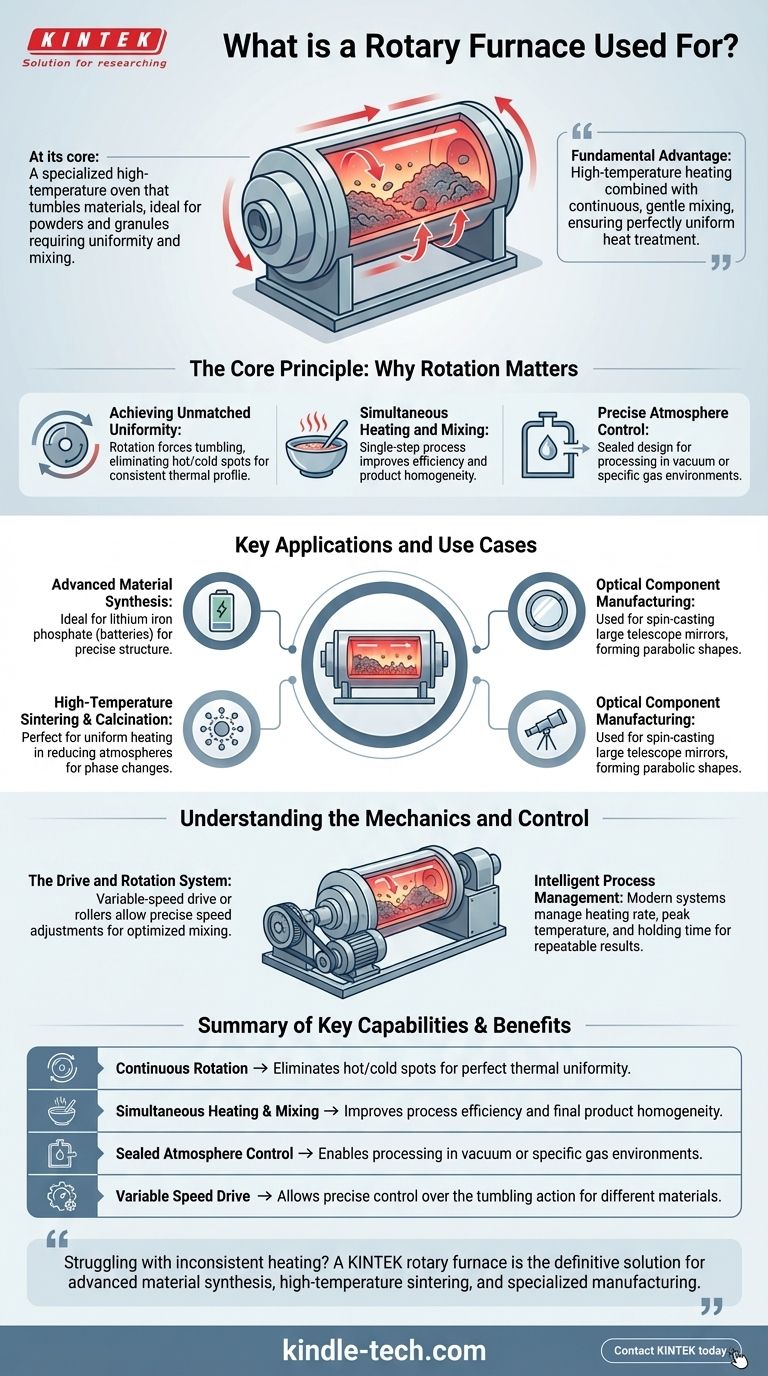
At its core, a rotary furnace is a specialized high-temperature oven that tumbles materials as it heats them. It is primarily used for processing powders and granular materials that require exceptional temperature uniformity and mixing, such as in the synthesis of advanced battery components, and in the unique manufacturing of large-scale optical mirrors for telescopes.
The fundamental advantage of a rotary furnace is its ability to combine high-temperature heating with continuous, gentle mixing. This solves the critical challenge of achieving perfectly uniform heat treatment across a bulk material, a task where static furnaces often fail.
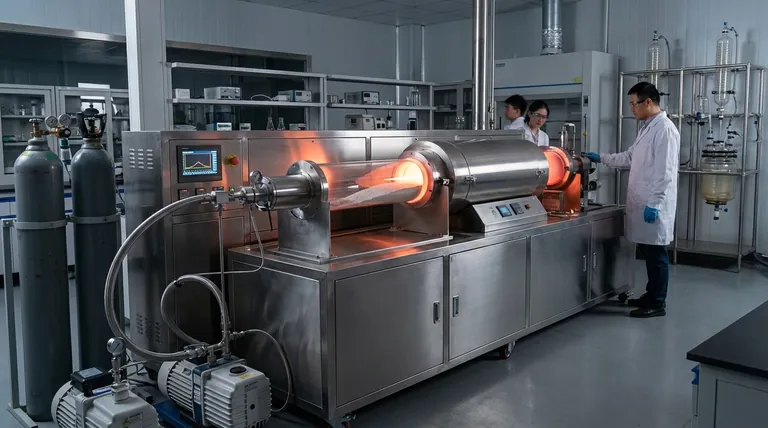

The Core Principle: Why Rotation Matters
A standard furnace heats materials from the outside in, creating significant temperature gradients. A rotary furnace solves this by constantly moving the material, ensuring every particle is exposed to the heat source and the surrounding atmosphere evenly.
Achieving Unmatched Uniformity
The rotational motion forces the material to tumble, which eliminates hot spots and cold spots. This guarantees that the entire batch of material experiences the same thermal profile, which is critical for consistent product quality.
Simultaneous Heating and Mixing
For chemical reactions, sintering, or coating processes, it is vital that materials are both heated and thoroughly mixed. The rotary tube accomplishes this in a single step, improving process efficiency and the homogeneity of the final product.
Precise Atmosphere Control
Many advanced material processes must occur in a vacuum or a specific gas environment to prevent oxidation or trigger a desired reaction. Rotary tube furnaces are designed to be sealed, allowing for complete control over the internal atmosphere while the material is being processed.
Key Applications and Use Cases
The unique capabilities of a rotary furnace make it indispensable for a range of demanding industrial and scientific applications.
Advanced Material Synthesis
The furnace excels at processing powders and granules. This makes it ideal for producing materials like lithium iron phosphate for batteries, where the final particle structure and performance are directly tied to the precision of the heat treatment process.
High-Temperature Sintering and Calcination
Sintering powders to form a solid mass or performing calcination to induce phase changes requires precise temperature control over time. The furnace's ability to heat uniformly in a reducing atmosphere is perfectly suited for these tasks.
Optical Component Manufacturing
In a highly specialized application, large rotary furnaces are used to cast primary mirrors for telescopes. The liquid glass is spun at a constant speed as it cools, and the combination of centrifugal force and gravity naturally forms the material into a perfect parabolic shape, dramatically reducing the grinding and polishing required.
Understanding the Mechanics and Control
The effectiveness of a rotary furnace comes from its sophisticated yet robust design, which allows for fine control over the entire process.
The Drive and Rotation System
The furnace tube is typically rotated by a variable-speed drive gear or by resting on a set of driven rollers. This allows operators to precisely adjust the rotation speed, controlling how vigorously the material is tumbled to optimize mixing for different material types.
Intelligent Process Management
Modern rotary furnaces use intelligent control systems to manage every critical variable. Operators can program the desired heating rate, peak temperature, and holding time. This ensures that complex thermal profiles are executed perfectly, leading to repeatable, high-quality results.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Choosing a furnace depends entirely on the specific requirements of the material and the desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is maximum uniformity for powders or granules: The rotary furnace is the superior choice for ensuring every particle receives identical thermal treatment.
- If your primary focus is processing in a controlled, non-oxidizing atmosphere: A sealable rotary tube furnace provides the ideal environment for heating sensitive materials.
- If your primary focus is creating a large, parabolic optical surface: The spin-casting method in a rotary furnace is the foundational manufacturing technique.
Ultimately, the rotary furnace is the definitive solution when simple heating is not enough and your process demands simultaneous, uniform thermal and mechanical treatment.
Summary Table:
| Key Capability | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|
| Continuous Rotation | Eliminates hot/cold spots for perfect thermal uniformity |
| Simultaneous Heating & Mixing | Improves process efficiency and final product homogeneity |
| Sealed Atmosphere Control | Enables processing in vacuum or specific gas environments |
| Variable Speed Drive | Allows precise control over the tumbling action for different materials |
Struggling with inconsistent heating or mixing in your material processing?
A KINTEK rotary furnace is the definitive solution for processes that demand more than just simple heating. Our furnaces deliver the simultaneous thermal and mechanical treatment required for superior results in advanced material synthesis, high-temperature sintering, and specialized manufacturing.
KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment, serving the exacting needs of laboratories and R&D facilities. Let us help you achieve perfect uniformity and repeatable, high-quality outcomes.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how a rotary furnace can transform your process.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is pyrolysis in short answer? A Simple Guide to Converting Waste into Value
- What is the water content of pyrolysis oil? A Key Factor in Bio-Oil Quality and Use
- What are the materials suitable for pyrolysis? Unlocking Value from Waste Streams
- What is the structure of a rotary hearth furnace? A Guide to Continuous, Uniform Heating
- What is the temperature of the rotary furnace? It Depends on the Heating Method
- Is pyrolysis a biological process? Unpacking the Thermochemical vs. Biological Breakdown
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis over gasification? Maximize Product Value and Energy Storage
- What is a rotary retort furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity in Continuous Heat Treatment



















