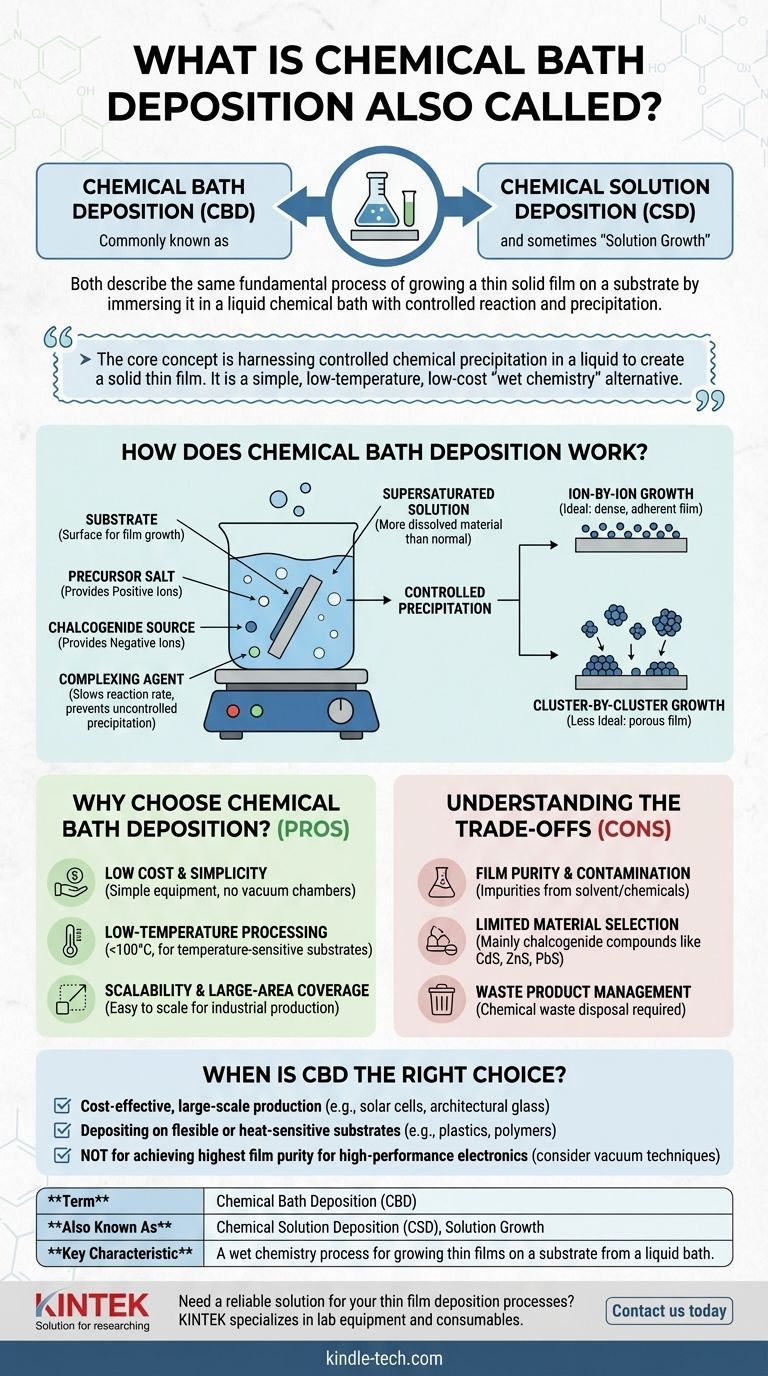
In short, Chemical Bath Deposition (CBD) is most commonly referred to as Chemical Solution Deposition (CSD). Both terms describe the same fundamental process of growing a thin solid film on a substrate by immersing it in a liquid chemical bath, where a controlled reaction causes the desired material to precipitate out of the solution. It is also sometimes simply called "solution growth."
The core concept behind Chemical Bath Deposition is harnessing controlled chemical precipitation in a liquid to create a solid thin film. It is a simple, low-temperature, and low-cost "wet chemistry" alternative to more complex vacuum-based deposition techniques.

How Does Chemical Bath Deposition Work?
To truly understand CBD, it's essential to look at the underlying mechanism. The process is a carefully balanced chemical reaction that encourages a solid to form on a surface rather than just randomly in the liquid.
The Core Principle: Controlled Precipitation
The entire process operates by making a solution supersaturated with the ions of the material you want to deposit. This means the solution contains more dissolved material than it can normally hold.
Under these conditions, the ions will begin to combine and precipitate out as a solid. By carefully controlling factors like temperature, pH, and chemical concentrations, this precipitation is directed to occur heterogeneously on the surface of a submerged substrate.
Key Components of the Bath
A typical chemical bath contains several critical ingredients:
- Substrate: The surface onto which the thin film will be grown.
- Precursor Salt: This provides the positive ions (cations) for the final film material (e.g., cadmium chloride for a CdS film).
- Chalcogenide Source: This provides the negative ions (anions) needed to form the compound (e.g., thiourea for a sulfide film).
- Complexing Agent: A chemical (like ammonia) that temporarily binds to the metal ions, slowing down their reaction rate. This is crucial for preventing rapid, uncontrolled precipitation in the solution and ensuring slow, orderly film growth on the substrate.
The Deposition Mechanism
Growth typically occurs through two main pathways, often simultaneously:
- Ion-by-Ion Growth: Individual ions in the solution attach directly to active sites on the substrate surface, forming a dense and adherent film. This is the ideal mechanism.
- Cluster-by-Cluster Growth: Small particles (clusters) precipitate within the bulk solution and then adhere to the substrate. This can lead to a more porous, less uniform film if not properly controlled.
Why Choose Chemical Bath Deposition?
CBD is not a high-tech, exotic process, but its simplicity is its greatest strength. It is chosen for specific, practical advantages over other methods like sputtering or evaporation.
Low Cost and Simplicity
The most significant advantage is the low cost of equipment. CBD requires little more than beakers, hot plates, and chemicals. It completely avoids the need for expensive high-vacuum chambers and power supplies.
Low-Temperature Processing
Deposition often occurs at temperatures below 100°C (the boiling point of water). This makes CBD ideal for depositing films onto temperature-sensitive substrates, such as flexible polymers and plastics, without damaging them.
Scalability and Large-Area Coverage
The process is easily scalable for industrial production. Coating a large area simply requires a larger container for the chemical bath, making it highly effective for applications like window coatings or large-scale solar cell manufacturing.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No technique is perfect, and CBD's strengths come with inherent trade-offs. Understanding these is key to deciding if it's the right process for your application.
Film Purity and Contamination
Because it is a "wet" chemical process, films can easily incorporate impurities from the solvent (usually water) or unreacted chemicals from the bath. This can result in lower-purity films compared to those grown in an ultra-high vacuum environment.
Limited Material Selection
CBD is primarily used for a specific class of materials, most notably chalcogenide compounds like Cadmium Sulfide (CdS), Zinc Sulfide (ZnS), and Lead Sulfide (PbS). It is not a universally applicable technique for all types of materials.
Waste Product Management
The process generates chemical waste that must be managed and disposed of responsibly. This environmental and safety consideration adds to the operational complexity, even if the initial equipment setup is simple.
When is CBD the Right Choice?
Your choice of deposition method should always be driven by your end goal. CBD excels in specific scenarios where its advantages outweigh its limitations.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, large-scale production: CBD is an excellent choice for applications like solar cells or architectural glass where minimizing cost per unit area is critical.
- If your primary focus is depositing on flexible or heat-sensitive substrates: The low-temperature nature of CBD makes it one of the few viable methods for coating plastics and other polymers.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible film purity for high-performance electronics: You should likely consider vacuum-based techniques like sputtering or molecular beam epitaxy, as CBD films may contain too many impurities.
Ultimately, Chemical Bath Deposition remains a powerful and relevant technique because it offers a practical, accessible path to creating functional thin films.
Summary Table:
| Term | Also Known As | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Bath Deposition (CBD) | Chemical Solution Deposition (CSD), Solution Growth | A wet chemistry process for growing thin films on a substrate from a liquid bath. |
Need a reliable solution for your thin film deposition processes? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing the tools and expertise for techniques like Chemical Bath Deposition. Whether you're working with temperature-sensitive substrates or require scalable production solutions, we can help enhance your laboratory's capabilities. Contact us today to discuss your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- How does plasma vapor deposition work? A Low-Temperature Coating Solution for Sensitive Materials
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- What is plasma CVD? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for Sensitive Materials
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What is plasma enhanced? A Guide to Low-Temperature, High-Precision Manufacturing
















