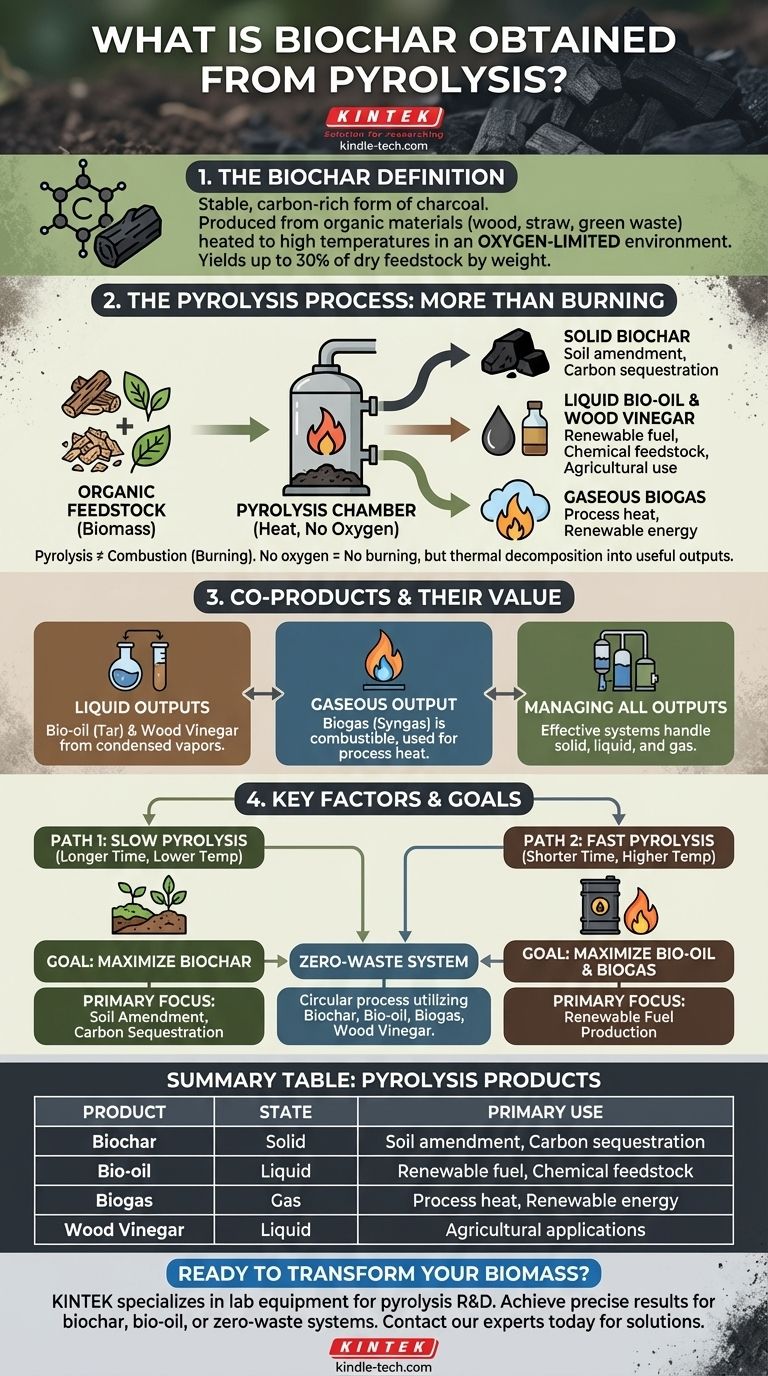
In short, biochar is a stable, carbon-rich form of charcoal produced when organic materials like wood, straw, or green waste are heated to high temperatures in an oxygen-limited environment. This thermal decomposition process is called pyrolysis. Biochar is the primary solid product of this reaction, with yields typically reaching up to 30% of the initial dry feedstock by weight.
Think of pyrolysis not as a simple charcoal-making process, but as a complete biomass conversion system. It transforms organic waste into a suite of useful products—solid biochar, liquid bio-oil, and combustible biogas—creating value from materials that might otherwise be discarded.

The Pyrolysis Process: More Than Just Burning
To understand biochar, it's essential to understand the process that creates it. Pyrolysis is fundamentally different from burning (combustion).
What is Pyrolysis?
Pyrolysis is the heating of an organic material, such as biomass, in the near or total absence of oxygen.
Because there is no oxygen, the material does not combust. Instead, its chemical compounds break down into a variety of valuable solid, liquid, and gaseous products.
The Starting Materials (Feedstock)
A wide range of organic materials can be used as feedstock for pyrolysis.
The source material directly influences the final characteristics of the biochar. Common feedstocks include pine wood, wheat straw, green waste, and even dried algae.
The Solid Output: Biochar
The primary solid product left after pyrolysis is biochar.
It is a black, lightweight, and highly porous material that is rich in carbon. This structure is what makes it valuable for applications like soil amendment and carbon sequestration.
Understanding the Co-Products of Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis does not only produce biochar. A successful operation must account for all the outputs, which are valuable in their own right.
Liquid Outputs: Bio-oil and Wood Vinegar
As the biomass breaks down, condensable vapors are released.
When these vapors are cooled and collected, they form liquids. These are often separated into bio-oil (also known as tar or pyrolysis oil) and wood vinegar.
Gaseous Output: Biogas
The process also releases non-condensable gases, collectively known as biogas or syngas.
This gas is combustible and can be collected and used as a fuel source. In many systems, the biogas is looped back to provide the heat required for the pyrolysis reaction, creating a more energy-efficient and self-sustaining operation.
Key Factors and Trade-offs
The exact mix of products you get from pyrolysis isn't fixed. It depends entirely on the feedstock and the specific process conditions.
Feedstock Determines Quality
The type of organic material you start with has a significant impact on the final products. For example, biochar made from dense wood will have different properties than biochar made from leafy green waste.
Process Conditions Matter
The references mention slow pyrolysis, which is a key distinction.
Slow pyrolysis (heating over a longer period) is optimized to maximize the yield of biochar. In contrast, fast pyrolysis uses higher temperatures and shorter times to maximize the yield of bio-oil.
Managing All Outputs is Essential
An effective pyrolysis system is not just a biochar producer. It is a biorefinery that must have the equipment to safely handle, cool, and store all three states of matter: solid biochar, liquid bio-oil, and flammable biogas.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding that pyrolysis creates a suite of products allows you to align the process with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is soil amendment and carbon sequestration: You will want to use slow pyrolysis to maximize the yield and quality of the solid biochar.
- If your primary focus is renewable fuel production: You may optimize for fast pyrolysis to generate the highest possible volume of liquid bio-oil and combustible biogas.
- If your primary focus is a zero-waste system: The goal is to create a circular process that captures and utilizes all outputs—biochar, bio-oil, biogas, and wood vinegar.
Ultimately, biochar is best understood not as a standalone substance, but as a key component in a sophisticated system for converting biomass into lasting value.
Summary Table:
| Pyrolysis Product | State | Primary Use |
|---|---|---|
| Biochar | Solid | Soil amendment, carbon sequestration |
| Bio-oil | Liquid | Renewable fuel, chemical feedstock |
| Biogas | Gas | Process heat, renewable energy |
| Wood Vinegar | Liquid | Agricultural applications |
Ready to transform your biomass into valuable products? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for pyrolysis research and development. Whether your goal is to produce high-quality biochar, optimize bio-oil yields, or design a complete zero-waste system, our expertise and reliable equipment can help you achieve precise and efficient results. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific laboratory needs and discover the right solutions for your biomass conversion projects.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What does calcination remove? A Guide to Thermal Decomposition for Material Processing
- What are the advantages of catalytic pyrolysis over thermal pyrolysis? Achieve Higher-Quality Bio-Oil and Chemicals
- What is the role of catalyst in pyrolysis? Transform Waste into High-Value Products
- Is pyrolysis eco friendly? Discover the Conditions for Sustainable Waste-to-Energy
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing
- What is pyrolysis decomposition of biomass? Unlock Value from Organic Waste
- What is the temperature range of a rotary kiln incinerator? Optimize Waste Destruction & Efficiency
- What is the temperature and time of pyrolysis? Control Your Product Output with Precision



















