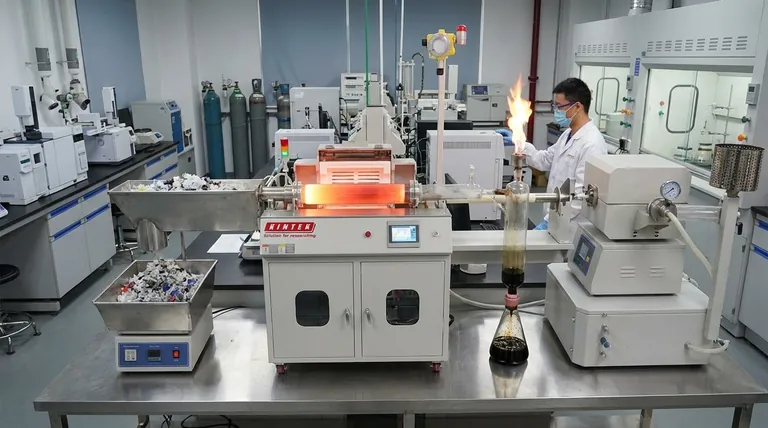
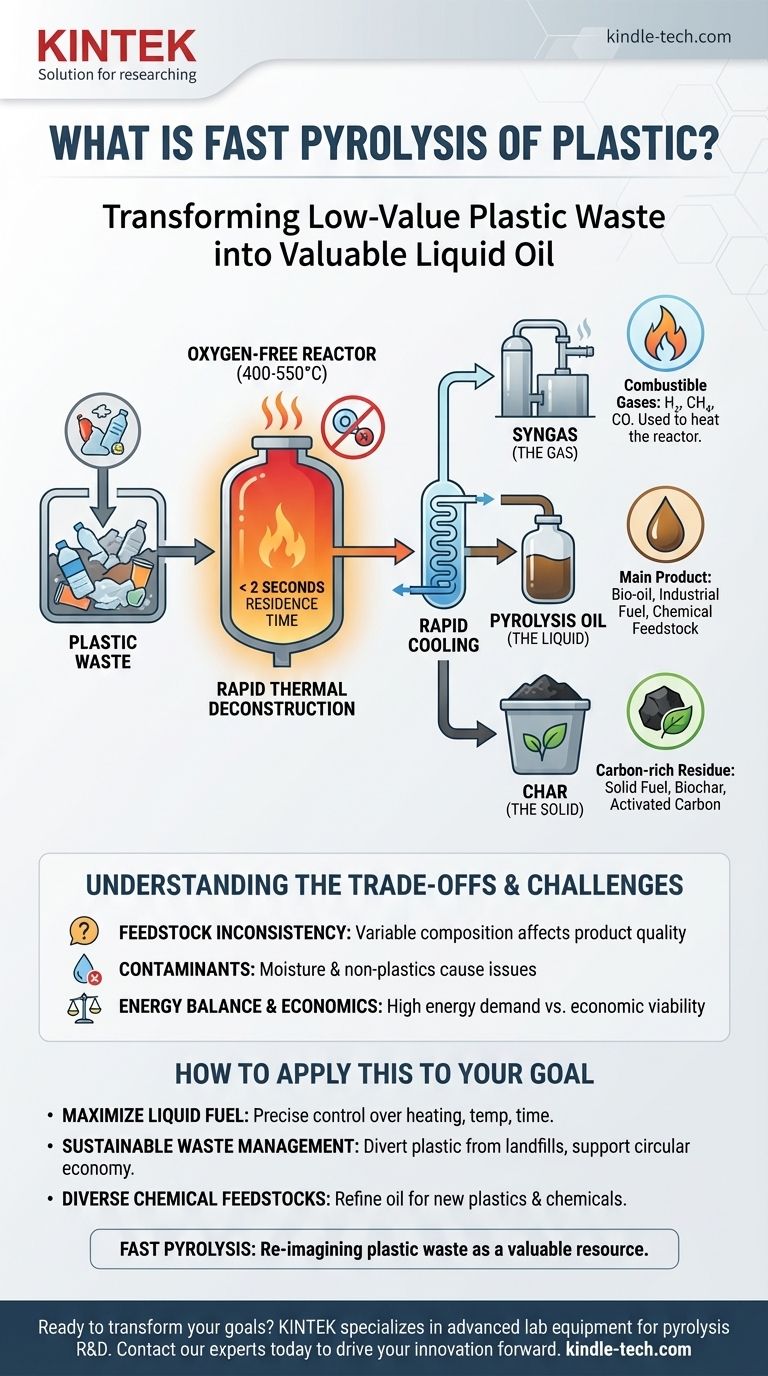
In essence, fast pyrolysis is a high-temperature process that rapidly breaks down plastic waste in an environment without oxygen. The primary goal is to transform low-value plastic into a valuable liquid known as pyrolysis oil. This is achieved by heating the plastic very quickly to around 400-550°C for less than two seconds, causing the large plastic molecules to "crack" into smaller, more useful components.
Fast pyrolysis is best understood not as burning plastic, but as a controlled thermal deconstruction. By applying intense heat at high speed in an oxygen-free reactor, it maximizes the conversion of plastic waste into a liquid oil, while also producing a combustible gas and a solid char.

How Fast Pyrolysis Deconstructs Plastic
To grasp fast pyrolysis, it's crucial to understand the distinct roles of heat, speed, and the absence of oxygen. These three factors work in concert to determine the final output.
The Core Principle: Heat Without Oxygen
Pyrolysis is fundamentally different from incineration (burning). It works by applying thermal energy in a controlled, oxygen-starved reactor.
Without oxygen, the plastic cannot combust. Instead, the intense heat (400-550°C) causes the long polymer chains that make up the plastic to vibrate and break apart into smaller, less complex molecules. This process is known as thermal cracking.
The Importance of Speed
The "fast" in fast pyrolysis is the defining characteristic. The process involves a very high heating rate and a short residence time—the plastic material is inside the hot zone of the reactor for less than two seconds.
This speed is intentional. It prevents the molecules from continuing to break down into the least valuable products (gases and solid carbon). By rapidly heating and then quickly cooling the resulting vapors, the process is optimized to produce the maximum possible yield of liquid pyrolysis oil.
The Three Primary Outputs of the Process
The precise yield of each product depends on the type of plastic used and the exact process conditions. However, the output always consists of a liquid, a gas, and a solid.
Pyrolysis Oil (The Liquid)
This is the main and most valuable product of fast pyrolysis. Often called bio-oil (when the feedstock is biomass), this dark, viscous liquid is a complex mixture of hydrocarbons.
It can be used directly as a fuel in industrial boilers, engines, and turbines. It can also be further refined to produce transportation fuels or serve as a feedstock for valuable chemical commodities.
Syngas (The Gas)
The process also creates a mixture of combustible gases, commonly called syngas or pyrolysis gas. This includes hydrogen, methane, and carbon monoxide.
This gas has significant value within the process itself. It can be captured and burned to provide the heat required for the pyrolysis reactor, creating a partially self-sustaining energy loop and reducing external energy needs.
Char (The Solid)
After the volatile components have been vaporized, a solid, carbon-rich residue called char remains. This material is similar to charcoal.
Depending on its purity, char can be used as a solid fuel, a soil amendment to improve fertility (biochar), or as a raw material for producing high-grade activated carbon, which is used in filtration systems.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While promising, fast pyrolysis is a complex industrial process with specific operational realities that must be managed for success.
Feedstock Inconsistency
The chemical composition of the final products is highly dependent on the type of plastic waste being processed. A batch of pure polyethylene will produce a different oil than a mixed batch of household plastic waste containing PVC and PET. This variability presents a significant challenge for achieving consistent, high-quality output.
The Problem of Contaminants
Real-world plastic waste is often contaminated with other materials. Moisture is a common issue; any water in the feedstock will turn to steam and can result in contaminated wastewater that requires treatment. Other non-plastic contaminants can also affect the process and the quality of the outputs.
Energy Balance and Economics
A pyrolysis plant requires a significant amount of energy to reach and maintain its high operating temperatures. While burning the syngas produced can offset a portion of this energy demand, the overall energy balance is a critical factor in the economic viability of a plant.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Your perspective on fast pyrolysis will depend on your ultimate objective.
- If your primary focus is maximizing liquid fuel production: You must prioritize precise control over the heating rate, reactor temperature, and residence time to favor the creation of liquids over gases and solids.
- If your primary focus is sustainable waste management: The key is its ability to divert large volumes of non-recyclable plastic from landfills and convert them into value-added products, supporting a more circular economy.
- If your primary focus is creating diverse chemical feedstocks: The value lies in the pyrolysis oil, which can be refined and separated into various hydrocarbon fractions to create new plastics, solvents, and other industrial chemicals.
Ultimately, fast pyrolysis is a powerful technology for re-imagining plastic waste as a valuable resource.
Summary Table:
| Output | Description | Primary Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Pyrolysis Oil | Dark, viscous liquid hydrocarbon mixture | Industrial fuel; feedstock for refining into chemicals/transportation fuels |
| Syngas | Combustible gas mixture (hydrogen, methane, carbon monoxide) | Fuel to heat the pyrolysis reactor, creating energy self-sufficiency |
| Char | Solid, carbon-rich residue | Solid fuel; biochar for soil amendment; raw material for activated carbon |
Ready to transform your plastic waste management or material processing goals? KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory equipment and consumables for research and development in pyrolysis and other thermal processes. Whether you're optimizing pyrolysis conditions, analyzing outputs, or scaling up your technology, our precise and reliable solutions can help. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's needs and drive your innovation forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of industrial CVD for solid boriding? Superior Process Control and Material Integrity
- What function does CVD equipment serve in rhodium-modified coatings? Achieve Deep Diffusion and Microstructural Precision
- How high of temperature do carbon nanotubes in air have the ability to sustain? Understanding the Oxidation Limit
- What is a CVD tube furnace? A Complete Guide to Thin-Film Deposition
- Why are carbon nanotubes important in industry? Unlocking Next-Generation Material Performance



















