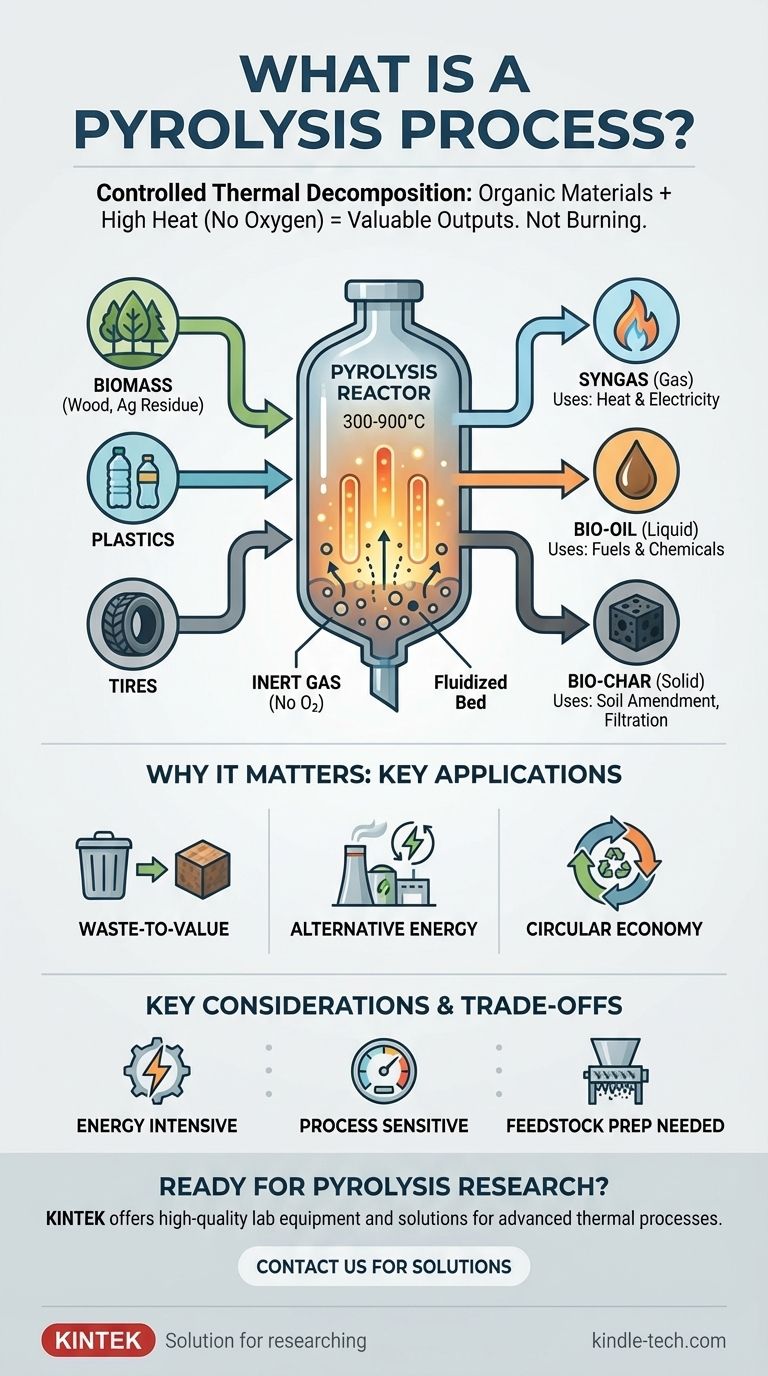
In essence, pyrolysis is a process of controlled thermal decomposition. It involves heating organic, carbon-based materials like biomass, plastics, or tires to very high temperatures in an environment completely devoid of oxygen. This prevents the material from burning and instead causes its chemical bonds to break down, transforming it into three distinct and valuable outputs: a gas (syngas), a liquid (bio-oil), and a solid (bio-char).
Pyrolysis is not burning; it's a sophisticated method of chemically transforming low-value organic waste into high-value energy and material resources by precisely applying heat in an oxygen-free environment.

How Pyrolysis Works: The Core Mechanism
Pyrolysis is a highly controlled engineering process designed to deconstruct materials at a molecular level. Understanding its key components reveals how it achieves this transformation.
The Principle: Heat Without Oxygen
The defining characteristic of pyrolysis is the absence of oxygen. When organic material is heated with oxygen, it combusts (burns), releasing energy primarily as heat and light.
By removing oxygen and introducing an inert gas like nitrogen, the process forces a different outcome. The intense heat (typically 300-900°C) breaks the complex chemical bonds within the material, a process known as thermochemical decomposition.
The Reactor Environment
This decomposition takes place inside a specialized vessel called a pyrolysis reactor. The goal is to manage heat transfer efficiently and maintain the inert atmosphere.
One common design is the fluidized-bed reactor. It uses a bed of sand or a similar material that is "fluidized" by the flow of inert gas from below. This creates a hot, turbulent medium that transfers heat to the feedstock material evenly and rapidly.
Precise control over temperature is critical, as it directly influences the ratio and quality of the final products. Modern systems use sensitive sensors and control systems to maintain exact conditions.
The Three Key Outputs
The decomposition process consistently yields three types of products:
- Syngas: A mixture of flammable gases (like hydrogen and carbon monoxide) that can be captured and used as a fuel source to generate heat or electricity.
- Bio-oil: A liquid, also known as pyrolysis oil, that can be refined into transportation fuels or used as a feedstock for producing chemicals.
- Bio-char: A stable, carbon-rich solid. It can be used as a soil amendment to improve fertility, as a filtration medium, or as the raw material for producing activated carbon.
Why This Process Matters: Key Applications
Pyrolysis is more than a scientific curiosity; it's a practical solution to major environmental and economic challenges.
Waste-to-Value Conversion
The primary application is converting organic waste streams that would otherwise end up in landfills—such as agricultural residue, non-recyclable plastics, and old tires—into valuable commodities.
Alternative Energy Production
The syngas and bio-oil produced through pyrolysis represent a significant source of renewable energy. This provides a clear pathway for generating power and fuel from waste, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Material Recovery for a Circular Economy
The process enables the recovery of fundamental chemical components from complex waste. For example, it can reclaim carbon from old tires, closing the loop and reducing the need to extract virgin raw materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
Like any technology, pyrolysis has specific requirements and challenges that are critical to understand for its successful implementation.
Significant Energy Input
Achieving and maintaining temperatures of up to 900°C is an energy-intensive process. The overall efficiency of a pyrolysis plant depends on its ability to use some of its own output (like syngas) to power the heating process.
Process Sensitivity
The final output is highly sensitive to the process conditions. Small variations in temperature, heating rate, or feedstock composition can significantly alter the ratio and quality of the gas, liquid, and solid products. This necessitates sophisticated control and monitoring systems.
Feedstock Preparation
For optimal efficiency, most pyrolysis reactors require the input material to be of a consistent size and dryness. This often means that waste must be pre-processed—shredded, dried, and cleaned—which adds complexity and cost to the overall operation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Pyrolysis is a versatile tool, but its suitability depends entirely on the problem you are trying to solve.
- If your primary focus is waste volume reduction: Pyrolysis offers a powerful method to convert large volumes of organic waste into a smaller, more stable volume of valuable products.
- If your primary focus is energy generation: The process is a direct route to creating combustible fuels like bio-oil and syngas from qualified waste streams.
- If your primary focus is material recovery: Pyrolysis is ideal for breaking down complex items like plastics and tires to reclaim their core chemical building blocks, supporting circular economy goals.
Ultimately, pyrolysis serves as a critical technology for reimagining waste not as a liability, but as a feedstock for a new generation of energy and materials.
Summary Table:
| Pyrolysis Output | Description | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Syngas | Flammable gas mixture (e.g., H2, CO) | Fuel for heat/electricity generation |
| Bio-oil | Liquid pyrolysis oil | Refined into transportation fuels or chemicals |
| Bio-char | Carbon-rich solid | Soil amendment, filtration, activated carbon |
Ready to harness the power of pyrolysis in your lab?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for advanced thermal processes. Whether you are researching waste-to-energy conversion, material recovery, or developing new pyrolysis applications, our reliable reactors and temperature control systems are designed for precision and efficiency.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can support your pyrolysis research and help you achieve your sustainability and material science goals. Get in touch via our contact form for a personalized consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- Which type of brazing is done in a vacuum? Achieve Clean, Strong Joints with Vacuum Brazing
- Why is vacuum heat treatment done? Achieve Superior Metal Properties with Pristine Surfaces
- What critical role does a halogen infrared heating furnace play in converting TiO2 to TiN? Optimize Your RTN Process
- What does heat treating do to aluminum? Transform it into a high-strength engineering material.
- How are pyrolysis reactors heated? Choosing the Right Method for Your Process
- What is catalytic vs thermal pyrolysis? Choosing the Right Process for Your Biomass
- What is a retort in heat treatment? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Metallurgical Control
- What is the process of an arc melting furnace? The Key to High-Volume Steel Scrap Recycling



















