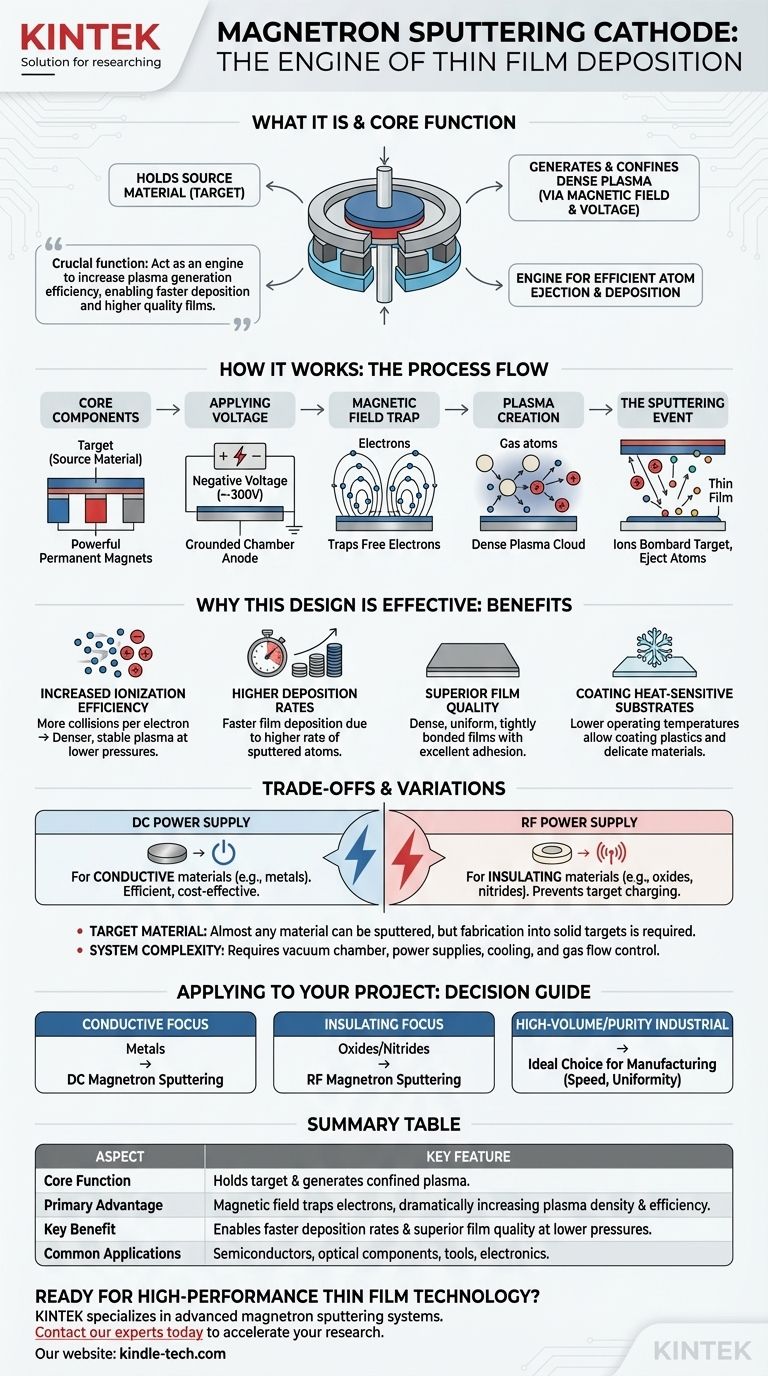
In short, a magnetron sputtering cathode is the central component in a vacuum deposition system that holds the source material (the "target") to be coated. It uses a powerful combination of a strong magnetic field and a high negative voltage. This arrangement creates and confines a dense plasma close to the target, which efficiently bombards the material and ejects atoms that then deposit as a thin film onto a substrate.
The critical function of a magnetron sputtering cathode is not just to hold the material, but to act as an engine for the entire process. By using a magnetic field to trap electrons, it dramatically increases the efficiency of plasma generation, enabling faster deposition rates and higher quality films at lower operating pressures.

How a Magnetron Sputtering Cathode Works
To understand magnetron sputtering, we must first understand the role of the cathode. It is a carefully engineered assembly that orchestrates an electric field, a magnetic field, and a source material to achieve a specific outcome.
The Core Components
The assembly consists of two primary parts working in unison. The target is a block of the pure material you wish to deposit (e.g., titanium, silicon, or an alloy). Behind this target sits a configuration of powerful permanent magnets.
Applying the Voltage
The entire cathode assembly, including the target, is electrically isolated and connected to a power supply. A strong negative voltage, typically around -300V, is applied to it. The vacuum chamber walls are typically grounded, acting as the anode.
The Role of the Magnetic Field
The magnets create a strong magnetic field with field lines that run parallel to the target's surface before arching away. This magnetic field acts as a trap for free electrons in the immediate vicinity of the target.
Creating the Plasma
As electrons are trapped in this magnetic field, they are forced to travel in long, spiral paths near the target surface instead of flying directly to the chamber walls. This dramatically increases the probability of them colliding with neutral gas atoms (like argon) introduced into the chamber.
These high-energy collisions knock electrons off the gas atoms, creating a dense cloud of positively charged gas ions and more free electrons. This self-sustaining cloud is the plasma.
The Sputtering Event
The newly created positive ions in the plasma are now strongly attracted to the negatively charged target. They accelerate towards the target, bombarding its surface with significant kinetic energy.
If the energy transferred by an ion is sufficient, it will physically knock out or "sputter" atoms from the target material. These sputtered atoms travel through the vacuum and deposit onto the substrate, building a thin film layer by layer.
Why This Design is So Effective
The genius of the magnetron cathode lies in its efficiency. The magnetic confinement of electrons is the key differentiator that elevates it above simpler diode sputtering methods.
Increased Ionization Efficiency
By trapping electrons, the magnetron ensures that each electron participates in many more ionizing collisions before it is lost. This creates a much denser and more stable plasma at significantly lower gas pressures.
Higher Deposition Rates
A denser plasma means there are more positive ions available to bombard the target. This directly translates to a higher rate of sputtered atoms, allowing for much faster film deposition, which is critical for industrial production.
Superior Film Quality
The high energy of the sputtered atoms helps them form a very dense, uniform, and tightly bonded film on the substrate. This results in coatings with excellent adhesion and durability.
Coating Heat-Sensitive Substrates
The high efficiency of the magnetron means less energy is wasted. The process can run at lower pressures, reducing the amount of gas-phase particle bombardment on the substrate. This keeps the substrate cooler, allowing for the coating of plastics and other heat-sensitive materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Variations
While incredibly powerful, the magnetron sputtering cathode is part of a system with specific requirements and variations that must be considered.
DC vs. RF Power
The choice of power supply is critical and depends entirely on the target material. A Direct Current (DC) power supply is used for conductive materials like metals. For insulating materials like ceramics, a Radio Frequency (RF) power supply is necessary to prevent a positive charge buildup on the target surface, which would otherwise stop the sputtering process.
Target Material and Geometry
The process is exceptionally versatile and can sputter almost any metal, alloy, or compound. However, the source material must first be fabricated into a solid target, which can sometimes be a challenge for brittle or complex materials.
System Complexity
A magnetron sputtering system is not a simple device. It requires a vacuum chamber, high-voltage power supplies, cooling systems for the cathode, and precise gas flow control, making it a significant investment in equipment and expertise.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your choice of magnetron sputtering setup is determined by the material you need to deposit and your production goals.
- If your primary focus is depositing conductive materials like metals: A DC magnetron sputtering system offers the most efficient and cost-effective solution for high-rate deposition.
- If your primary focus is depositing insulating materials like oxides or nitrides: An RF magnetron sputtering system is essential to overcome the technical challenge of target charging.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, high-purity industrial coating: The speed, uniformity, and excellent adhesion provided by magnetron sputtering make it an ideal choice for manufacturing.
Ultimately, the magnetron sputtering cathode is a precisely engineered tool designed to control plasma at the atomic level, enabling the creation of advanced materials and high-performance surfaces.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Feature |
|---|---|
| Core Function | Holds the target material and generates a confined plasma for sputtering. |
| Primary Advantage | Magnetic field traps electrons, dramatically increasing plasma density and efficiency. |
| Key Benefit | Enables faster deposition rates and superior film quality at lower pressures. |
| Common Applications | Coating semiconductors, optical components, tools, and consumer electronics. |
Ready to integrate high-performance thin film technology into your lab?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including magnetron sputtering systems designed for precision and reliability. Whether you are developing new materials or scaling up production, our expertise ensures you get the right solution for depositing conductive or insulating films with excellent adhesion and uniformity.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project requirements and discover how KINTEK's sputtering solutions can accelerate your research and development.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- Advanced Engineering Fine Ceramics Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Parts
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Battery Lab Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of plasma enhanced CVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma enhanced? A Guide to Low-Temperature, High-Precision Manufacturing
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma activated chemical vapor deposition? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition


















