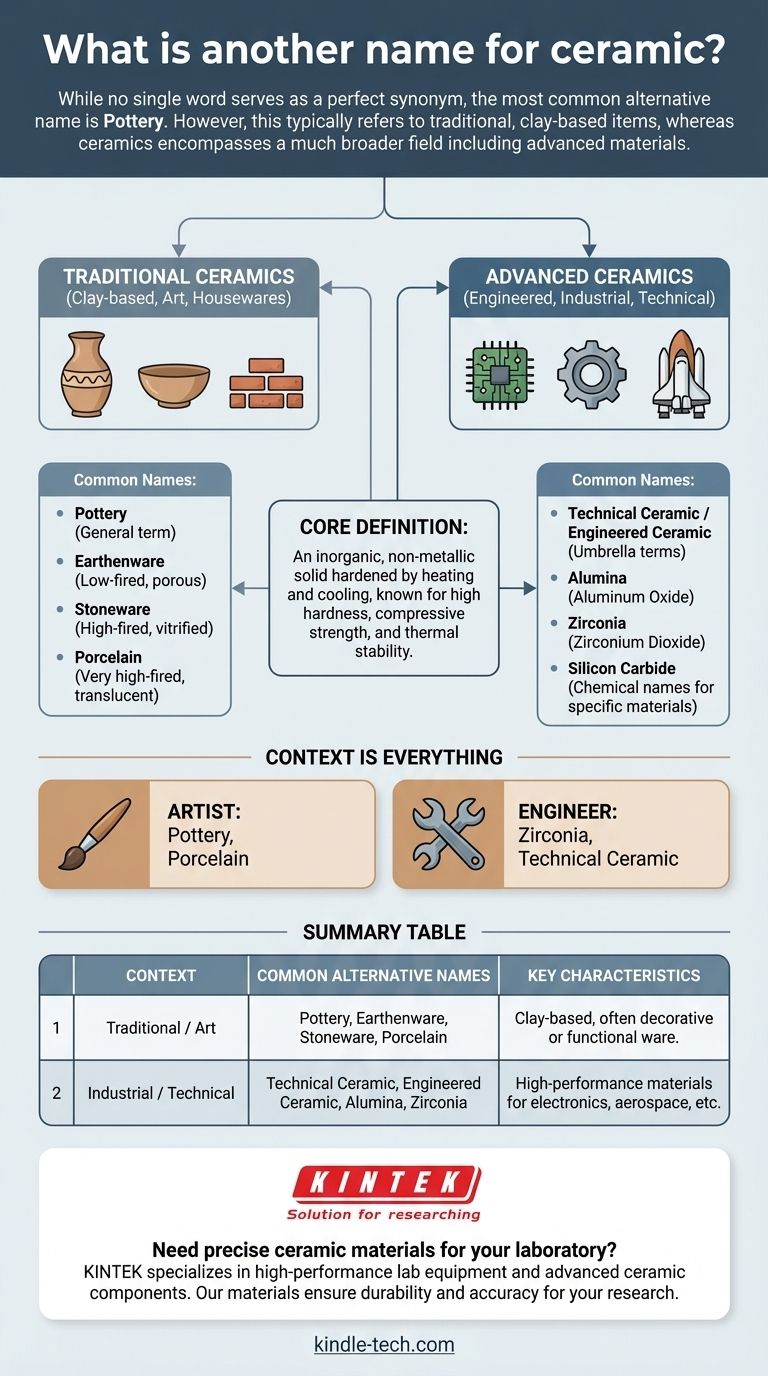
While no single word serves as a perfect synonym, the most common alternative name for ceramic is pottery. However, this term typically refers only to traditional, clay-based items like vases and dishes, while the field of ceramics is far broader, encompassing advanced materials used in electronics, aerospace, and medicine.
The term "ceramic" describes a vast class of materials, not a single substance. The correct "other name" depends entirely on the context: "pottery" is suitable for art and housewares, while specific chemical names like "alumina" are used for advanced industrial applications.
Deconstructing the Term "Ceramic"
To understand the different names for ceramic, we first must define what a ceramic is from a materials science perspective. This clarity reveals why a single synonym is insufficient.
The Core Definition
A ceramic is an inorganic, non-metallic solid that is hardened by a process of heating and cooling. These materials are defined by their strong ionic and covalent bonds, which give them characteristics like high hardness, compressive strength, and high-temperature stability.
Traditional vs. Advanced Ceramics
The word "ceramic" is often used in two very different contexts. Traditional ceramics are clay-based materials like bricks and pottery. Advanced ceramics (or technical ceramics) are materials engineered with highly controlled properties for specific industrial functions.
Common Names for Traditional Ceramics
When most people ask for another name for ceramic, they are usually thinking of traditional, clay-based objects. In this context, several terms are used, each with a specific meaning.
Pottery
Pottery is the most general alternative. It broadly refers to functional or decorative objects made from fired clay. It is often used interchangeably with "ceramic" in non-technical discussions.
Earthenware
Earthenware is a specific type of pottery that is fired at relatively low temperatures. It remains slightly porous after firing and requires a glaze to become waterproof. Terracotta is a well-known example of earthenware.
Stoneware
Stoneware is fired at a higher temperature, causing the clay to become vitrified—meaning it is dense, non-porous, and waterproof even without a glaze. It is more durable than earthenware.
Porcelain
Porcelain is a very high-fired type of stoneware known for its exceptional hardness, strength, and translucency. It is often considered the most refined type of traditional ceramic.
Names for Advanced Ceramics
In scientific and industrial fields, the alternative names for ceramic are highly specific and describe the material's chemical composition or engineered purpose.
Technical or Engineered Ceramic
This is the umbrella term for modern, high-performance ceramics. Unlike traditional ceramics, these are not necessarily clay-based and are valued for their mechanical, electrical, or thermal properties rather than aesthetics.
Specific Material Names
In a technical context, a ceramic is almost always referred to by its specific chemical name. Examples include aluminum oxide (alumina), zirconium dioxide (zirconia), and silicon carbide. These names provide precise information that a general term cannot.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Why a Single Synonym Fails
The lack of a perfect, one-to-one synonym for "ceramic" is not a failure of language but a reflection of the material's diversity. Using the wrong term can lead to significant confusion.
The Problem of Specificity
Using a term like pottery is too specific. It incorrectly excludes the vast world of technical ceramics, from the tiles on a space shuttle to the components in your smartphone.
The Problem of Breadth
Using a technical definition like "inorganic non-metallic solid" is too broad and cumbersome for everyday use. While accurate, it lacks the immediate clarity of the word "ceramic."
Context is Everything
Ultimately, the correct term is dictated by the context. An artist discussing their work will use "pottery" or "porcelain," while an engineer will use "zirconia" or "technical ceramic." The word "ceramic" itself is the only term that successfully bridges both worlds.
Choosing the Right Term for Your Purpose
Use this guide to select the most accurate and effective term based on your specific goal.
- If your primary focus is on art, dinnerware, or handmade items: Use specific terms like pottery, earthenware, stoneware, or porcelain to be more precise.
- If your primary focus is on industrial or technical applications: Use the term "technical ceramic" or refer to the specific material composition, such as alumina or silicon carbide.
- If your primary focus is to find a general, all-encompassing term: "Ceramic" itself is the most accurate and universally understood name.
Understanding this distinction empowers you to communicate with greater precision and clarity.

Summary Table:
| Context | Common Alternative Names | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional / Art | Pottery, Earthenware, Stoneware, Porcelain | Clay-based, often decorative or functional ware. |
| Industrial / Technical | Technical Ceramic, Engineered Ceramic, Alumina, Zirconia | High-performance materials for electronics, aerospace, etc. |
Need precise ceramic materials for your laboratory? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including advanced ceramic components. Our materials ensure the durability and accuracy your research demands. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Sheet Wear-Resistant Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Precision Machined Zirconia Ceramic Ball for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Conductive Boron Nitride BN Ceramics Composite for Advanced Applications
- Advanced Engineering Fine Ceramics Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Parts
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature resistance of silicon carbide? Withstands Extreme Heat Up to 1500°C
- What are the properties of SiC? Unlock High-Temperature, High-Frequency Performance
- What is the resistivity of silicon carbide? It's a tunable property from <0.1 ohm-cm to highly resistive.
- Which is harder silicon carbide or tungsten carbide? Discover the Key to Material Selection
- Is silicon carbide heat resistant? Unlock Superior Performance in Extreme Temperatures



















