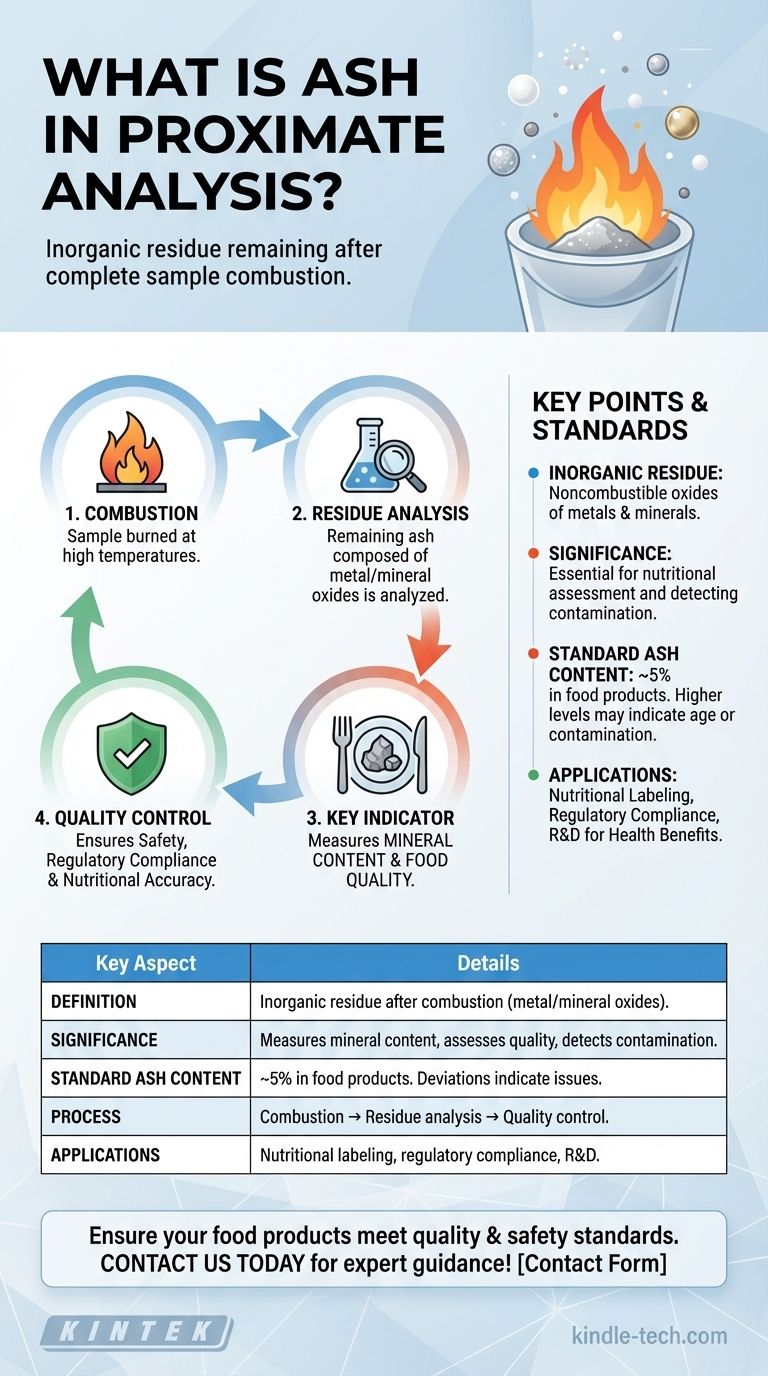
Ash in proximate analysis refers to the inorganic residue that remains after a sample is completely burned. This residue typically consists of oxides of inorganic elements such as metals and minerals. The ash content is a critical parameter in food quality assessment, as it helps determine the mineral content in food products. A standard acceptable ash content is around 5%, with higher levels potentially indicating the age or contamination of the food. This measurement is essential for ensuring the quality and safety of food products, as it provides insights into the noncombustible, inorganic components present.

Key Points Explained:
-
Definition of Ash in Proximate Analysis:
- Ash is the inorganic residue left after a sample is completely burned.
- It consists primarily of oxides of inorganic elements like metals and minerals.
- This residue is noncombustible and represents the mineral content of the sample.
-
Significance of Ash Content:
- Mineral Content Measurement: Ash content is a direct indicator of the mineral content in a sample. It helps quantify the inorganic components, which are essential for nutritional assessment.
- Food Quality Assessment: In food products, ash content is crucial for determining quality and safety. It helps identify the presence of essential minerals and detect potential contamination or adulteration.
- Indicator of Food Age: Higher ash content can sometimes indicate the age of food products, as older products may accumulate more inorganic residues over time.
-
Standard Acceptable Ash Content:
- The generally accepted standard for ash content in food products is around 5%.
- Deviations from this standard can signal issues such as contamination, adulteration, or degradation of the product.
-
Process of Determining Ash Content:
- Combustion: The sample is burned at high temperatures until all organic matter is combusted, leaving behind the inorganic residue.
- Residue Analysis: The remaining ash is then analyzed to determine its composition and quantity.
- Quality Control: This process is a key part of quality control in food production, ensuring that products meet safety and nutritional standards.
-
Applications of Ash Content Analysis:
- Nutritional Labeling: Ash content is used to provide accurate nutritional information, particularly regarding mineral content.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring that food products comply with regulatory standards for mineral content and safety.
- Research and Development: Used in R&D to develop new food products with optimal mineral content for health benefits.
By understanding ash content and its significance, purchasers of equipment and consumables can make informed decisions about the quality and safety of the products they are evaluating. This knowledge is essential for ensuring that food products meet the necessary standards for consumption and regulatory compliance.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Inorganic residue after combustion, consisting of oxides of metals/minerals. |
| Significance | Measures mineral content, assesses food quality, and detects contamination. |
| Standard Ash Content | ~5% in food products; deviations indicate potential issues. |
| Process | Combustion → Residue analysis → Quality control. |
| Applications | Nutritional labeling, regulatory compliance, R&D for food products. |
Ensure your food products meet quality and safety standards—contact us today for expert guidance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is a muffle furnace used to measure? Unlock Precise Sample Analysis with High-Temp Heating
- What is a muffle furnace and its uses? Achieve Contamination-Free High-Temperature Processing
- What is the function of an electric muffle furnace? Achieve Pure, Uniform High-Temp Processing
- What is the difference between a muffle furnace and a drying oven? Choose the Right Thermal Tool
- What is the heating mechanism of a muffle furnace? Achieve Clean, Uniform High-Temperature Processing



















