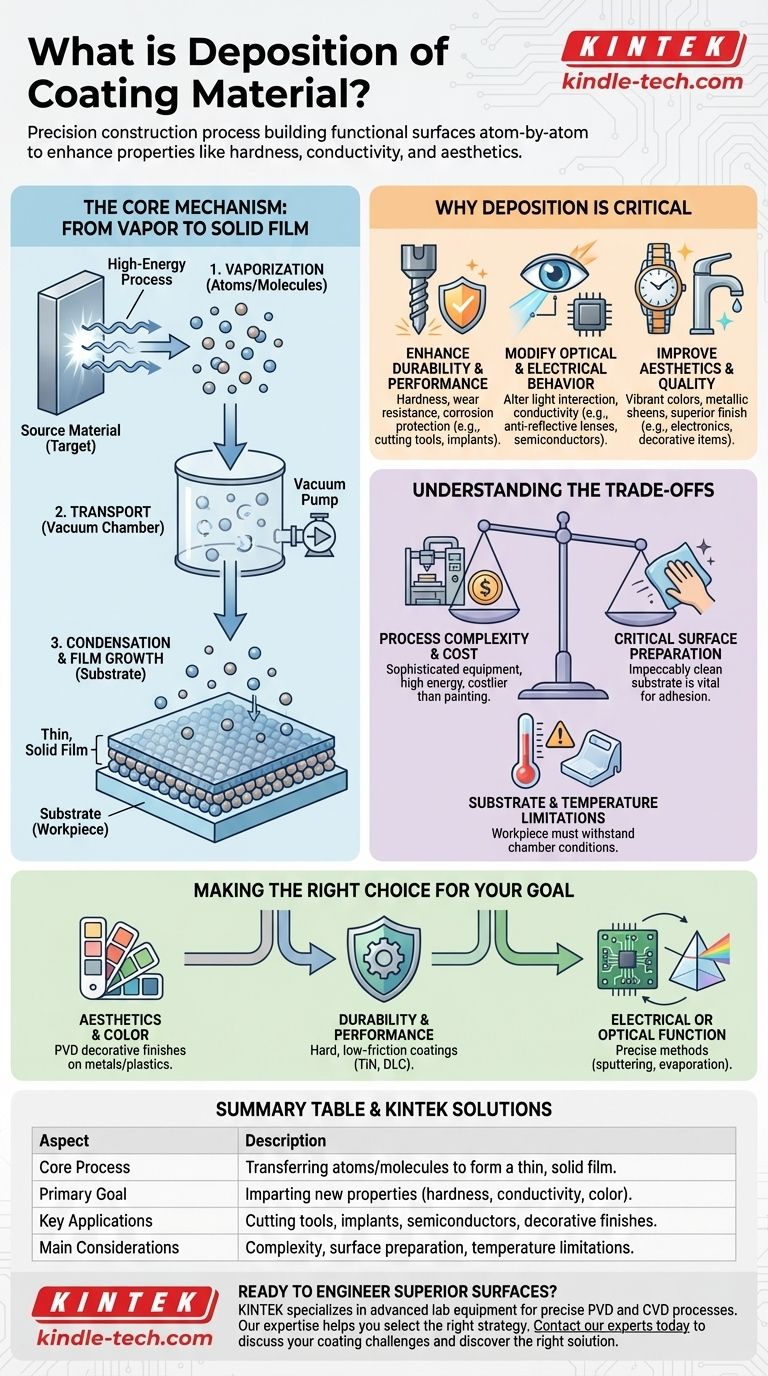
In the context of material science and manufacturing, deposition is the fundamental process where atoms or molecules from a source material are transferred onto a surface—known as a substrate—to form a thin, solid film. This controlled, atom-by-atom layering is what creates the final coating, which can be used to enhance everything from aesthetic vibrancy to functional durability.
Deposition is more than just applying a layer of material; it's a precise construction process that builds a new functional surface on an object. The goal is to impart properties—like hardness, conductivity, or specific colors—that the base material does not possess on its own.

The Core Mechanism: From Vapor to Solid Film
Deposition typically occurs within a vacuum chamber and involves a sequence of highly controlled physical steps. The basic principle is to turn a solid source material into a vapor, transport it, and then condense it onto the target object.
Step 1: Generating the Coating Material (Vaporization)
Before a film can be formed, the source coating material must be converted into a vapor phase. This is often achieved using high-energy processes that liberate individual atoms or molecules from a solid "target."
Step 2: Transporting the Vapor
Once vaporized, these atoms travel through the low-pressure environment of the chamber. The vacuum is critical as it prevents the coating atoms from colliding with air molecules, ensuring a clean and direct path to the substrate.
Step 3: Condensation and Film Growth
When the vaporized atoms strike the relatively cool surface of the workpiece, they rapidly lose energy, condense back into a solid state, and adhere to the surface. This process builds up, layer by layer, to form a uniform and dense thin film.
Why Deposition is a Critical Manufacturing Process
The true value of deposition lies in its ability to decouple the bulk properties of an object from its surface properties. You can use a cheap, strong, or lightweight base material and add a high-performance surface.
Enhancing Durability and Performance
Deposition is essential for creating coatings that provide exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and corrosion protection. This is common for cutting tools, engine components, and medical implants.
Modifying Optical and Electrical Behavior
Functional films can alter how a surface interacts with light or electricity. Examples include anti-reflective coatings on eyeglass lenses, reflective layers on mirrors, and conductive tracks in semiconductor chips and solar panels.
Improving Aesthetics and Quality
As noted, deposition is a key method for adding high-quality decorative finishes. The process allows for vibrant, durable colors and metallic sheens—like those on watches, faucets, and high-end electronics—that are far more resilient than paint.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, deposition processes are not a universal solution. They come with specific technical requirements and limitations that must be considered.
Process Complexity and Cost
Most deposition methods, particularly Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), require sophisticated vacuum equipment and high energy inputs. This makes the process significantly more complex and costly than simple painting or plating.
The Critical Role of Surface Preparation
The success of deposition is entirely dependent on the adhesion between the film and the substrate. The workpiece surface must be impeccably clean and properly prepared, as any contamination will lead to the coating peeling or flaking off.
Substrate and Temperature Limitations
The workpiece must be able to withstand the conditions inside the deposition chamber. Some processes involve high temperatures or plasma bombardment, which can damage sensitive materials like certain plastics or electronics.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a deposition strategy requires matching the process capabilities to your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is aesthetics and color: You can choose from a range of PVD processes that offer brilliant, durable decorative finishes on metals and some plastics.
- If your primary focus is durability and performance: Prioritize processes known for creating hard, low-friction coatings (like TiN or DLC) and ensure the base material can withstand the process heat.
- If your primary focus is electrical or optical function: You will need a highly precise method like sputtering or evaporation that allows for meticulous control over film thickness, purity, and structure.
Ultimately, understanding deposition empowers you to see a coating not as a simple layer, but as an engineered component of your final product.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Process | Transferring atoms/molecules from a source to a substrate to form a thin, solid film. |
| Primary Goal | Imparting new properties (hardness, conductivity, color) that the base material lacks. |
| Key Applications | Cutting tools, medical implants, semiconductors, solar panels, decorative finishes. |
| Main Considerations | Process complexity, surface preparation, substrate temperature limitations. |
Ready to Engineer Superior Surfaces for Your Products?
Deposition is a powerful tool for enhancing your materials, whether your goal is extreme durability, specific optical properties, or vibrant aesthetics. KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables needed for precise coating processes like PVD and CVD.
Our expertise helps you select the right deposition strategy for your specific application, ensuring optimal performance and quality. Let us help you build the perfect surface for your product.
Contact our experts today to discuss your coating challenges and discover the right solution for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What color diamonds are CVD? Understanding the Process from Brown Tint to Colorless Beauty
- What are the steps of the CVD process? A Guide to Precision Thin Film Deposition
- What is the process of vacuum vapor deposition? Mastering CVD and PVD Thin-Film Coating
- What are the different types of thin films? A Guide to Optical, Electrical, and Functional Coatings
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition



















