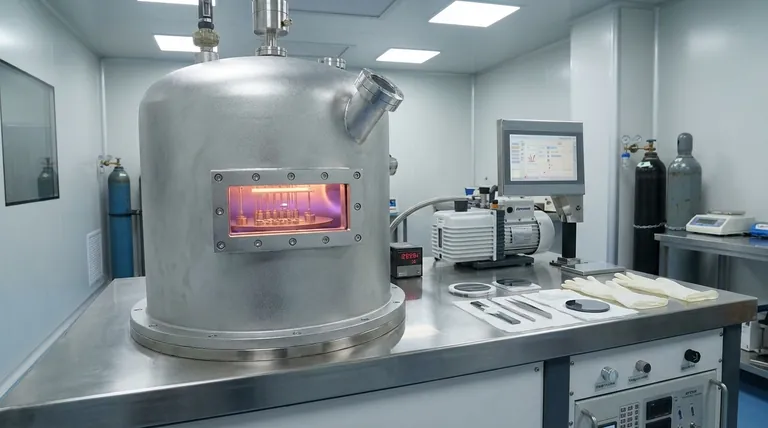
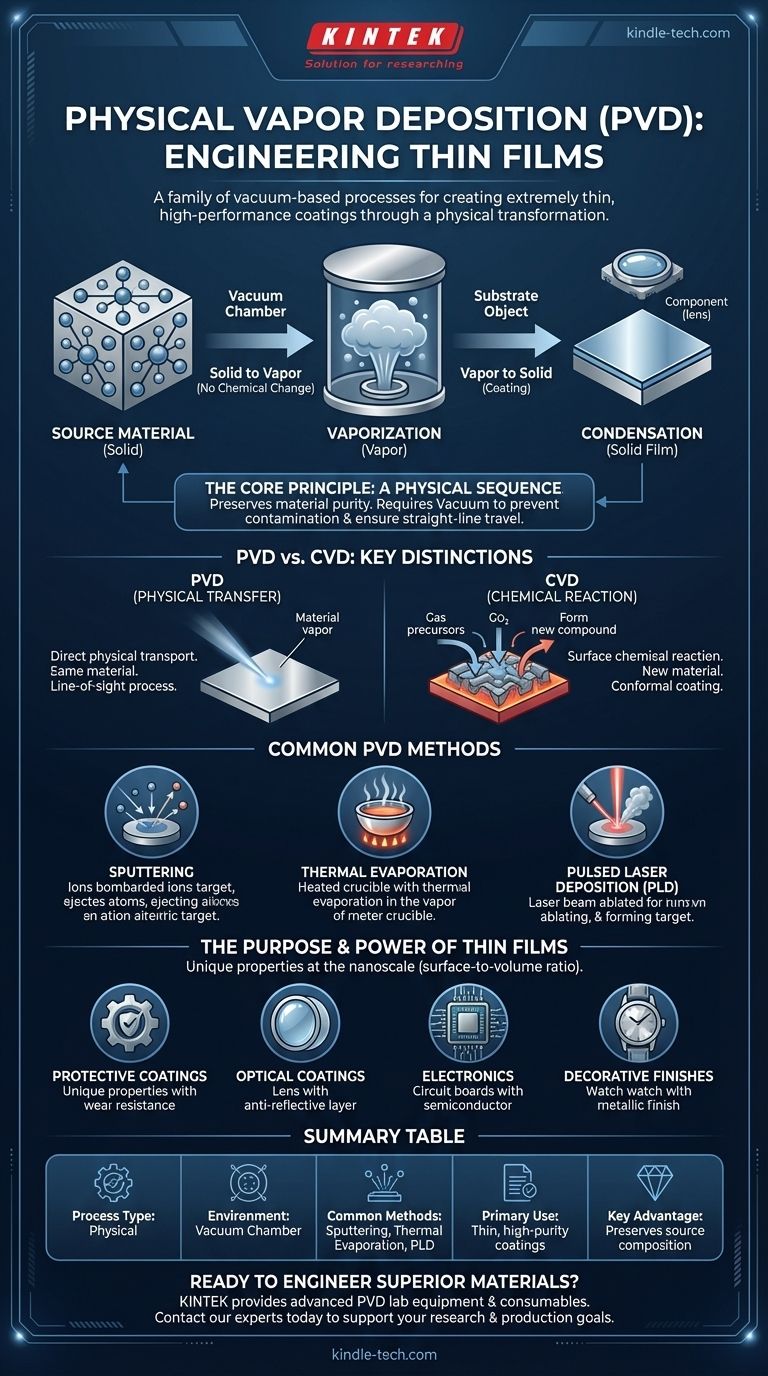
In essence, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a family of vacuum-based processes used to create extremely thin films of material. It works by taking a solid source material, vaporizing it into individual atoms or molecules inside a vacuum chamber, and then allowing this vapor to travel and condense onto a target object, known as a substrate, forming a solid, high-performance coating.
The core principle of PVD is a physical transformation, not a chemical one. Think of it like boiling water to create steam (vapor) and then letting that steam condense back into a layer of water on a cold surface—the material itself never changes its chemical identity.

The Fundamental Principle: From Solid to Vapor to Solid
PVD processes are a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, enabling the creation of materials with unique properties simply by reducing them to atomic-scale layers. The entire process hinges on a simple, three-step physical sequence.
What "Physical" Means in PVD
The term "physical" is critical. It distinguishes this method from processes that rely on chemical reactions. In PVD, the material being deposited starts as a solid, is converted into a gas, and then deposits as a solid again, all without undergoing a chemical change.
This direct transfer preserves the purity and composition of the source material, which is crucial for many high-tech applications.
The Critical Role of the Vacuum
PVD is always performed in a vacuum chamber. This controlled environment is essential for two reasons.
First, removing air and other gases prevents the vaporized material from reacting with contaminants like oxygen or nitrogen. Second, the vacuum ensures the vaporized atoms can travel in a straight line from the source to the substrate without colliding with other particles.
Common PVD Methods
While the principle is the same, the method of vaporizing the source material can differ. The references mention several key physical methods that fall under the PVD umbrella:
- Sputtering: High-energy ions are used to bombard the source material, knocking atoms off its surface.
- Thermal Evaporation: The source material is heated in the vacuum until it evaporates or sublimes.
- Pulsed Laser Deposition (PLD): A high-power laser ablates the surface of the source material, creating a vapor plume.
PVD vs. Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): A Key Distinction
To fully understand PVD, it is helpful to contrast it with its chemical counterpart, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). While both create thin films, their underlying mechanisms are fundamentally different.
PVD: A Physical Transfer
As established, PVD physically transports material from a source to a substrate. It's a line-of-sight process where the final film is composed of the exact same material as the source.
CVD: A Surface Chemical Reaction
CVD, by contrast, introduces precursor gases into a chamber. These gases react on the hot surface of the substrate, and the solid product of that chemical reaction is what forms the thin film. The film material is therefore entirely different from the initial gases.
The Purpose and Power of Thin Films
The goal of PVD and other deposition techniques is to create thin films, which are layers of material ranging from a few nanometers to several micrometers thick. At this scale, materials exhibit unique properties not found in their bulk form.
New Properties at the Nanoscale
This is due to the dramatic change in the surface-to-volume ratio. With more atoms at the surface, properties like electrical conductivity, optical reflectivity, and mechanical hardness can be precisely engineered.
A Broad Spectrum of Applications
This ability to engineer material properties has led to widespread industrial use. Thin films are critical for:
- Protective Coatings: Improving resistance to wear, corrosion, and high temperatures on tools and aerospace components.
- Optical Coatings: Creating anti-reflective layers on eyeglass lenses, mirrors, and architectural glass for thermal insulation.
- Electronics: Manufacturing semiconductors, solar cells, and touch-panel displays.
- Decorative Finishes: Applying durable and attractive metallic layers on items from jewelry to bathroom fixtures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a deposition method depends entirely on the desired properties of the final film, the material being used, and production factors like cost and efficiency.
- If your primary focus is depositing pure materials or complex alloys without changing their composition: PVD is often the superior choice due to its direct physical transfer mechanism.
- If your primary focus is creating a conformal coating on a complex, non-flat surface: A gas-based process like CVD may be more effective as the gases can reach all surfaces to react.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature or extremely hard coatings like diamond-like carbon: CVD is a common and highly effective method for producing these specific materials.
Understanding the fundamental difference between physical and chemical deposition empowers you to select the right tool for engineering the next generation of materials.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process Type | Physical (no chemical change) |
| Environment | Vacuum Chamber |
| Common Methods | Sputtering, Thermal Evaporation, Pulsed Laser Deposition |
| Primary Use | Creating thin, high-purity coatings |
| Key Advantage | Preserves source material composition |
Ready to engineer superior materials with high-purity thin films? KINTEK specializes in providing advanced PVD lab equipment and consumables to meet your research and production needs. Whether you're developing protective coatings, optical layers, or electronic components, our solutions ensure precision and reliability. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific challenges and goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
People Also Ask
- What is the role of the HF-CVD system in preparing BDD electrodes? Scalable Solutions for Boron-Doped Diamond Production
- How are reactants introduced into the reaction chamber during a CVD process? Mastering Precursor Delivery Systems
- What is microwave plasma CVD? A Guide to High-Purity Diamond and Material Synthesis
- How does a Hot Filament Chemical Vapor Deposition (HFCVD) reactor function? Expert Guide to Diamond Film Fabrication
- How is something diamond coated? A Guide to CVD Growth vs. Plating Methods



















