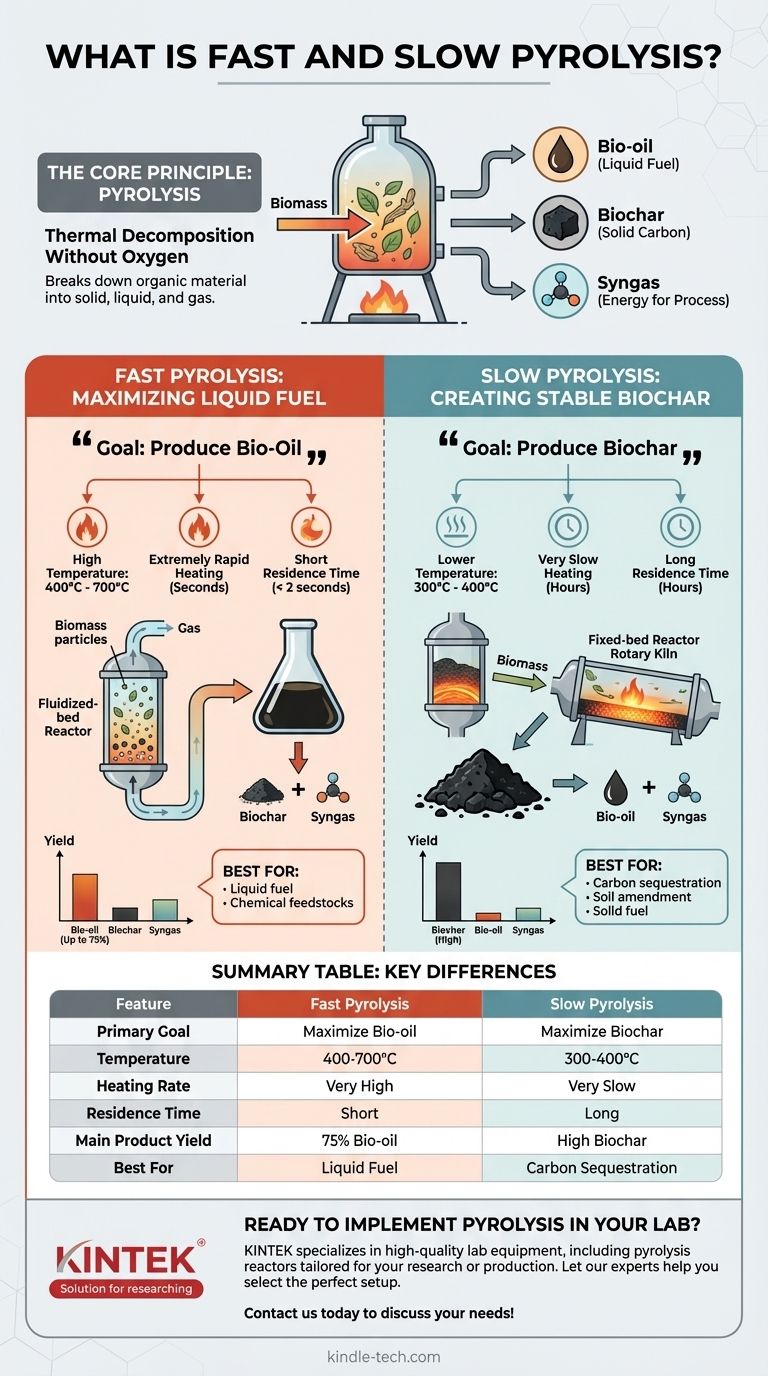
At their core, fast and slow pyrolysis are two distinct thermal processes for breaking down organic material, like biomass, in the absence of oxygen. The primary difference is that fast pyrolysis uses high temperatures and rapid heating to maximize the production of a liquid fuel called bio-oil. In contrast, slow pyrolysis uses lower temperatures over a much longer period to maximize the output of a solid, carbon-rich product called biochar.
The choice between fast and slow pyrolysis is not about which is "better," but about the desired end product. Your goal dictates the process: fast pyrolysis is for producing liquid fuel, while slow pyrolysis is for creating a stable, solid carbon product.

The Core Principle: What is Pyrolysis?
Thermal Decomposition Without Oxygen
Pyrolysis is a process of heating an organic material, such as wood, agricultural waste, or plastic, in a completely or nearly oxygen-free environment.
Instead of combusting (burning), the material thermally decomposes. The molecular bonds break down, reforming into smaller, different molecules in solid, liquid, and gas forms.
The Three Primary Products
Regardless of the speed, pyrolysis yields three main products in varying proportions:
- Bio-oil (Pyrolysis Oil): A dark, dense liquid that can be used as an industrial fuel or further refined into advanced biofuels and chemicals.
- Biochar (Coke): A stable, solid material rich in carbon. It is functionally similar to charcoal.
- Syngas (Pyrolysis Gas): A mixture of non-condensable gases like hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and methane. This gas is almost always captured and used to provide the heat needed to power the pyrolysis process itself, making the system more energy-efficient.
Fast Pyrolysis: Maximizing Liquid Fuel
The Goal: Produce Bio-Oil
The entire fast pyrolysis process is optimized to produce the highest possible yield of liquid bio-oil, often converting up to 75% of the initial biomass weight into oil.
This is achieved by rapidly heating the biomass to a temperature where it vaporizes, and then immediately cooling those vapors to condense them into a liquid before they can break down further into gases.
Key Process Conditions
To maximize liquid yield, fast pyrolysis requires very specific conditions:
- High Temperature: Typically between 400°C and 700°C.
- Extremely Rapid Heating: The biomass must be heated to the target temperature in seconds.
- Short Residence Time: The resulting vapors are removed from the hot zone almost instantly (usually in less than 2 seconds) to be quenched into a liquid.
Common Reactor Types
Achieving such rapid heat transfer requires specialized reactors. Fluidized-bed and ablative reactors are common because they allow for intense mixing and near-instantaneous heating of fine biomass particles.
Slow Pyrolysis: Creating Stable Biochar
The Goal: Produce Biochar
Slow pyrolysis is engineered to maximize the production of biochar, the solid carbon residue. This process is much older and simpler, resembling traditional charcoal making.
The gradual heating allows volatile components to escape slowly while promoting the formation of stable carbon structures, resulting in a high-quality, porous biochar.
Key Process Conditions
The conditions for slow pyrolysis are the opposite of those for fast pyrolysis:
- Lower Temperature: Generally between 300°C and 400°C.
- Very Slow Heating: The process can take several hours to complete.
- Long Residence Time: The biomass remains in the heated chamber for an extended period, allowing the slow conversion to char to complete.
Common Reactor Types
The slow heating rate means simpler technology can be used. Fixed-bed reactors, rotary kilns, and batch furnaces are well-suited for slow pyrolysis because they allow for gradual and controlled heating of the material.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Product Yield vs. Process Goal
The trade-off is fundamentally about the state of the final product. Fast pyrolysis sacrifices biochar and gas yields to create a transportable liquid fuel.
Slow pyrolysis sacrifices liquid and gas yields to create a stable, solid product ideal for soil amendment, carbon sequestration, or use as a solid fuel.
Feedstock and Infrastructure
Fast pyrolysis requires finely ground, dry biomass to ensure rapid heat transfer, which can add processing costs. The reactors are also more complex.
Slow pyrolysis is more forgiving and can handle larger, more varied chunks of biomass. However, the primary product, biochar, is a bulk solid that is less energy-dense than bio-oil, making it more expensive to transport long distances.
Energy and Complexity
While the syngas produced in both methods can power the reaction, the high-energy, rapid-heating demands of fast pyrolysis make it a more complex and technically sensitive process to operate and control compared to the slower, more robust nature of slow pyrolysis.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Choosing the right pyrolysis method depends entirely on the economic and environmental objective you want to achieve.
- If your primary focus is liquid fuel production: Fast pyrolysis is the correct path, as it is specifically designed to maximize the bio-oil yield for energy or chemical upgrading.
- If your primary focus is carbon sequestration or soil improvement: Slow pyrolysis is the superior choice, as its main output is stable biochar that can lock away carbon in soil for centuries.
- If your primary focus is creating a solid fuel: Slow pyrolysis is also the appropriate method for producing biochar or coke, which can be used as a solid fuel source.
Ultimately, both processes are powerful tools for converting low-value biomass into high-value products.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Fast Pyrolysis | Slow Pyrolysis |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Maximize liquid bio-oil production | Maximize solid biochar production |
| Temperature | 400°C - 700°C | 300°C - 400°C |
| Heating Rate | Very High (seconds) | Very Slow (hours) |
| Residence Time | Short (< 2 seconds) | Long (hours) |
| Main Product Yield | Up to 75% Bio-oil | High Biochar |
| Best For | Liquid fuel, chemical feedstocks | Carbon sequestration, soil amendment, solid fuel |
Ready to Implement Pyrolysis in Your Lab?
Choosing the right pyrolysis technology is critical for your research or production goals. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including pyrolysis reactors and systems tailored for both fast and slow processes. Our experts can help you select the perfect setup to efficiently convert biomass into bio-oil, biochar, or syngas.
Contact us today to discuss your specific needs and let KINTEK provide the reliable equipment and support your laboratory requires. Get in touch via our contact form to get started!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions



















