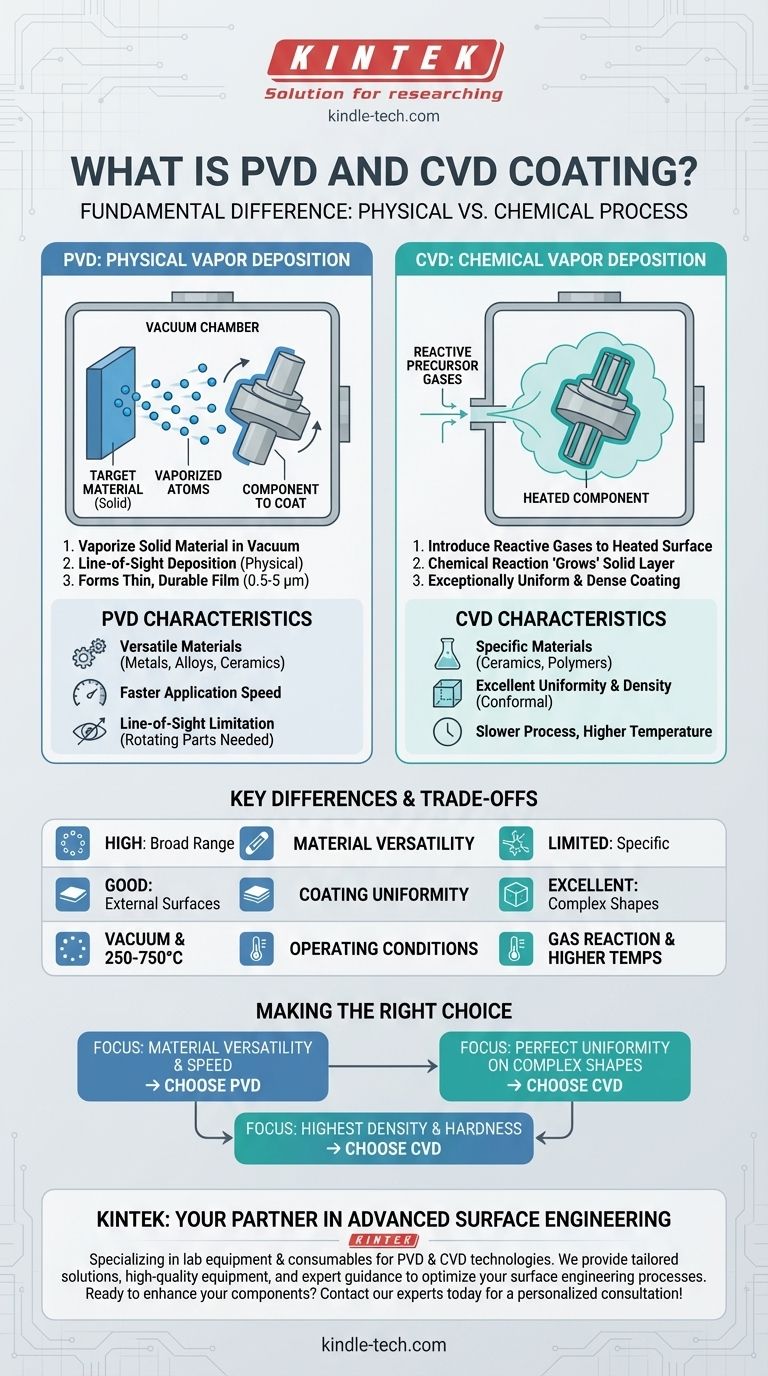
Fundamentally, the difference between PVD and CVD lies in how the coating is created. Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a physical process that takes a solid material, vaporizes it in a vacuum, and deposits it atom by atom onto a surface. In contrast, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a chemical process where precursor gases react on a heated surface to "grow" a new, solid layer.
Your choice between PVD and CVD is not about which is universally "better," but which process aligns with your material requirements and the geometry of your part. PVD physically plates a surface with a wide range of materials, while CVD chemically grows a highly uniform layer ideal for complex shapes.

The Core Distinction: Physical vs. Chemical Process
To select the right coating, you must first understand the fundamental difference in how they are applied. This core mechanism dictates the properties, advantages, and limitations of the final product.
How PVD Works: The Physical Approach
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a line-of-sight process performed in a high-vacuum chamber. It is best visualized as a type of high-tech spray painting with atoms.
The solid coating material, known as the target, is vaporized using methods like sputtering or evaporation. This creates a vapor of atoms that travel at high speed across the vacuum chamber.
These atoms physically embed themselves onto the component being coated, forming a very thin (0.5 – 5 μm) but durable film. Because it is a line-of-sight process, parts often need to be carefully rotated to ensure even coverage.
How CVD Works: The Chemical Approach
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) does not use a solid target. Instead, it introduces specific reactive gases into a chamber containing the heated component.
When these gases come into contact with the hot surface, a chemical reaction is triggered. This reaction causes a new, solid material to form and deposit directly onto the component's surface.
This method "grows" the coating on the part. Because the gas can penetrate all exposed areas, CVD is not limited by line-of-sight, resulting in an exceptionally uniform layer even on complex geometries.
Key Differences in Application and Outcome
The distinction between a physical and chemical process leads to significant differences in material compatibility, coating properties, and operating conditions.
Material Compatibility
PVD is highly versatile and can deposit a broad range of materials. This includes pure metals, alloys, and various ceramics.
CVD is typically more limited in its material selection, excelling at depositing specific ceramics and polymers.
Coating Properties and Uniformity
CVD coatings are known for being extremely dense and highly uniform. The chemical growth process ensures that all surfaces, including internal channels and complex angles, receive an even coating.
PVD coatings can be slightly less dense and uniform by comparison. However, the process is generally faster to apply than CVD.
Operating Environment
The PVD process must be performed at high temperatures, typically ranging from 250°C to 750°C in a vacuum.
Reactive gases like nitrogen or oxygen can be introduced during the PVD process. This allows for the creation of specific compound coatings with tailored structural and performance properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither method is a perfect solution for every scenario. Understanding their inherent limitations is critical for making an informed decision.
PVD: Versatility vs. Line-of-Sight
The primary strength of PVD is its versatility with different materials and its application speed. This makes it a go-to choice for many applications requiring wear resistance, corrosion protection, or specific aesthetic finishes.
Its main limitation is the line-of-sight nature of the deposition. Coating complex internal surfaces or intricate geometries can be challenging and may result in uneven thickness. PVD is also often considered more environmentally friendly than traditional CVD processes.
CVD: Conformity vs. Complexity
CVD's greatest advantage is its ability to create a perfectly uniform, or "conformal," coating on parts of any complexity. This makes it ideal for components where even, dense coverage is a non-negotiable requirement.
The trade-offs are a slower deposition time and a more limited palette of applicable materials. The chemical process itself can also be more complex to manage than PVD.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific application and desired outcome should dictate your choice between these two powerful technologies.
- If your primary focus is material versatility and speed: PVD is the logical choice, offering a broad range of coatings for metals, alloys, and ceramics.
- If your primary focus is perfect uniformity on complex shapes: CVD's ability to "grow" a coating from gas makes it superior for intricate geometries and internal surfaces.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible density and hardness: The dense, non-porous layers from CVD often provide a performance advantage for applications demanding extreme wear resistance.
By understanding the fundamental process behind each method, you can confidently select the coating that delivers the precise performance your components require.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) | CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) |
|---|---|---|
| Process Type | Physical (line-of-sight) | Chemical (gas reaction) |
| Coating Uniformity | Good on external surfaces | Excellent, even on complex shapes |
| Material Versatility | High (metals, alloys, ceramics) | Limited (specific ceramics, polymers) |
| Operating Temperature | 250°C - 750°C | Higher temperatures typically required |
| Best For | Material versatility, speed | Complex geometries, extreme density |
Ready to enhance your components with the right coating technology?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced lab equipment and consumables for surface engineering applications. Whether you're developing new materials or optimizing production processes, our expertise in PVD and CVD technologies can help you achieve superior performance, durability, and precision.
We provide:
- Tailored solutions for your specific coating requirements
- High-quality equipment for research and production
- Expert guidance on deposition method selection
Let's discuss how our solutions can benefit your laboratory or manufacturing process. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between thermal CVD and PECVD? Choose the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- What are the examples of CVD method? Discover the Versatile Applications of Chemical Vapor Deposition
- What is the difference between CVD and PECVD? Choose the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- What are the advantages of PECVD over CVD? Achieve High-Quality Thin Films at Lower Temperatures
- What is the precursor gas in PECVD? The Key to Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















