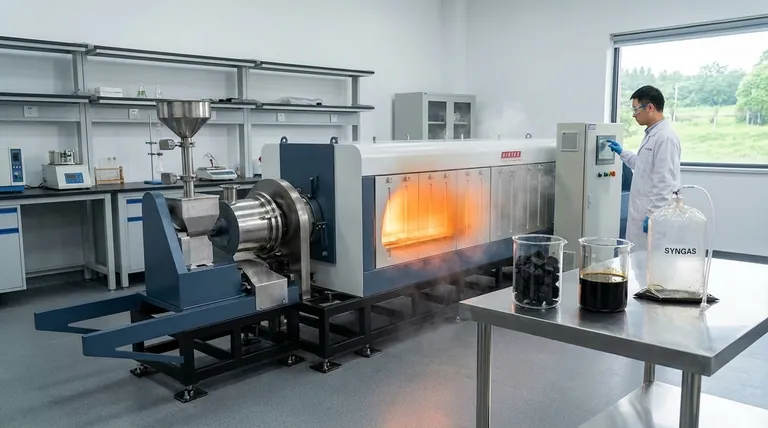
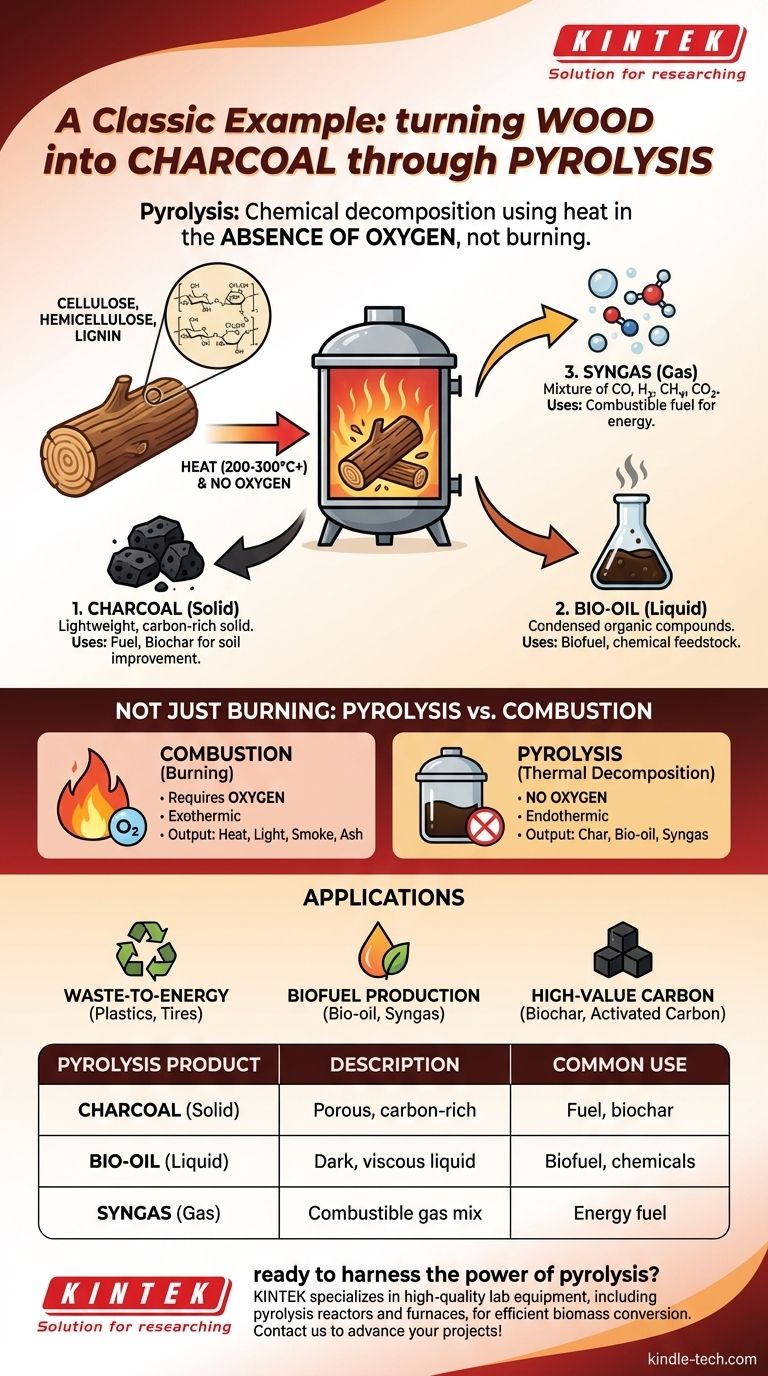
A classic example of a pyrolysis reaction is the production of charcoal from wood. When wood is heated to high temperatures in an environment with little to no oxygen, it doesn't simply burn; instead, its complex organic polymers break down into simpler, more stable substances. This thermal decomposition is the essence of pyrolysis.
The critical distinction to understand is that pyrolysis is not burning. It is the chemical decomposition of a material using heat in the absence of oxygen, which prevents combustion and results in entirely different products like char, oil, and gas instead of ash and smoke.

A Classic Example: Turning Wood into Charcoal
To truly understand pyrolysis, we can walk through the common and historical example of making charcoal. This process perfectly illustrates the core principles.
The Starting Material (Wood)
Wood is primarily composed of large organic polymers. The three main components are cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin, which give wood its rigid structure.
The Process (Heating Without Oxygen)
The key step is heating the wood in a controlled environment, such as a kiln or retort, where the oxygen supply is severely restricted. As the temperature rises above 200–300°C (400–570°F), these long polymer chains become unstable and begin to break apart.
The Solid Product (Charcoal)
The solid material left behind after the volatile components have been driven off is charcoal. This substance is a lightweight, black, and highly porous form of carbon, with most of the other original elements removed.
The Liquid Product (Bio-oil)
Many of the smaller organic molecules that vaporize during heating will cool and condense into a dark, viscous liquid. This is known as pyrolysis oil or bio-oil, a complex mixture of water and hundreds of different organic compounds.
The Gaseous Product (Syngas)
Some components do not condense back into a liquid and remain as gases. This mixture, often called syngas, includes carbon monoxide, hydrogen, methane, and carbon dioxide, and is itself a combustible fuel.
Why This Isn't Just Burning
The most common point of confusion is differentiating pyrolysis from combustion (burning). The presence or absence of oxygen is the deciding factor.
The Role of Oxygen
Combustion is an exothermic reaction that requires oxygen. It rapidly oxidizes a material, releasing energy as heat and light, and produces simple molecules like carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water (H₂O).
Pyrolysis is an endothermic process that occurs without oxygen. It uses external heat to break down a material, producing a carbon-rich solid (char) and other valuable chemical products.
Different Inputs, Different Outputs
If you burn wood in a campfire (combustion), you are left with heat, light, smoke, and a small amount of ash. If you heat wood in a kiln (pyrolysis), you are left with charcoal, bio-oil, and syngas.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Applications
Pyrolysis is a powerful tool, but its application depends entirely on the desired outcome and the material being processed. It is more complex and often more expensive to implement than simple combustion.
Waste-to-Energy
Pyrolysis is a key technology in advanced recycling and waste management. It can thermally decompose materials like plastics, tires, and other forms of biomass into useful fuels, reducing landfill volume.
Biofuel Production
The bio-oil and syngas produced from the pyrolysis of biomass are considered biofuels. They can be refined and used to generate electricity or power engines, offering a renewable alternative to fossil fuels.
Creation of High-Value Carbon
The solid char product has numerous applications. When made from biomass for agricultural purposes, it is called biochar, which can improve soil health and sequester carbon for long periods.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the distinct outputs of pyrolysis allows you to see its role in different industrial and environmental contexts.
- If your primary focus is a stable, carbon-rich solid: Pyrolysis is the process used to create products like charcoal for fuel or biochar for agriculture.
- If your primary focus is creating liquid fuels from biomass: The pyrolysis process is what uniquely yields bio-oil from organic materials like wood or agricultural waste.
- If your primary focus is breaking down complex waste: Pyrolysis offers a way to deconstruct materials like plastics into simpler, often reusable, chemical components without burning them.
Ultimately, pyrolysis is a fundamental process of thermal transformation, breaking down complexity to create new forms of value.
Summary Table:
| Pyrolysis Product | Description | Common Use |
|---|---|---|
| Charcoal (Solid) | Porous, carbon-rich solid | Fuel, biochar for soil improvement |
| Bio-oil (Liquid) | Dark, viscous liquid from condensed vapors | Biofuel, chemical feedstock |
| Syngas (Gas) | Mixture of CO, H₂, CH₄, and CO₂ | Combustible fuel for energy |
Ready to harness the power of pyrolysis in your lab? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including pyrolysis reactors and furnaces, to help you efficiently convert biomass or waste into valuable products like biofuels and biochar. Whether you're in research, waste management, or biofuel production, our solutions ensure precise temperature control and safety. Contact us today to explore how our expertise can advance your projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products



















