In the world of watches, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a high-tech vacuum coating process that molecularly bonds a thin film of hard material onto the watch's steel components. This technique is used to impart both a durable, protective layer and a specific color—such as black, gold, or gunmetal—to the watch case, bracelet, and crown.
The crucial takeaway is that PVD is not a paint or a simple plating. It is an advanced process that integrates a new, harder surface into the original metal, offering significantly more resistance to wear and corrosion than traditional coating methods.
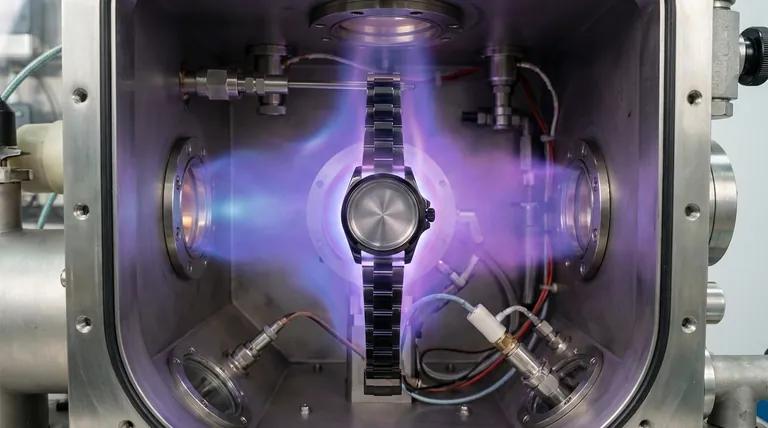
How PVD Transforms a Watch's Surface
To understand why PVD is so widely used, it's helpful to look at both the process and the result. It fundamentally changes the character and resilience of a watch's exterior.
The Core Principle: From Solid to Vapor
The PVD process takes place in a high-vacuum chamber. A solid source material, often a durable ceramic like titanium nitride, is vaporized into a plasma.
This vaporized material is then deposited, atom by atom, onto the watch components. It forms a new, thin, and extremely dense surface layer that is molecularly bonded to the base metal underneath.
The Functional Benefit: Durability and Resistance
The primary functional advantage of PVD is hardness. The resulting coating is highly resistant to scratches from daily wear.
This technique is borrowed from other industries where it's used to create hard, corrosion-resistant coatings for high-performance tools and aerospace components. For a watch, this translates to superior protection against scuffs, sweat, and environmental exposure.
The Aesthetic Benefit: A Spectrum of Color
PVD allows manufacturers to achieve a wide range of consistent and durable colors that would otherwise be impossible.
From matte black "stealth" looks to rich gold tones and modern gunmetal greys, PVD provides a stable and long-lasting finish that won't easily chip or fade.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While PVD offers significant advantages, it is not an invincible solution. Objectivity requires acknowledging its limitations.
Scratch-Resistant, Not Scratch-Proof
A PVD coating dramatically increases surface hardness, but it is not invulnerable. A sufficiently hard or sharp impact can create a deep gouge that penetrates the coating.
When a PVD watch does get a deep scratch, the silver-colored stainless steel underneath will be exposed, which can be more noticeable than a scratch on a uniform steel surface.
The Challenge of Refinishing
Unlike a standard stainless steel watch that can be polished to remove scratches, a PVD-coated surface cannot be spot-repaired.
Fixing a deep scratch would require the entire component to be stripped and professionally recoated, a complex and often costly process that may not be offered by the original manufacturer.
PVD vs. Traditional Plating
It is critical to distinguish PVD from older, less durable methods like electroplating. Plating applies a thicker, softer layer of metal that is prone to chipping, flaking, and wearing away over time.
PVD, by contrast, is a molecular bond. The coating doesn't flake off and its thinness ensures that the fine details and sharp edges of the watch design are preserved perfectly.
Making the Right Choice for Your Watch
Your ideal watch finish depends entirely on your priorities for aesthetics and long-term wear.
- If your primary focus is a classic look that can be easily maintained: A traditional, uncoated stainless steel watch is the best choice, as scratches can be polished out over its lifetime.
- If your primary focus is a specific color or a modern, tactical aesthetic: PVD is the premier technology for achieving a durable, long-lasting colored finish that resists daily wear far better than any alternative.
- If your primary focus is maximum scratch resistance above all else: Seek out watches with advanced PVD coatings like DLC (Diamond-Like Carbon), which offers one of the hardest surfaces available.
Ultimately, choosing a PVD-coated watch is a decision to prioritize a specific, resilient aesthetic over the refinishing capabilities of bare metal.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | PVD Coating | Traditional Plating |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | Extremely hard, scratch-resistant | Softer, prone to chipping/flaking |
| Process | Molecular bond in a vacuum chamber | Electrochemical deposition |
| Appearance | Consistent, long-lasting colors | Can wear away or fade over time |
| Maintenance | Difficult to refinish; requires recoating | Can be polished, but may wear thin |
Ready to enhance your laboratory's capabilities with precision equipment?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, serving the exacting needs of modern laboratories. Whether you require advanced coating technologies or other precision tools, our solutions are designed for durability, accuracy, and reliability.
Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific laboratory requirements and help you achieve superior results.
Visual Guide

Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- What is the process of PECVD in semiconductor? Enabling Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the process capabilities of ICPCVD systems? Achieve Low-Damage Film Deposition at Ultra-Low Temperatures
- Why does a PECVD vacuum system require both a rotary vane and turbo pump? Ensure High-Purity Coatings
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- How do PECVD systems improve DLC coatings on implants? Superior Durability and Biocompatibility Explained



















