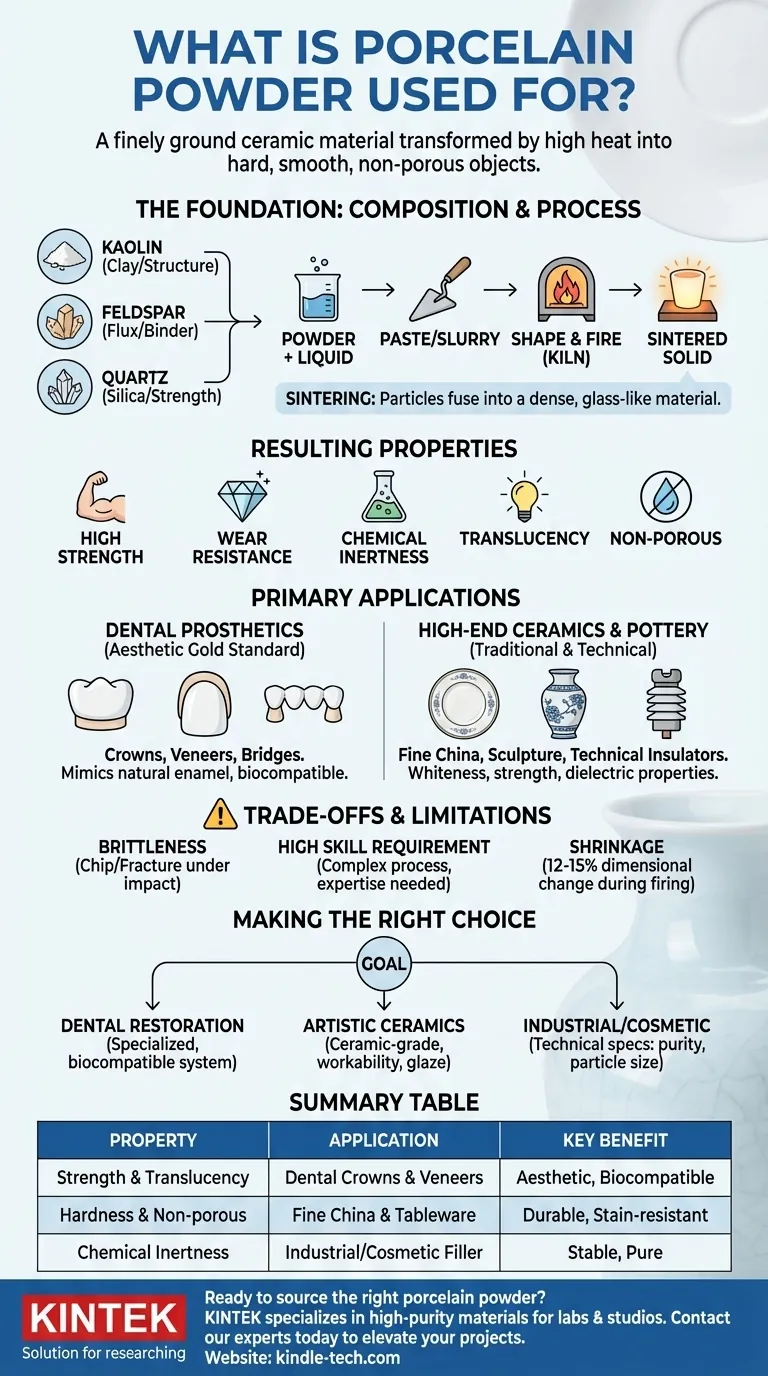
At its core, porcelain powder is a finely ground ceramic material used to create hard, smooth, and non-porous objects after being fired at high temperatures. Its primary applications are in the creation of high-end ceramics like fine china, durable and aesthetic dental restorations such as crowns and veneers, and as a specialized functional filler in cosmetics and industrial products.
The term "porcelain powder" is not monolithic; it describes a range of formulations tailored for specific tasks. The powder's ultimate use is dictated by its precise composition, particle size, and purity, determining whether it's destined for a dental lab, an artist's studio, or an industrial plant.

The Foundation: From Powder to Solid Form
To understand its uses, you must first understand what porcelain powder is and how it works. It is not used as a powder in its final state but as a raw material for a transformation process.
Core Components and Their Roles
Porcelain is traditionally a composite of three key minerals.
- Kaolin: A pure clay that provides plasticity and structure, making the powder workable when mixed with a liquid.
- Feldspar: This acts as a flux, melting at high temperatures to form a glass matrix that binds the other components.
- Quartz (Silica): This provides structural strength and helps the final object maintain its shape during firing.
The Sintering Process
Porcelain powder is mixed with a liquid (often distilled water or a special modeling liquid) to form a paste or slurry. This paste is then shaped, dried, and fired in a kiln. During firing, the feldspar melts and fuses the particles together in a process called sintering, creating a dense, vitrified, and glass-like final material.
Resulting Material Properties
The final sintered porcelain is prized for a unique combination of properties: high strength, excellent wear resistance, chemical inertness, and a characteristic translucency. It is also non-porous, making it highly resistant to staining.
Primary Applications: A Tale of Two Industries
While porcelain has niche uses, its reputation is built on its dominance in two distinct fields: dentistry and high-end ceramics.
Dental Prosthetics: The Aesthetic Gold Standard
In dentistry, porcelain powder is the cornerstone of cosmetic and restorative work. It is used to create crowns, bridges, veneers, and inlays/onlays that are both strong and lifelike.
The material's translucency mimics the appearance of natural tooth enamel better than any other material. Dental-grade porcelain is formulated for biocompatibility and is layered in different shades and opacities to perfectly match a patient's existing teeth before being fired.
High-End Ceramics and Pottery
This is porcelain's most traditional application. Artists and manufacturers use it to create fine china, decorative sculptures, and durable tableware. The formulation for "hard-paste" porcelain results in a final product known for its whiteness, strength, and resonance.
Beyond art, specific porcelain formulations are used to create technical ceramics, such as electrical insulators, due to their excellent dielectric properties and resistance to high voltage.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
Porcelain's strengths are significant, but it is not without its challenges. Understanding these is critical for its successful application.
Brittleness Under Impact
While very hard and resistant to wear, porcelain can be brittle. In dentistry, this means a porcelain crown can chip or fracture under sudden, sharp impact or extreme bite forces, though modern formulations have greatly improved toughness.
High Technical Skill Requirement
Working with porcelain powder is a craft that demands expertise. Achieving correct consistency, preventing air bubbles, accurately compensating for shrinkage, and managing complex firing schedules requires significant training and experience, particularly in dental applications.
Shrinkage During Firing
All porcelain bodies shrink as they are fired, typically between 12% and 15%. This dimensional change is a critical factor that must be precisely calculated and accounted for during the initial shaping of the object, whether it's a dental crown or a ceramic vessel.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The specific type of porcelain powder you choose must be directly aligned with your end goal, as the formulations are not interchangeable.
- If your primary focus is dental restoration: You must use a specialized, biocompatible dental-grade porcelain powder system with matched shades and liquids.
- If your primary focus is artistic ceramics: You need a ceramic-grade body formulated for your desired workability, firing temperature (cone), and glaze compatibility.
- If your primary focus is cosmetic or industrial formulation: Your selection will be based on technical specifications like particle size distribution, purity, and inertness, not its firing properties.
Ultimately, mastering the use of porcelain begins with selecting the powder engineered for your specific outcome.
Summary Table:
| Property | Application | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Strength & Translucency | Dental Crowns & Veneers | Aesthetic, Biocompatible |
| Hardness & Non-porous | Fine China & Tableware | Durable, Stain-resistant |
| Chemical Inertness | Industrial/Cosmetic Filler | Stable, Pure |
Ready to source the right porcelain powder for your lab's needs? KINTEK specializes in high-purity materials and equipment for dental labs, ceramics studios, and R&D facilities. Our experts can help you select the perfect powder for your application, ensuring optimal results for your crowns, restorations, or technical ceramics. Contact our team today to discuss your specific requirements and elevate your projects with KINTEK's trusted solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Tube
- High Temperature Resistant Optical Quartz Glass Sheet
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Hollow Etching Flower Basket ITO FTO Developing Glue Removal
People Also Ask
- What kind of solid is SiC? Unlocking the Secrets of Its Covalent Network Structure
- What is the strength of sintered ceramics? Achieve Maximum Density and Durability
- How high temperature can ceramic withstand? A Guide to Extreme Heat Performance
- What role does a carbon template play in nanocasting magnesium oxide? Master Porous Material Precision
- How do alumina ceramic tubes address technical challenges in electrochemical devices? Ensure Peak Signal Integrity.
- What catalytic effects do alumina ceramic surfaces have on biomass gasification? Boost Syngas Heating Value
- What is the new technology for veneers? Discover the Digital Revolution for a Perfect Smile
- What are the process advantages of selecting an alumina plate for CuO nanofilm synthesis? Achieve Superior Purity







