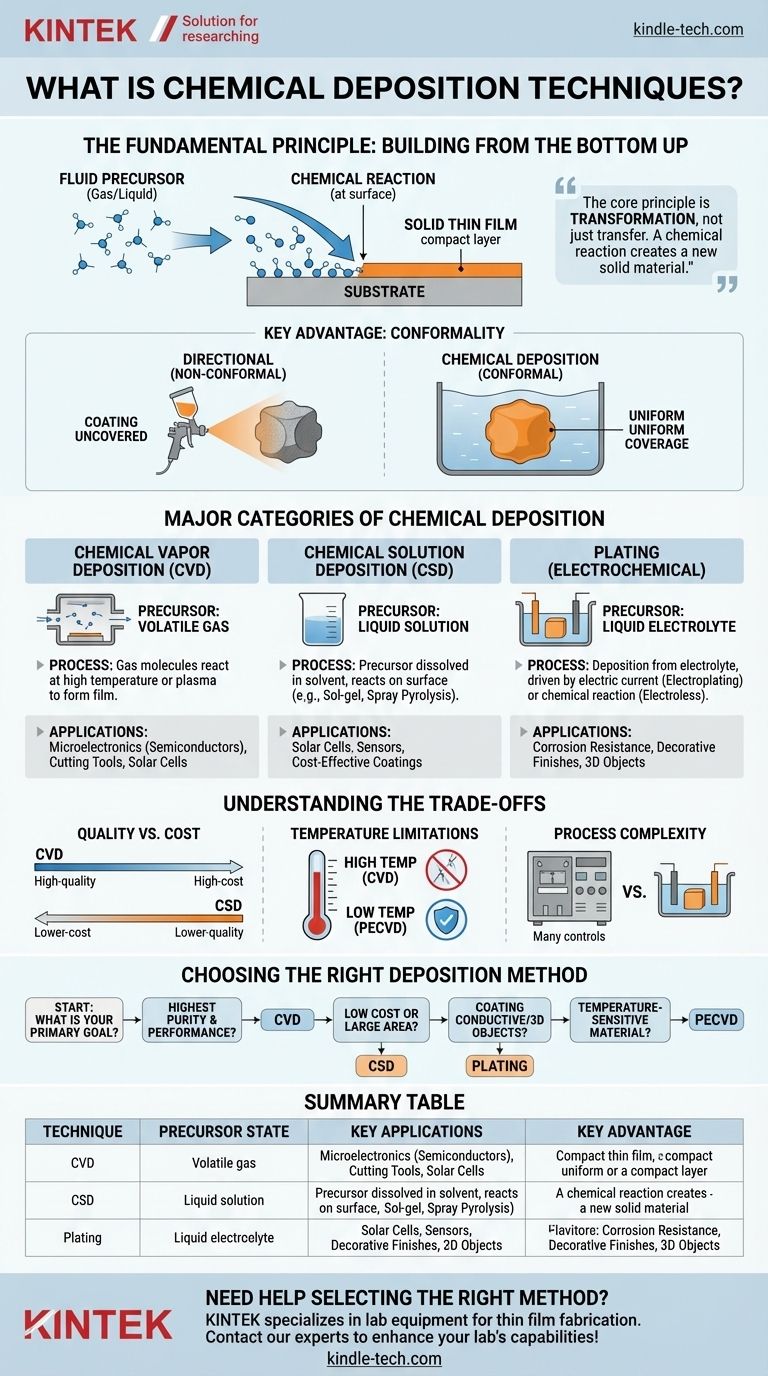
In essence, chemical deposition is a family of techniques used to create a solid thin film or coating on a surface (known as a substrate) through a chemical reaction. A fluid starting material, called a precursor, reacts at the substrate's surface, depositing a layer of the desired new material. This process allows for the precise, atom-by-atom or molecule-by-molecule construction of high-quality films.
The core principle of all chemical deposition is transformation, not just transfer. Unlike physical methods that move a material from a source to a target, chemical deposition uses a chemical reaction to create an entirely new solid material directly on the surface you want to coat.

The Fundamental Principle: Building from the Bottom Up
How Chemical Deposition Works
The process is fundamentally about controlled chemical change. A precursor, which can be a gas or a liquid, is introduced into a reaction environment containing the substrate.
When the precursor molecules encounter the substrate under the right conditions—such as high temperature or the presence of a plasma—they react and decompose. This chemical change leaves behind a solid layer that adheres to the substrate, building up the desired thin film.
The Key Advantage: Conformality
One of the most significant advantages of chemical deposition is its ability to produce conformal coatings. This means the film covers all surfaces of a substrate uniformly, regardless of its shape or complexity.
Imagine dipping a textured object in paint versus spray-painting it from one angle. The dipping action covers every nook and cranny evenly—this is analogous to conformal chemical deposition. Directional methods, in contrast, create thicker coatings on surfaces facing the source and thinner "shadowed" areas on others.
Major Categories of Chemical Deposition
While the principle is the same, the methods are categorized based on the state of the precursor and the reaction conditions.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
In CVD, the precursor is a volatile gas. This technique is renowned for producing extremely pure, high-performance thin films.
Because of its precision, CVD is a cornerstone of the electronics industry for creating semiconductor layers on silicon wafers. It's also used for durable, wear-resistant coatings on cutting tools and for manufacturing high-efficiency thin-film solar cells.
Chemical Solution Deposition (CSD)
CSD uses a precursor dissolved in a liquid solvent. This category includes several accessible and versatile techniques.
Common CSD methods include the sol-gel technique, where a solution gels into a solid network; chemical bath deposition, which involves submerging the substrate in a reactive solution; and spray pyrolysis, where a precursor solution is sprayed onto a heated substrate. These methods are often simpler and less expensive than CVD.
Plating (Electrochemical Deposition)
Plating involves depositing a material, typically a metal, from a liquid solution (an electrolyte bath) onto a substrate.
Electroplating uses an external electric current to drive the deposition onto a conductive surface. Electroless plating achieves a similar result through an autocatalytic chemical reaction without the need for external power, allowing it to coat non-conductive surfaces that have been properly prepared.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single technique is universally superior. The choice depends on a balance of quality, cost, and material compatibility.
Quality vs. Cost
Generally, CVD offers the highest film quality, purity, and structural perfection, but it requires sophisticated and expensive equipment like vacuum chambers. CSD methods are often significantly lower in cost and complexity but may yield films with different structural properties or lower purity.
Temperature and Substrate Limitations
Many CVD processes require very high temperatures to initiate the chemical reaction. This heat can damage sensitive substrates like plastics or certain electronic components.
To overcome this, specialized low-temperature methods like Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) were developed. PECVD uses an energy-rich plasma to drive the reaction, allowing for high-quality film growth at much lower temperatures.
Process Complexity
CVD requires precise control over gas flow, pressure, and temperature, making the process complex. Plating, on the other hand, can be a relatively straightforward method for coating large or complex 3D objects, making it highly scalable for many industrial applications.
Choosing the Right Deposition Method
Your choice should be guided by your end goal, budget, and the materials you are working with.
- If your primary focus is highest purity and performance (e.g., for microelectronics): CVD is the industry standard for creating superior semiconductor and dielectric films.
- If your primary focus is low cost or coating a large area (e.g., for certain solar cells or sensors): CSD methods like spray pyrolysis or chemical bath deposition offer a cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is coating a conductive or complex 3D object (e.g., for corrosion resistance or decorative finishes): Electroplating or electroless plating provides excellent conformal coverage on intricate shapes.
- If your primary focus is depositing a high-quality film on a temperature-sensitive material: A low-temperature technique like PECVD is the necessary choice.
Understanding these core techniques empowers you to select the optimal tool to fabricate materials with the precise properties your project demands.
Summary Table:
| Technique | Precursor State | Key Applications | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | Gas | Microelectronics, cutting tools | High purity, performance |
| Chemical Solution Deposition (CSD) | Liquid solution | Solar cells, sensors | Low cost, large area coverage |
| Plating (Electrochemical) | Liquid electrolyte | Corrosion resistance, decorative finishes | Conformal coverage on 3D objects |
Need help selecting the right deposition method for your project? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for thin film fabrication. Our experts can help you choose the optimal chemical deposition technique for your specific application—whether you're working in electronics, coatings, or materials research. Contact us today to discuss your requirements and discover how our solutions can enhance your lab's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
People Also Ask
- What are different types of thin films? A Guide to Function, Material, and Deposition Methods
- What is the difference between plasma CVD and thermal CVD? Choose the Right Method for Your Substrate
- Can plasma enhanced CVD deposit metals? Why PECVD is rarely used for metal deposition
- Why does a PECVD vacuum system require both a rotary vane and turbo pump? Ensure High-Purity Coatings
- What is the difference between PECVD and APCVD? Choose the Right CVD Method for Your Application



















