnace is the essential tool for isolating your sample from the ambient atmosphere.
By matching the furnace's capabilities to your specific material and desired outcome, you transform a simple heat source into a powerful instrument for discovery.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Key Features | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Muffle Furnace | Separate heating elements, versatile | Ashing, heat-treating, sintering |
| Tube Furnace | Cylindrical chamber, gas/vacuum control | CVD, oxygen-sensitive material synthesis |
| Melting Furnace | High-temp crucible containment | Metallurgy, alloy creation, casting |
Ready to find the perfect furnace for your lab's needs? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including muffle, tube, and melting furnaces, designed for precision, safety, and reliability. Whether you're in research, metallurgy, or sample preparation, we provide solutions tailored to your specific requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your workflow and deliver consistent results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between a muffle furnace and a chamber furnace? Understand the Key Distinctions for Your Lab
- What is the difference between a lab oven and a muffle furnace? A Guide to Temperature Applications
- What are the advantages of dry ashing over wet ashing? Streamline Your Lab's Sample Prep
- What temperature is required for calcination? Master Material-Specific Thermal Decomposition
- What is the maximum temperature of muffle furnace? A Guide from 1100°C to 1800°C



















