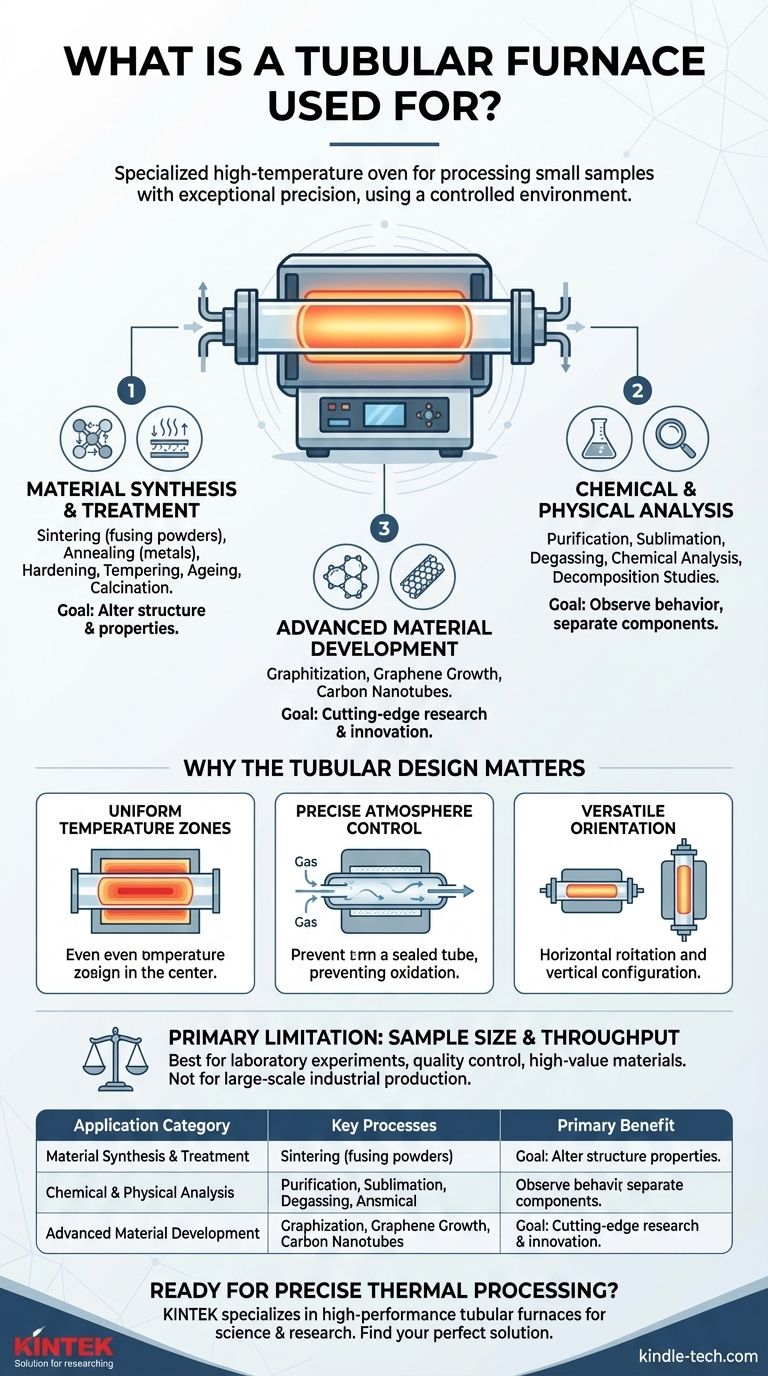
In essence, a tubular furnace is a specialized high-temperature oven used to process small samples with exceptional precision. Its core function is to heat materials in a controlled environment, making it indispensable for a wide range of applications from treating metals and ceramics to conducting advanced scientific analysis and developing new materials.
The primary value of a tubular furnace is its ability to create a highly uniform temperature zone within a tightly controlled atmosphere. This unique combination of precision and control is what makes it essential for advanced material processing, testing, and research.

The Core Function: Precision Thermal Processing
A tubular furnace provides the high-energy environment necessary to fundamentally alter or analyze materials. Its applications can be grouped into several key categories.
Material Synthesis and Treatment
Many processes use heat to change a material's internal structure and, therefore, its physical properties.
A tubular furnace is ideal for sintering, where powdered materials (like ceramics) are heated to fuse them into a solid mass. It is also used for annealing, a process that heats and slowly cools metals to reduce hardness and increase ductility.
Other common treatments include hardening, tempering, ageing, and calcination—all of which require precise temperature cycles to achieve a desired outcome.
Chemical and Physical Analysis
The furnace is a critical tool for observing how materials behave at high temperatures.
It is frequently used for purification, sublimation, and degassing, where heat is used to separate components or remove impurities. Scientists also use it for chemical analysis and studying the physical decomposition of samples in a controlled setting.
Advanced Material Development
In research settings, tubular furnaces are at the forefront of innovation.
Specialized graphite tube furnaces are used for graphitization treatment and cutting-edge research, including graphene growth and the preparation of carbon nanotubes.
Why a Tubular Design is Critical
The cylindrical shape of the furnace is not arbitrary; it is central to its primary advantages over other furnace types like box or muffle furnaces.
Uniform Temperature Zones
The circular cross-section of the heating chamber allows for extremely even heat distribution. This creates a highly uniform temperature "hot zone" in the center of the tube, ensuring that the entire sample is processed under identical conditions.
Precise Atmosphere Control
The tube's simple geometry makes it easy to seal at both ends. This allows operators to purge the air and introduce a specific gas, creating a controlled atmosphere. This is critical for preventing unwanted oxidation or for using reactive gases as part of the treatment process.
Versatile Orientation
Tube furnaces can be designed to operate horizontally or vertically. This flexibility allows them to accommodate different types of samples and processes, such as those involving liquids or vapors that benefit from a vertical orientation.
Understanding the Primary Limitation
While incredibly versatile, the design of a tubular furnace comes with an inherent trade-off that defines its appropriate use.
Sample Size and Throughput
The primary limitation of a tubular furnace is batch size. The tubular chamber is designed for small samples, making it perfect for laboratory-scale experiments, quality control tests, and processing high-value materials.
However, it is not suitable for large-scale industrial production, where higher throughput is required.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a furnace depends entirely on your end goal. The tubular furnace excels where precision outweighs the need for volume.
- If your primary focus is materials science research: A tubular furnace is essential for the precise temperature and atmosphere control needed to develop novel materials.
- If your primary focus is process testing or quality control: Its ability to perfectly replicate thermal conditions makes it ideal for annealing or sintering small parts to validate an industrial process.
- If your primary focus is chemical analysis: The sealed, controlled environment is perfect for purification, decomposition studies, or observing reactions at high temperatures.
Ultimately, a tubular furnace is the instrument of choice whenever precision, uniformity, and atmospheric control are more critical than production scale.
Summary Table:
| Application Category | Key Processes | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Material Synthesis & Treatment | Sintering, Annealing, Hardening, Calcination | Alters material structure and properties |
| Chemical & Physical Analysis | Purification, Degassing, Decomposition Studies | Controlled environment for accurate analysis |
| Advanced Material Development | Graphene Growth, Carbon Nanotube Preparation | Enables cutting-edge research and innovation |
Ready to achieve precise thermal processing in your lab?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance tubular furnaces designed for materials science, quality control, and advanced research. Our lab equipment delivers the uniform temperature zones and exact atmosphere control you need for sintering, annealing, and material analysis.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect tubular furnace for your specific application and enhance your laboratory's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the pressure on a tube furnace? Essential Safety Limits for Your Lab
- What is the ceramic tube high temperature? From 1100°C to 1800°C, Choose the Right Material
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- What happens when quartz is heated? A Guide to Its Critical Phase Transitions and Uses
- What is the primary advantage of using a tube furnace? Achieve Superior Temperature and Atmosphere Control



















