Autoclave testing is the formal process of validating that a sterilization cycle is effective. It is a series of controlled tests used to prove that the correct parameters of time, temperature, and saturated steam pressure have been achieved throughout the entire load, successfully killing all microorganisms. This process transforms the assumption of sterility into a verifiable, documented fact.
Simply running an autoclave and seeing the cycle complete does not guarantee sterility. Autoclave testing is the only way to provide objective, physical proof that your equipment and process are performing correctly, mitigating risks in critical applications from healthcare to research.
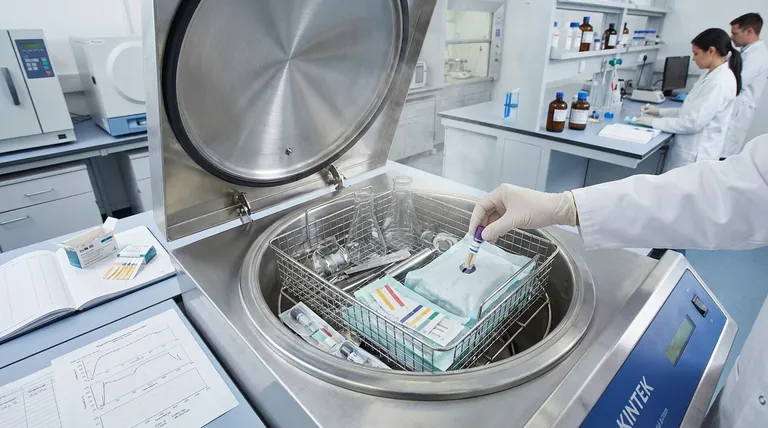

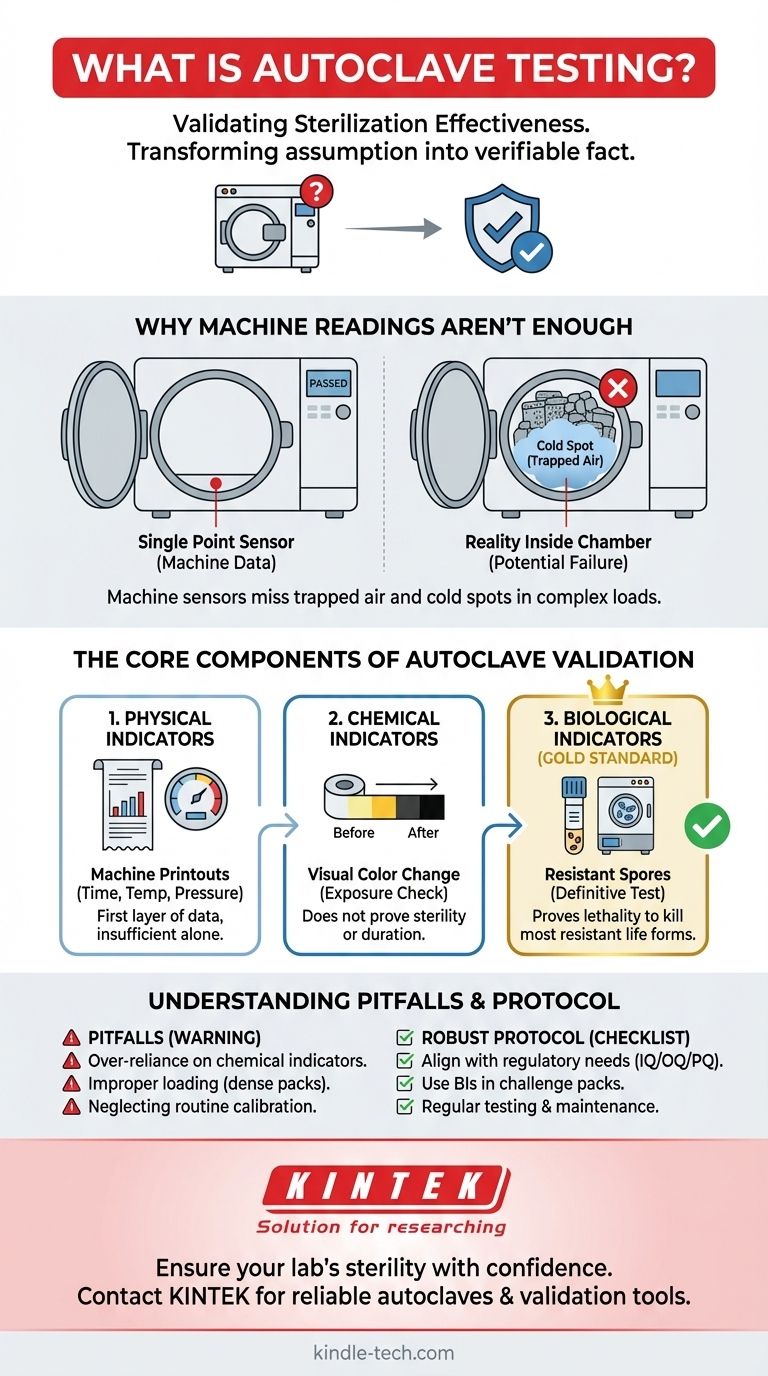
Why Machine Readings Aren't Enough
Relying solely on the autoclave's digital display or printout is a common but risky practice. The machine's internal sensors report on conditions at a single point, which may not reflect the reality inside the entire chamber.
The Problem of "Cold Spots"
The most significant challenge in steam sterilization is ensuring uniform conditions. Cold spots are areas within the chamber or load that fail to reach the target temperature due to trapped air. Air is a poor conductor of heat and prevents steam from making direct contact with the items, rendering the sterilization process ineffective in those locations.
The Impact of Load Configuration
How you load an autoclave dramatically affects its performance. A densely packed load can create barriers that inhibit steam penetration. If steam cannot freely circulate and reach every surface, air pockets will form, and parts of the load will not be sterilized, regardless of what the machine's primary sensor reads.
The Limits of a "Passed" Cycle
A cycle can complete and be reported as "passed" by the machine's controller even if significant cold spots existed. The controller only knows what its single sensor detected; it is blind to the varied conditions throughout a complex load.
The Core Components of Autoclave Validation
Effective autoclave testing, or validation, relies on a multi-faceted approach using different types of indicators. Each serves a distinct purpose in building a complete picture of the cycle's performance.
Physical Indicators
These are the charts, graphs, and digital printouts from the autoclave itself. They provide a record of the time, temperature, and pressure at the machine's sensor (typically near the drain). This is the first layer of data, but it is insufficient on its own.
Chemical Indicators
Chemical indicators are strips, tapes, or labels that change color when exposed to specific temperatures. They are useful for a quick, visual confirmation that a package has been through a cycle. However, they typically only confirm that a certain temperature was reached; they do not indicate for how long it was maintained, nor do they prove that microorganisms were killed.
Biological Indicators (The Gold Standard)
Biological indicators (BIs) are the definitive test for sterilization. A BI contains a known population of highly resistant bacterial spores, most commonly Geobacillus stearothermophilus, which are far more difficult to kill than typical microorganisms.
These indicators are placed in the most challenging locations within the load (e.g., deep inside a dense pack, near the chamber door). After the cycle, the BI is incubated. If the spores show no growth, it provides conclusive proof that the cycle was lethal enough to kill even the most resistant life forms, confirming true sterility.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
A robust testing protocol is not just about passing; it's about understanding the limits and potential failure points of your process.
Over-reliance on Chemical Indicators
The most common pitfall is treating a color change on a chemical indicator as proof of sterility. This can lead to a false sense of security. They are best used to differentiate processed from unprocessed items, not to validate the cycle itself.
Improper Loading and Packaging
Using sealed plastic containers, packing items too tightly, or creating dense layers prevents steam penetration. Testing with biological indicators placed inside these challenging configurations is the only way to identify and correct these critical loading errors.
Neglecting Routine Testing and Calibration
Validation is not a one-time event. Equipment performance can drift over time. Regular testing (e.g., weekly or monthly with BIs, depending on standards) and annual calibration of the machine's sensors are critical to ensure the process remains in a validated state. A failed BI test is often the first sign that maintenance is required.
Implementing a Robust Testing Protocol
Your testing strategy should align directly with your operational and regulatory requirements.
- If your primary focus is regulatory compliance (e.g., medical devices, pharmaceuticals): You must perform formal installation, operational, and performance qualification (IQ/OQ/PQ) using biological indicators and extensive documentation.
- If your primary focus is routine laboratory assurance: Use a chemical indicator in every pack or load and perform a weekly test with a biological indicator placed in a representative "challenge pack."
- If your primary focus is troubleshooting a failed cycle: Place multiple biological and chemical indicators throughout the chamber to map temperature distribution and identify the precise location of any cold spots.
Ultimately, rigorous autoclave testing empowers you with objective data, ensuring the absolute integrity of your sterilization process.
Summary Table:
| Test Component | Purpose | Key Insight |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Indicators | Record time, temp, pressure at machine sensor | First layer of data, but insufficient alone |
| Chemical Indicators | Visual confirmation of temperature exposure | Does not prove sterility or duration |
| Biological Indicators (BIs) | Definitive test using resistant spores | Gold standard for proving sterility |
Ensure your lab's sterility with confidence. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable autoclaves and validation tools, including biological indicators, to help laboratories in healthcare, research, and pharmaceuticals achieve and maintain compliance. Don't leave sterility to chance—contact our experts today to optimize your autoclave testing protocol and safeguard your critical processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Centrifuge Tube Racks
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function and principle of autoclaving? Master Lab Sterilization with High-Pressure Steam
- What role do laboratory autoclaves play in pectin extraction? Optimize Prebiotic Yield from Citrus and Apple Biomass
- What is the primary function of a laboratory autoclave in the pre-treatment of medical plastic waste for liquid fuel?
- What experimental conditions do stainless steel autoclaves provide for PCT-A leaching? Optimize Phosphate Glass Testing
- What are the standard operating parameters for an autoclave? Master Temperature, Pressure, and Time for Sterilization













