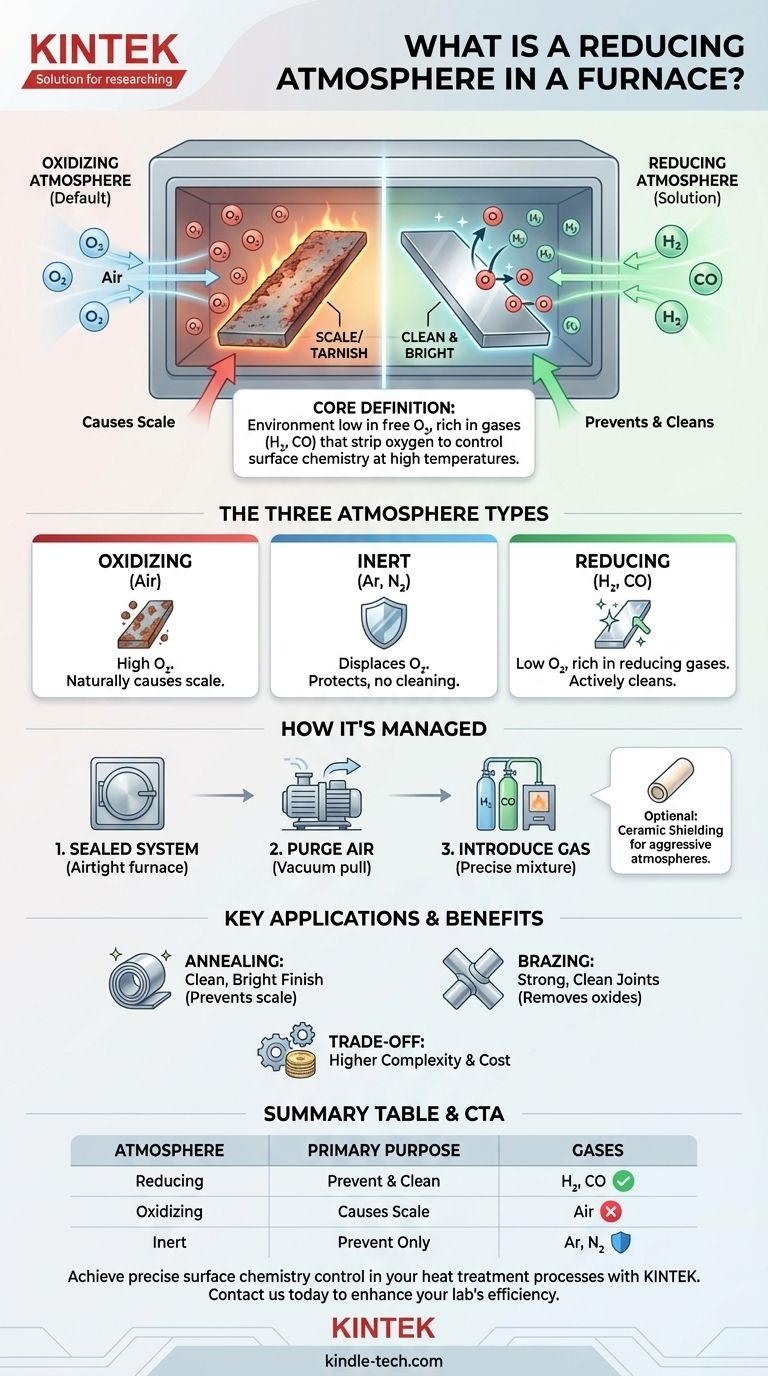
At its core, a reducing atmosphere in a furnace is an environment that actively prevents or reverses oxidation on a material's surface during heat treatment. It achieves this by being intentionally low in free oxygen and rich in gases, such as hydrogen or carbon monoxide, that chemically strip oxygen atoms from the material.
The fundamental purpose of a reducing atmosphere is to control surface chemistry at high temperatures. Instead of simply heating a material in air (which would cause rust or scale), a reducing atmosphere protects the material and can even clean its surface by removing existing oxides.

The Purpose of Atmosphere Control
When processing materials at high temperatures, the surrounding atmosphere is as critical as the temperature itself. The furnace environment can be engineered to be protective and inert or to be chemically active and reactive.
The Default: An Oxidizing Atmosphere
The air we breathe is approximately 21% oxygen and is naturally oxidizing. When you heat metals in an open-air furnace, this oxygen readily reacts with the hot surfaces.
This reaction forms an oxide layer, commonly known as scale or tarnish. For many applications, this is a defect that must be avoided.
The Solution: A Reducing Atmosphere
A reducing atmosphere is the chemical opposite of an oxidizing one. It is created by purging the ambient air from a sealed furnace and replacing it with specific gases.
These gases have a strong affinity for oxygen. At high temperatures, they react with and remove any oxygen present on the material's surface, effectively "reducing" the oxides back to their base metal.
The Third Option: An Inert Atmosphere
An inert atmosphere, typically using gases like argon or nitrogen, serves a purely protective role. It doesn't actively clean the surface like a reducing atmosphere, but it displaces oxygen to prevent any new oxidation from occurring.
How a Reducing Atmosphere is Managed
Creating and maintaining a specific furnace atmosphere requires specialized equipment and precise control over the process parameters.
A Tightly Sealed System
Atmosphere control is only possible in a furnace that can be sealed airtight. Atmosphere furnaces use features like high-temperature silica gel seals on the door to prevent ambient air from leaking in and contaminating the controlled environment.
Purging and Gas Introduction
The process begins by removing the air, often by pulling a vacuum. The desired atmospheric gases are then introduced through an inlet port. This ensures the internal environment is composed entirely of the intended gas mixture.
Protecting the Material
Interestingly, a strongly reducing atmosphere can sometimes be too aggressive for certain materials. In these cases, the sample can be shielded inside a low-porosity ceramic tube (made of materials like alumina or magnesia) to create a separate micro-environment.
Key Applications and Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace atmosphere depends entirely on the desired outcome for the material being processed.
Primary Benefit: Clean, Bright Finishes
The most common reason to use a reducing atmosphere is to prevent oxidation. This is critical in processes like annealing, where the goal is to soften a metal without creating a surface scale, resulting in a clean, bright part.
Active Surface Cleaning
Beyond prevention, a reducing atmosphere can actively clean parts. In brazing, for example, a reducing atmosphere removes light surface oxides, ensuring the brazing alloy can wet the pure metal surfaces to create a strong, clean joint.
The Challenge of Control
The main trade-off is complexity and cost. Operating an atmosphere furnace requires more sophisticated equipment, a supply of specific gases, and precise process control compared to simply heating a part in air.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of atmosphere is dictated by your process objective.
- If your primary focus is preventing scale during heat treatment: A reducing or inert atmosphere is necessary to displace oxygen and ensure a clean surface finish.
- If your primary focus is joining metals via brazing: A reducing atmosphere is essential not only to prevent oxidation but to actively remove existing oxides for a strong metallurgical bond.
- If your primary focus is simply heating a stable material: An inert atmosphere provides excellent protection from oxidation without the chemical reactivity of a reducing atmosphere.
Ultimately, controlling the furnace atmosphere gives you control over the chemical reactions on your material's surface, which is often just as important as controlling the temperature.
Summary Table:
| Atmosphere Type | Key Characteristic | Primary Purpose | Common Gases Used |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reducing | Low in oxygen, rich in reducing gases (H₂, CO) | Prevent oxidation & actively clean surfaces | Hydrogen, Carbon Monoxide |
| Oxidizing | High in oxygen (like air) | Naturally causes scale/tarnish | Air (21% Oxygen) |
| Inert | Chemically inactive, displaces oxygen | Prevent oxidation without surface cleaning | Argon, Nitrogen |
Achieve precise surface chemistry control in your heat treatment processes with KINTEK.
Whether you're annealing metals to prevent scale or brazing components for strong joints, the right furnace atmosphere is critical. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing reliable solutions for your laboratory's specific needs.
Contact us today to discuss how our atmosphere furnace solutions can enhance your material processing results and improve your lab's efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is an inert condition? A Guide to Preventing Fires and Explosions
- Why nitrogen is used in annealing furnace? To prevent oxidation and decarburization for superior metal quality
- How do you make an inert atmosphere? Master Safe, Pure Processes with Inerting
- What is meant by inert atmosphere? A Guide to Preventing Oxidation & Ensuring Safety
- What provides an inert atmosphere? Achieve Safety and Purity with Nitrogen, Argon, or CO2



















