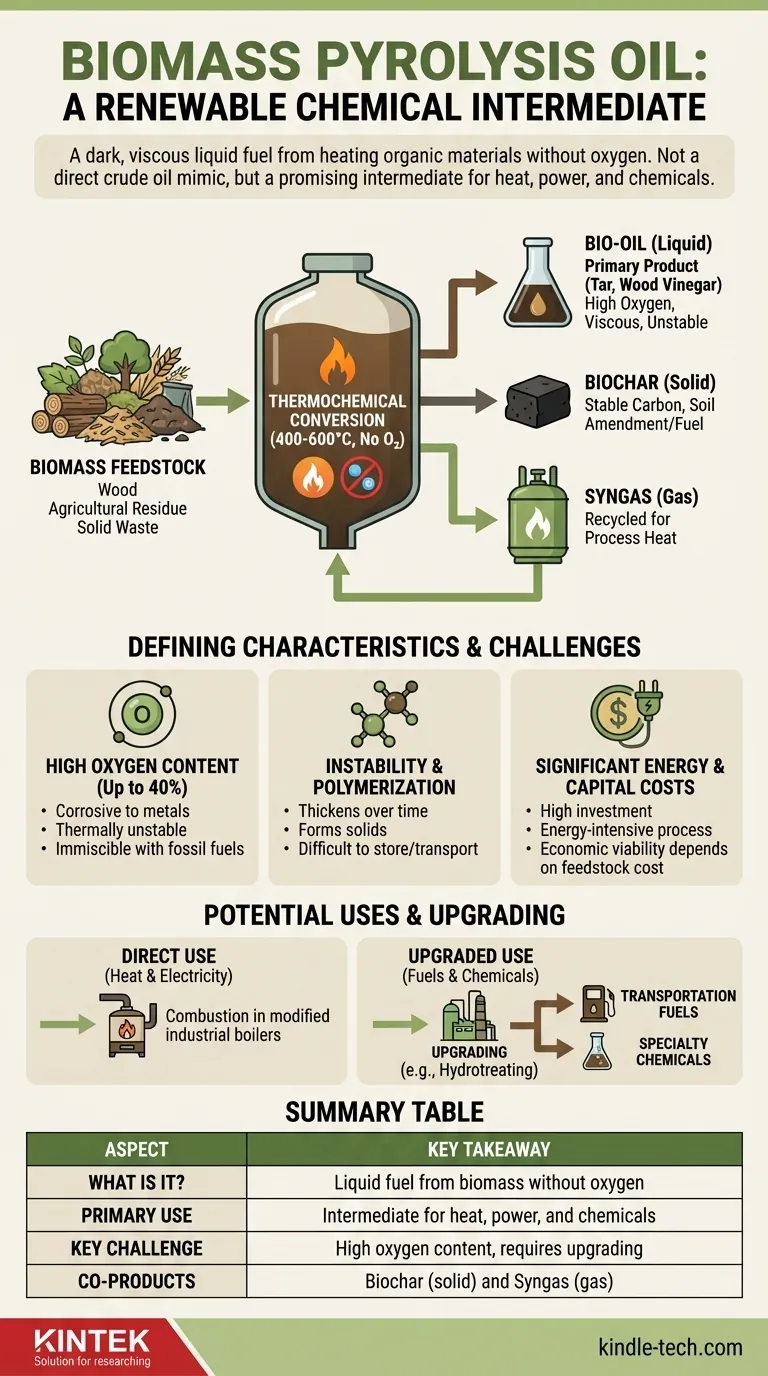
In short, biomass pyrolysis oil is a renewable, liquid fuel produced by heating organic materials like wood, agricultural residue, or solid waste in the absence of oxygen. Often called "bio-oil" or "bio-crude," it is a dark, viscous liquid that concentrates the energy from bulky biomass into a dense, transportable form. However, its chemical properties, particularly its high oxygen content, make it fundamentally different from petroleum-based crude oil.
While often discussed as a potential "green" replacement for crude oil, the reality is more complex. Biomass pyrolysis oil is best understood not as a direct substitute, but as a unique chemical intermediate that holds significant promise for heat, power, and renewable chemicals—provided its inherent challenges of instability and corrosiveness are properly managed.

How Pyrolysis Oil is Produced
The creation of pyrolysis oil is a process of controlled thermal decomposition. It breaks down complex organic matter without burning it.
The Core Principle: Thermochemical Conversion
The goal of pyrolysis is to rapidly heat biomass to high temperatures (typically 400-600°C) inside a sealed reactor without oxygen. This process vaporizes the biomass, breaking it down into smaller molecules.
These vapors are then rapidly cooled, or "quenched," which condenses them into a liquid—the pyrolysis oil. This preserves a significant portion of the carbon from the original biomass in a more energy-dense liquid state.
The Spectrum of Pyrolysis Products
Pyrolysis oil is never the sole product. The process inherently yields three distinct outputs:
- Bio-oil (Liquid): The primary liquid product, also referred to as tar or wood vinegar in some contexts. This is the focus.
- Biochar (Solid): A stable, carbon-rich charcoal that can be used as a soil amendment or solid fuel.
- Syngas (Gas): A mix of non-condensable gases (like carbon monoxide and hydrogen) that are typically recycled to provide heat for the pyrolysis process itself.
The Anatomy of a Pyrolysis Plant
A typical plant is built around four key systems working in concert: a feeding line to introduce biomass, the oxygen-free pyrolysis reactor, a discharging line for the solid biochar, and an emission cleaning line to manage exhaust.
The Defining Characteristics of Pyrolysis Oil
The properties of bio-oil are what make it both promising and challenging. It is not simply "oil from plants."
High Oxygen Content: The Central Challenge
Unlike petroleum crude, which is almost entirely hydrocarbons, pyrolysis oil can contain up to 40% oxygen by weight. This high oxygen content is the root cause of its most difficult properties.
This oxygen makes the oil corrosive to standard metals, thermally unstable, and largely immiscible (it will not mix) with conventional fossil fuels like diesel or gasoline.
Instability and Polymerization
Pyrolysis oil is not a stable final product. Over time, or when exposed to air and heat, its molecules can react with each other and polymerize, causing the oil to thicken, form solids, and become difficult to pump or use.
This instability creates significant hurdles for long-term storage and transportation, requiring specialized handling procedures.
Potential Uses: From Heat to Chemicals
Despite these challenges, the oil has several valuable applications. It can be combusted directly in modified industrial boilers or furnaces to produce heat and electricity.
More advanced applications involve "upgrading" the oil through processes like hydrotreating to remove oxygen, creating a more stable, hydrocarbon-like product suitable for refining into transportation fuels or specialty chemicals.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
Pursuing pyrolysis oil as an energy solution involves navigating significant technical and economic hurdles.
Significant Energy and Capital Costs
Building and operating a pyrolysis plant requires a high capital investment. Furthermore, the process itself is energy-intensive, as it relies on maintaining very high temperatures within the reactor.
The overall energy balance and economic viability are highly dependent on the cost of the biomass feedstock and the market value of the end products.
The Necessity of Upgrading
For most high-value applications, especially as a transportation fuel, raw pyrolysis oil is unsuitable. It must undergo further refining or "upgrading" to remove oxygen, reduce acidity, and improve stability.
This upgrading step adds significant cost and complexity to the production chain, making it difficult to compete with petroleum on price alone.
Feedstock and Logistical Constraints
The economics of pyrolysis are tied to the logistics of biomass. Transporting bulky, low-density materials like corn stover or wood chips to a centralized processing facility can be prohibitively expensive.
Therefore, successful pyrolysis operations are often co-located with a large, consistent source of biomass waste, such as a sawmill or large agricultural operation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The strategic value of pyrolysis oil depends entirely on your objective.
- If your primary focus is immediate, large-scale fuel replacement: Pyrolysis oil is not a drop-in solution; its use requires dedicated infrastructure or significant investment in upgrading technology.
- If your primary focus is waste valorization and local energy: Pyrolysis is an excellent technology for converting local biomass waste into a storable liquid fuel for on-site heat and power, creating valuable biochar as a co-product.
- If your primary focus is developing next-generation green chemicals: Bio-oil is a rich, albeit complex, feedstock for renewable phenols and other chemical building blocks, representing a major frontier for sustainable chemistry.
Ultimately, viewing biomass pyrolysis oil as a unique chemical intermediate, rather than a direct crude oil mimic, is crucial for unlocking its true potential in a circular economy.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| What is it? | A dark, viscous liquid fuel produced by heating biomass without oxygen. |
| Primary Use | An intermediate for heat, power, and renewable chemicals; not a direct petroleum substitute. |
| Key Challenge | High oxygen content causes instability, corrosiveness, and requires upgrading. |
| Co-products | Process also yields valuable biochar (solid) and syngas. |
Ready to Explore Biomass Conversion Solutions?
Navigating the complexities of pyrolysis and bio-oil handling requires the right equipment and expertise. KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory equipment and consumables for biomass research and analysis.
Whether you are developing new pyrolysis processes, analyzing bio-oil stability, or testing upgraded biofuels, our precise and reliable tools can support your R&D goals. We help laboratories like yours drive innovation in renewable energy and sustainable chemicals.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your biomass conversion research and development.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the products of pyrolysis and gasification? Unlock the Value in Biomass Conversion
- What is the effect of torrefaction on fast pyrolysis bio-oil? Achieve Higher Quality, More Stable Bio-Fuel
- What is spray pyrolysis method? A Guide to Precision Thin Film & Powder Synthesis
- What are the applications of calcination? A Guide to Thermal Processing in Industry
- What are the risks of the process of pyrolysis? A Guide to Environmental, Operational, and Economic Challenges
- What are the main outputs from the pyrolysis step in the gasification process? Tune Your Process for Gas, Liquid, or Solid
- What is the best feedstock for biochar? Match Your Material to Your Goal for Maximum Impact
- What is the operating temperature of pyrolysis? Master the Key to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Production

