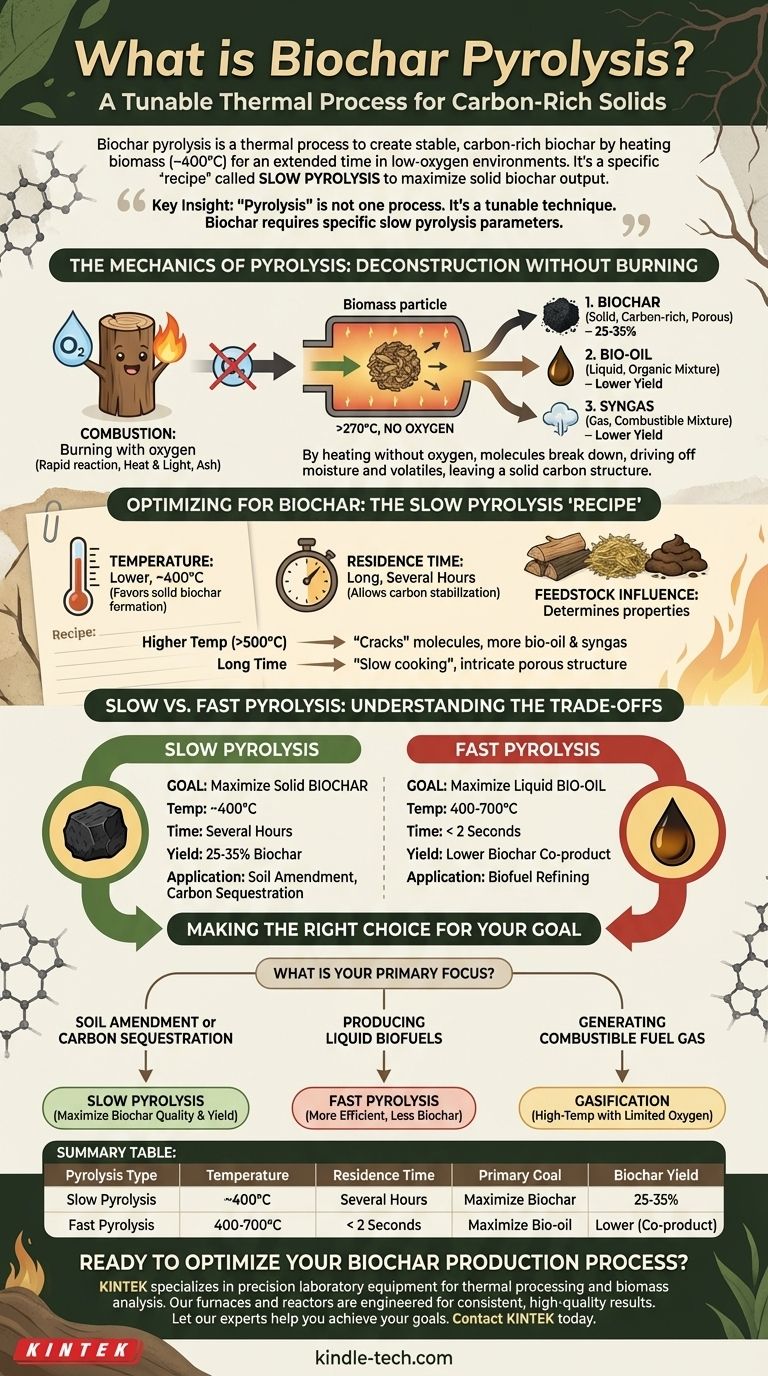
In essence, biochar pyrolysis is a specific thermal process designed to create a stable, carbon-rich solid known as biochar. It involves heating organic materials, or biomass, to moderate temperatures (around 400°C) for an extended period in a low-oxygen or oxygen-free environment. This controlled deconstruction maximizes the production of the solid biochar, as opposed to liquid bio-oil or gas.
The critical insight is that "pyrolysis" is not one single process. It is a tunable technique, and producing biochar requires a specific "recipe"—slow pyrolysis—which uses lower temperatures and longer heating times to prioritize the creation of a solid, carbon-based output over liquid or gas fuels.
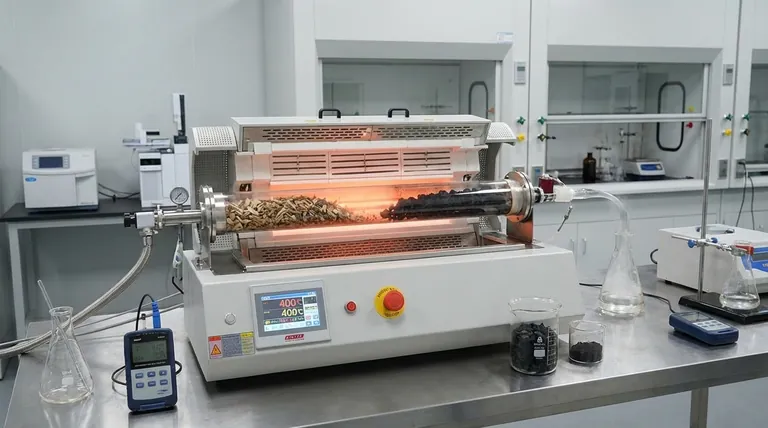

The Mechanics of Pyrolysis: Deconstruction Without Burning
Pyrolysis is fundamentally a process of thermal decomposition. It breaks down complex organic materials using heat in the absence of a key reactant: oxygen.
Heating vs. Burning
When you burn wood with ample oxygen (combustion), it reacts rapidly, releases energy as heat and light, and leaves behind a small amount of mineral ash.
Pyrolysis is different. By heating biomass above 270°C without oxygen, you prevent combustion. Instead, the material's large molecules break down, driving off moisture and volatile compounds, and leaving behind a solid carbon structure.
The Three Potential Outputs
Any pyrolysis process will generate three primary products in varying proportions:
- Biochar: A black, porous, and stable solid that is mostly carbon.
- Bio-oil (Pyrolysis Oil): A dense, acidic liquid mixture of hundreds of organic compounds.
- Syngas: A mixture of non-condensable, combustible gases like hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and methane.
The ratio of these three outputs is not accidental; it is determined entirely by the process conditions.
Optimizing for Biochar: The Slow Pyrolysis "Recipe"
To maximize the yield of biochar, a specific method known as slow pyrolysis is used. This process intentionally manipulates key variables to favor the formation of a solid residue.
The Critical Role of Temperature
Temperature is the most influential factor. Slow pyrolysis for biochar production typically operates at lower temperatures, often around 400°C.
Higher temperatures (above 500°C) tend to "crack" the molecules further, favoring the production of liquid bio-oil and syngas at the expense of the solid biochar.
The Importance of Residence Time
Residence time—how long the biomass is held at the target temperature—is the second key variable.
Slow pyrolysis uses a long residence time, often lasting several hours. This slow "cooking" process allows the carbon to stabilize and form the intricate porous structure characteristic of high-quality biochar.
The Influence of Feedstock
While temperature and time are the primary controls, the initial biomass used also matters. Different feedstocks, such as wood, agricultural waste, or manure, will produce biochar with distinct properties, even under identical pyrolysis conditions.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Slow vs. Fast Pyrolysis
The goal of the process dictates the method used. The choice between slow and fast pyrolysis is a strategic decision based on whether you want to produce a solid material or a liquid fuel.
Slow Pyrolysis: Maximizing the Solid
This is the standard method for biochar production. By using lower heat and longer residence times, it reliably converts 25-35% of the initial biomass into solid biochar. It is the preferred method when the primary product desired is a soil amendment or a carbon sequestration agent.
Fast Pyrolysis: Maximizing the Liquid
Conversely, fast pyrolysis uses higher temperatures (400-700°C) and extremely short residence times (often less than two seconds). This rapid thermal shock is designed to maximize the yield of liquid bio-oil, which can be refined into a potential biofuel. In this process, biochar is a smaller co-product, not the primary output.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The term "biochar pyrolysis" refers to a specific application of a broader technology. Your intended outcome determines which process parameters are correct.
- If your primary focus is soil amendment or carbon sequestration: Slow pyrolysis is the required method to maximize the yield and quality of solid biochar.
- If your primary focus is producing liquid biofuels: Fast pyrolysis is the more efficient pathway, though it generates less biochar as a co-product.
- If your primary focus is generating combustible fuel gas: Gasification, a related high-temperature process that introduces a limited amount of oxygen, is the designed method.
Understanding these process variables allows you to select the precise thermal treatment needed to achieve your specific material or energy goals.
Summary Table:
| Pyrolysis Type | Temperature | Residence Time | Primary Goal | Biochar Yield |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slow Pyrolysis | ~400°C | Several Hours | Maximize Biochar | 25-35% |
| Fast Pyrolysis | 400-700°C | < 2 Seconds | Maximize Bio-oil | Lower (Co-product) |
Ready to optimize your biochar production process?
KINTEK specializes in precision laboratory equipment for thermal processing and biomass analysis. Whether you're researching pyrolysis parameters, scaling up production, or analyzing biochar properties, our robust furnaces and reactors are engineered for the exacting conditions required for consistent, high-quality results.
Let our experts help you achieve your material and energy goals. Contact KINTEL today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect solution for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do tube furnaces or muffle furnaces ensure stoichiometric accuracy during synthesis? Mastering Li4GeO4 & Li4VO4
- What is the temperature of a rotary hearth furnace? Find the Right Heat for Your Process
- What is the process of zirconium production? From Ore to High-Performance Metal & Ceramic
- What is the function of a high-temperature furnace during burnout? Master Aluminum Foam Production with Precision
- How are composites processed using sintering? Engineered Material Solutions Through Advanced Thermal Bonding



















