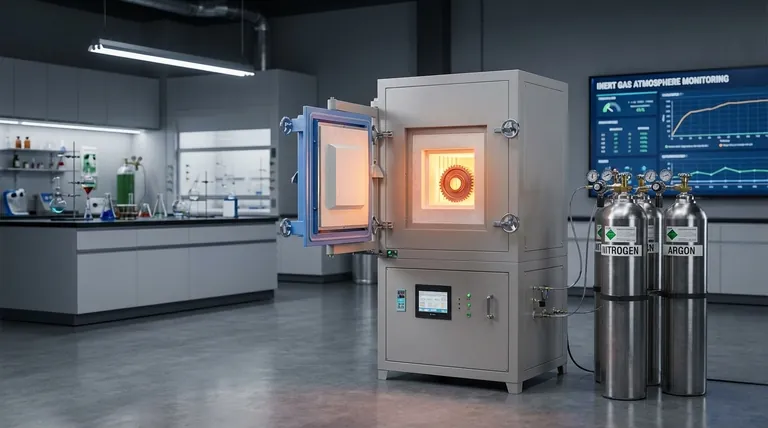
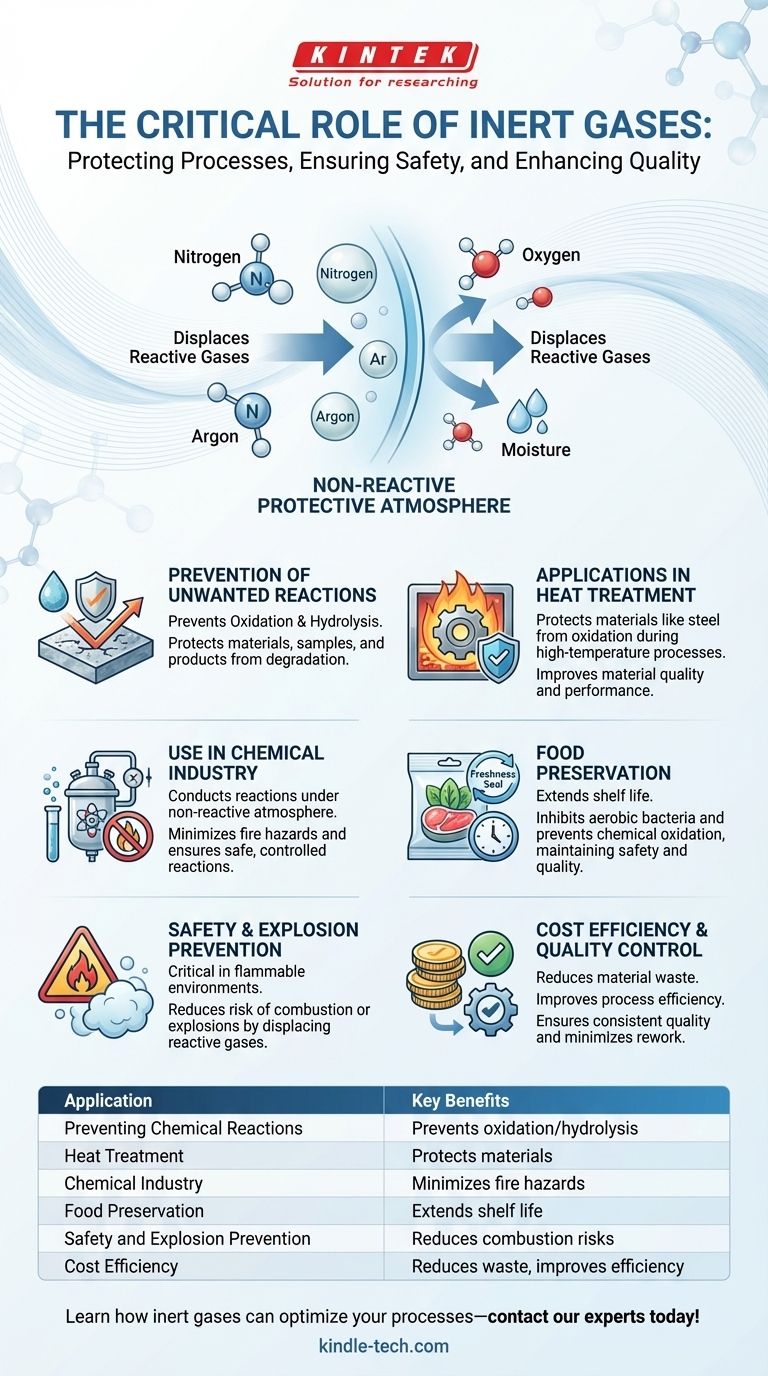
Inert gases play a critical role in various industries and applications due to their non-reactive properties. They are primarily used to prevent unwanted chemical reactions, such as oxidation and hydrolysis, which can degrade samples, materials, or products. Inert gases like nitrogen and argon are commonly employed to create protective atmospheres in processes like heat treatment, chemical reactions, and food packaging. Their ability to displace reactive gases like oxygen and moisture makes them essential for ensuring safety, quality, and preservation in industrial, chemical, and food-related applications.

Key Points Explained:
-
Prevention of Unwanted Chemical Reactions
- Inert gases are chemically non-reactive, meaning they do not readily form compounds with other elements or molecules.
- This property makes them ideal for preventing oxidation (reaction with oxygen) and hydrolysis (reaction with moisture), which can degrade materials, samples, or products.
- For example, in food packaging, inert gases like nitrogen are used to replace oxygen, preventing bacterial growth and chemical oxidation that could spoil the food.
-
Applications in Heat Treatment
- Inert gases are widely used in heat treatment processes to protect materials like steel from oxidation.
- Nitrogen and argon are commonly used to create a protective atmosphere in furnaces, ensuring that carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen do not react with the steel during high-temperature processes.
- This results in improved material quality and performance while reducing waste and costs.
-
Use in Chemical Industry
- Inert gases are essential in the chemical industry for conducting reactions under a non-reactive atmosphere.
- They help minimize fire hazards and prevent unwanted side reactions that could compromise product quality or safety.
- Additionally, inert gases are used to purge transfer lines and vessels, reducing the risk of explosions or fires caused by reactive gases.
-
Food Preservation
- Inert gases are used in food packaging to extend shelf life and maintain freshness.
- By replacing oxygen with inert gases like nitrogen or argon, the growth of aerobic bacteria is inhibited, and chemical oxidation is prevented.
- This ensures that the food remains safe and retains its quality for longer periods.
-
Safety and Explosion Prevention
- Inert gases are critical for safety in environments where flammable or reactive gases are present.
- By displacing oxygen or other reactive gases, inert gases reduce the risk of combustion or explosions.
- This is particularly important in industries like oil and gas, chemical manufacturing, and metalworking.
-
Cost Efficiency and Quality Control
- The use of inert gases in industrial processes often leads to cost savings by reducing material waste and improving process efficiency.
- For example, in heat treatment furnaces, the use of inert gases ensures consistent quality and reduces the need for rework or scrap.
- Advanced systems with precision controls and energy-efficient insulation further enhance these benefits.
In summary, inert gases are indispensable in a wide range of applications due to their ability to create stable, non-reactive environments. Their use ensures safety, preserves quality, and enhances efficiency across industries, making them a vital component in modern manufacturing and processing.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefits |
|---|---|
| Preventing Chemical Reactions | Prevents oxidation and hydrolysis, preserving materials and products. |
| Heat Treatment | Protects materials like steel from oxidation, improving quality and performance. |
| Chemical Industry | Minimizes fire hazards and ensures safe, controlled reactions. |
| Food Preservation | Extends shelf life by inhibiting bacterial growth and oxidation. |
| Safety and Explosion Prevention | Reduces combustion risks in flammable environments. |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduces waste, improves process efficiency, and ensures consistent quality. |
Learn how inert gases can optimize your processes—contact our experts today!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- High Performance Laboratory Freeze Dryer
People Also Ask
- What are the functions of nitrogen (N2) in controlled furnace atmospheres? Achieve Superior Heat Treatment Results
- Can nitrogen be used for brazing? Key Conditions and Applications Explained
- Why nitrogen is used in annealing furnace? To prevent oxidation and decarburization for superior metal quality
- What is an example of an inert atmosphere? Discover the Best Gas for Your Process
- How does a high-temperature furnace with atmosphere control optimize spinel coatings? Achieve Redox Sintering Precision
















