In essence, a pelletizing machine is a piece of industrial equipment that takes loose, raw materials and compresses them into small, dense, uniform cylinders known as pellets. This process, called pelletization, fundamentally transforms materials like sawdust, agricultural waste, animal feed ingredients, or plastic scrap by forcing them through a steel die under intense pressure.
The true purpose of a pelletizing machine isn't just to change a material's shape. It is a value-add process that converts low-density, inconsistent, and difficult-to-handle raw goods into a standardized, flowable, and far more valuable commodity.

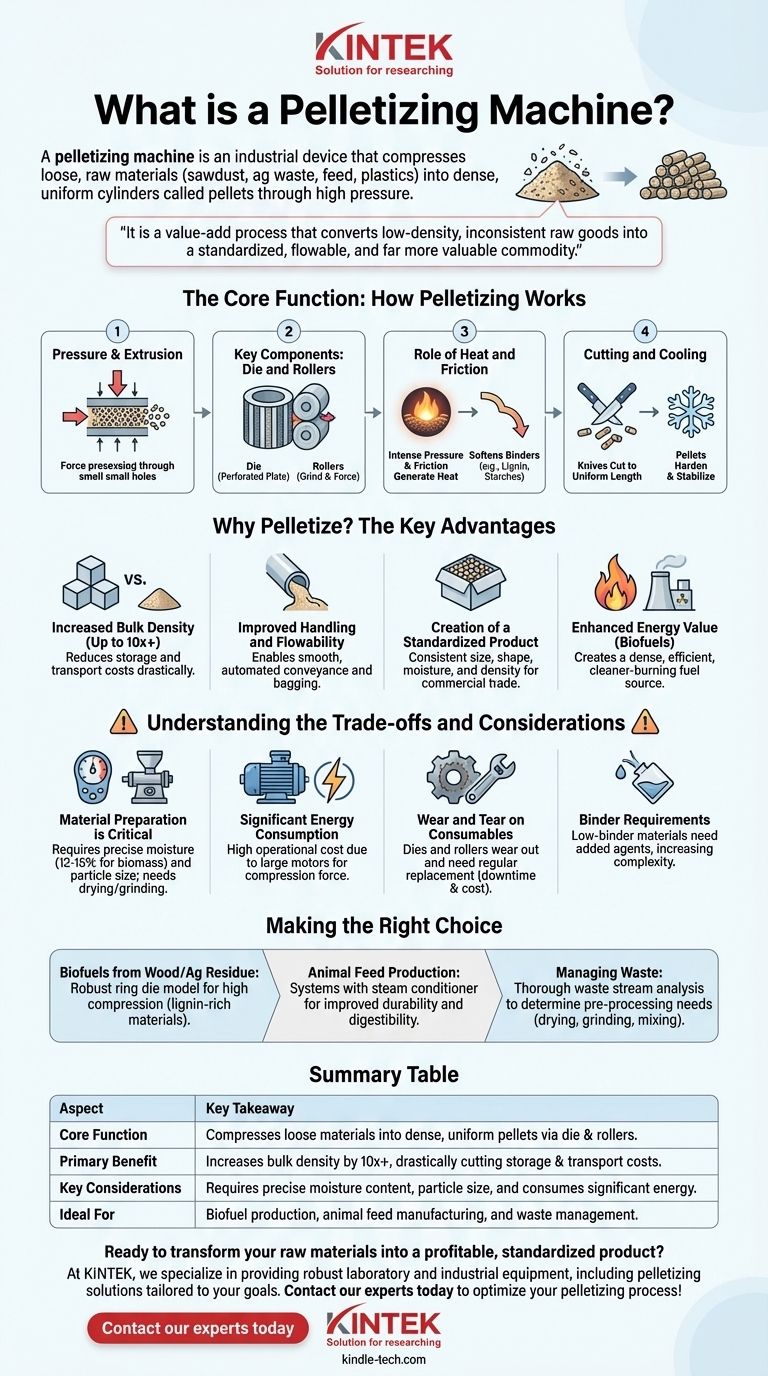
The Core Function: How Pelletizing Works
A pelletizer operates on a straightforward principle of compression and extrusion, but its effectiveness hinges on the precise interplay of several key components and conditions.
The Principle of Pressure and Extrusion
At its heart, the machine uses immense force to squeeze feedstock material through small, precisely-engineered holes in a thick metal plate. As the material is forced through, it is compacted and shaped into a dense cylinder.
Key Components: The Die and Rollers
The central components are the die and the rollers.
- The die is a heavy, circular steel plate perforated with numerous channels. It can be a flat die (a horizontal disc) or a ring die (a vertical cylinder).
- The rollers press against the die, rotating to grind and force the raw material into and through the die's channels.
The Role of Heat and Friction
As the rollers force material into the die, the intense pressure and friction generate significant heat. This heat is crucial, as it helps to soften natural binders within the material, such as lignin in wood or starches in grain. This softening process allows the material to fuse together, creating a durable, stable pellet after it cools.
Cutting and Cooling
As the dense strands of material exit the other side of the die, a set of knives cuts them to a uniform, predetermined length. These hot, soft pellets are then typically moved to a cooling system where they harden and stabilize, ready for storage or transport.
Why Pelletize? The Key Advantages
The decision to invest in a pelletizing system is driven by a few powerful and compounding benefits that solve critical logistical and commercial problems.
Increased Bulk Density
This is the most significant advantage. Pelletizing can increase the bulk density of a material by a factor of 10 or more. This dramatic compaction means you can store and transport the same mass of material in a fraction of the space, drastically cutting logistics costs.
Improved Handling and Flowability
Raw materials like sawdust, chopped straw, or ground feed are often difficult to handle. They don't flow predictably and can clog automated systems. Uniform, dense pellets, however, behave like a fluid, enabling smooth, reliable, and automated conveyance, bagging, and dispensing.
Creation of a Standardized Product
Pelletization transforms a variable raw material into a commodity with consistent size, shape, moisture content, and density. This standardization is essential for commercial trade, whether for high-grade wood pellets used in power plants or precisely formulated animal feed sold to farmers.
Enhanced Energy Value (Biofuels)
For biomass, concentrating the material into a dense pellet creates a more energy-dense fuel source. This makes it a more efficient and cleaner-burning alternative to burning the loose raw material.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, pelletizing is not a magic bullet. Success requires a clear understanding of the process limitations and operational requirements.
Material Preparation is Critical
You cannot simply feed any material into a pelletizer. The two most critical factors are moisture content (typically 12-15% for biomass) and particle size. Material that is too wet, too dry, or too large will not form proper pellets and can damage the machine. This often necessitates additional investment in drying and grinding equipment.
Significant Energy Consumption
Pelletizing is an energy-intensive process. The motors required to generate the necessary compression force are large and consume a substantial amount of electricity, which represents a primary operational cost.
Wear and Tear on Consumables
The die and rollers are the workhorses of the machine and are subject to extreme abrasion and pressure. These are consumable parts that wear out over time and must be regularly replaced. The cost and downtime associated with replacing these components are a key part of the total cost of ownership.
Binder Requirements
Some materials, especially those low in natural binders like lignin or starch, will not form a durable pellet on their own. In these cases, a binding agent must be added to the feedstock, which adds complexity and cost to the process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The right approach to pelletizing depends entirely on your raw material and your end goal.
- If your primary focus is creating biofuels from wood or agricultural residue: Prioritize a robust machine, likely a ring die model, designed for high-compression work with lignin-rich materials.
- If your primary focus is producing animal feed: Look for systems that include a steam conditioner to pre-treat the mash, which improves pellet durability and nutrient digestibility.
- If your primary focus is managing industrial or agricultural waste: Your first step is to conduct a thorough analysis of the waste stream to determine the exact pre-processing (drying, grinding, mixing) needed to create a suitable feedstock.
By understanding that pelletizing is a complete process, not just a single machine, you can effectively design a system that transforms a low-value material into a high-value asset.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Core Function | Compresses loose materials into dense, uniform pellets via a die and rollers. |
| Primary Benefit | Increases bulk density by 10x+, drastically cutting storage and transport costs. |
| Key Considerations | Requires precise moisture content, particle size, and consumes significant energy. |
| Ideal For | Biofuel production, animal feed manufacturing, and waste management. |
Ready to transform your raw materials into a profitable, standardized product?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing robust laboratory and industrial equipment, including pelletizing solutions tailored to your specific material and production goals. Whether you're processing biomass for biofuel, formulating animal feed, or managing waste streams, our expertise ensures you get a system that delivers maximum value and efficiency.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project and discover how KINTEK can help you optimize your pelletizing process from feedstock to finished product.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Single Punch Tablet Press Machine and Mass Production Rotary Tablet Punching Machine for TDP
- Rubber Vulcanizer Vulcanizing Machine Plate Vulcanizing Press for Lab
- Single Punch Manual Tablet Press Machine TDP Tablet Punching Machine
- Manual Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- How does a laboratory hydraulic press ensure the accuracy of test results? Master Precision Specimen Preparation
- What is the function of a laboratory hydraulic press in post-torrefaction? Transform Biochar into Energy-Dense Fuel
- How does a laboratory hydraulic press contribute to electrolyte layers in solid-state batteries? Achieve Peak Density
- How is a laboratory hydraulic press used to evaluate the mechanical performance of nano-modified concrete? Expert Guide
- What industries use hydraulic press? Powering Manufacturing, Construction, and R&D
- Why are laboratory hydraulic presses critical for assessing geopolymer performance? Ensure Reliable Material Testing
- How is a laboratory hydraulic press used to evaluate the stability of solid biopesticide formulations? Optimize Pellets
- How do you prepare samples for IR spectroscopy as KBr disks? Master the Technique for Clear, Accurate Spectra



















