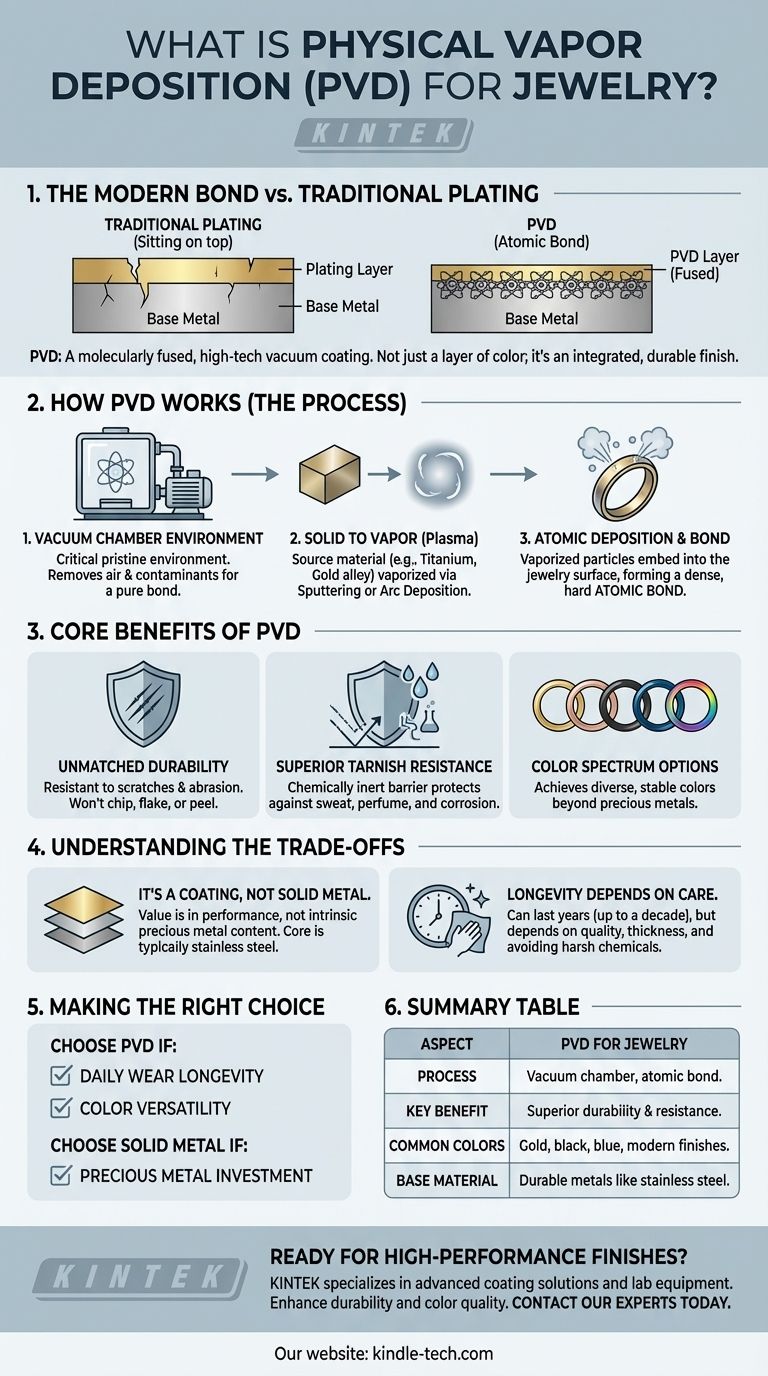
In the world of modern jewelry, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a high-tech vacuum coating process used to apply a durable, decorative finish onto a base metal. Unlike traditional plating, PVD physically bonds a thin layer of metal or alloy to the jewelry's surface at an atomic level, resulting in a finish that is significantly more resistant to scratches, fading, and tarnishing.
PVD is not simply a layer of color sitting on top of your jewelry; it is a micro-thin ceramic or metallic layer that has been molecularly fused to the base material. This fundamental difference is the source of its superior durability and color stability compared to conventional plating methods.

How PVD Actually Works
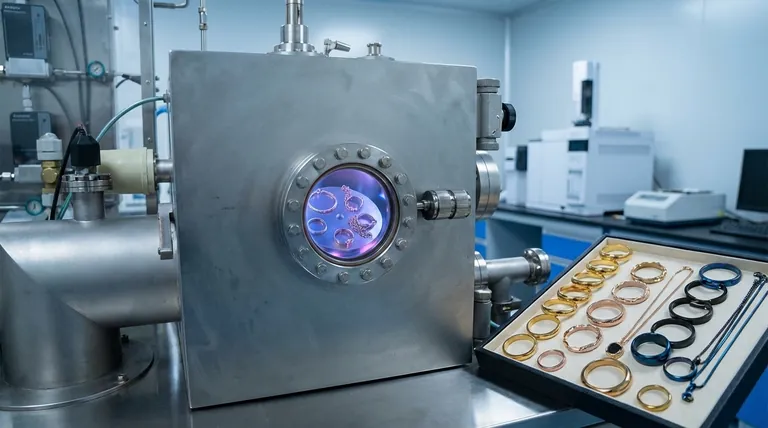
To understand why PVD is different, you must understand the process. It is a sophisticated technique conducted inside a high-vacuum chamber, which is critical for ensuring a pure and powerful bond.
The Vacuum Chamber Environment
The entire PVD process takes place in a vacuum. This is crucial because it removes all air and water vapor, eliminating any particles that could contaminate the surface of the jewelry or interfere with the coating process. This pristine environment ensures a perfect bond.
From Solid to Vapor
Inside the chamber, a solid source material—such as titanium, zirconium, or a gold alloy—is vaporized into a plasma of atoms or molecules. This is typically achieved through methods like sputtering, where the material is bombarded with high-energy ions, or cathodic-arc deposition, which uses an electric arc to evaporate the material.
The Atomic Bond
This cloud of vaporized metal is then deposited onto the jewelry, which is placed in the chamber. Due to the high energy and vacuum environment, the vaporized particles don't just coat the surface; they embed into it, forming a strong, atomic bond with the base metal (often stainless steel). This bonded layer is incredibly dense and hard.
The Core Benefits of PVD for Jewelry
The unique nature of the PVD process translates directly into tangible benefits for the wearer. The result is fashion jewelry that performs more like a high-end tool.
Unmatched Durability
Because the coating is molecularly bonded to the base metal, it does not chip, flake, or peel away like traditional plating. This makes PVD-coated jewelry exceptionally resistant to scratches and abrasion from daily wear.
Superior Tarnish and Corrosion Resistance
The PVD layer creates a chemically inert barrier on the surface of the jewelry. This barrier protects the base metal from the effects of sweat, perfume, and air, making it highly resistant to the tarnishing and corrosion that plague many other types of jewelry.
A Spectrum of Color Options
PVD allows for the creation of a wide array of colors that are difficult or impossible to achieve with precious metals alone. Finishes can range from convincing gold and rose gold tones to modern blacks, blues, coffee tones, and even iridescent rainbow effects.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While PVD offers significant advantages, it is essential to understand its context and limitations to make an informed decision.
It's a Coating, Not Solid Metal
The primary trade-off is that PVD jewelry is not made of a solid precious material. The core is typically a durable and hypoallergenic metal like stainless steel, with the PVD layer providing the color and enhanced protection. Its value is in performance, not in its intrinsic metal content.
Longevity Depends on Quality and Care
While a well-applied PVD coating can last for many years—sometimes up to a decade—its lifespan is not infinite. Longevity depends on the thickness of the coating, the quality of the application process, and how the jewelry is cared for. Exposure to harsh chemicals or consistent, heavy abrasion can still wear down the finish over time.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
PVD technology empowers you to select jewelry based on your specific priorities.
- If your primary focus is longevity for daily wear: PVD-coated stainless steel jewelry offers the best durability and resistance to wear and tear in its price class.
- If your primary focus is color versatility: PVD provides access to a stable and durable palette of modern colors like black, blue, and rich golds that traditional methods cannot replicate.
- If your primary focus is precious metal investment: You should still choose solid gold or platinum, as the value of PVD jewelry lies in its technological performance, not its material wealth.
Ultimately, understanding PVD allows you to appreciate and choose modern jewelry for its advanced performance and aesthetic possibilities.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | PVD for Jewelry |
|---|---|
| Process | Vacuum chamber vaporizes metal, forming an atomic bond with the base material. |
| Key Benefit | Superior durability and resistance to scratches, tarnish, and fading. |
| Common Colors | Gold, rose gold, black, blue, and other stable, modern finishes. |
| Base Material | Typically applied to durable metals like stainless steel. |
Ready to explore durable, high-performance finishes for your jewelry line? KINTEK specializes in advanced coating solutions and lab equipment. Whether you're developing new products or enhancing quality control, our expertise can help you achieve superior durability and vibrant colors. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory and production needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- What is the process of PECVD in semiconductor? Enabling Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- Why does a PECVD vacuum system require both a rotary vane and turbo pump? Ensure High-Purity Coatings
- What are the process capabilities of ICPCVD systems? Achieve Low-Damage Film Deposition at Ultra-Low Temperatures
- Can plasma enhanced CVD deposit metals? Why PECVD is rarely used for metal deposition
- Why is a Matching Network Indispensable in RF-PECVD for Siloxane Films? Ensure Stable Plasma and Uniform Deposition



















