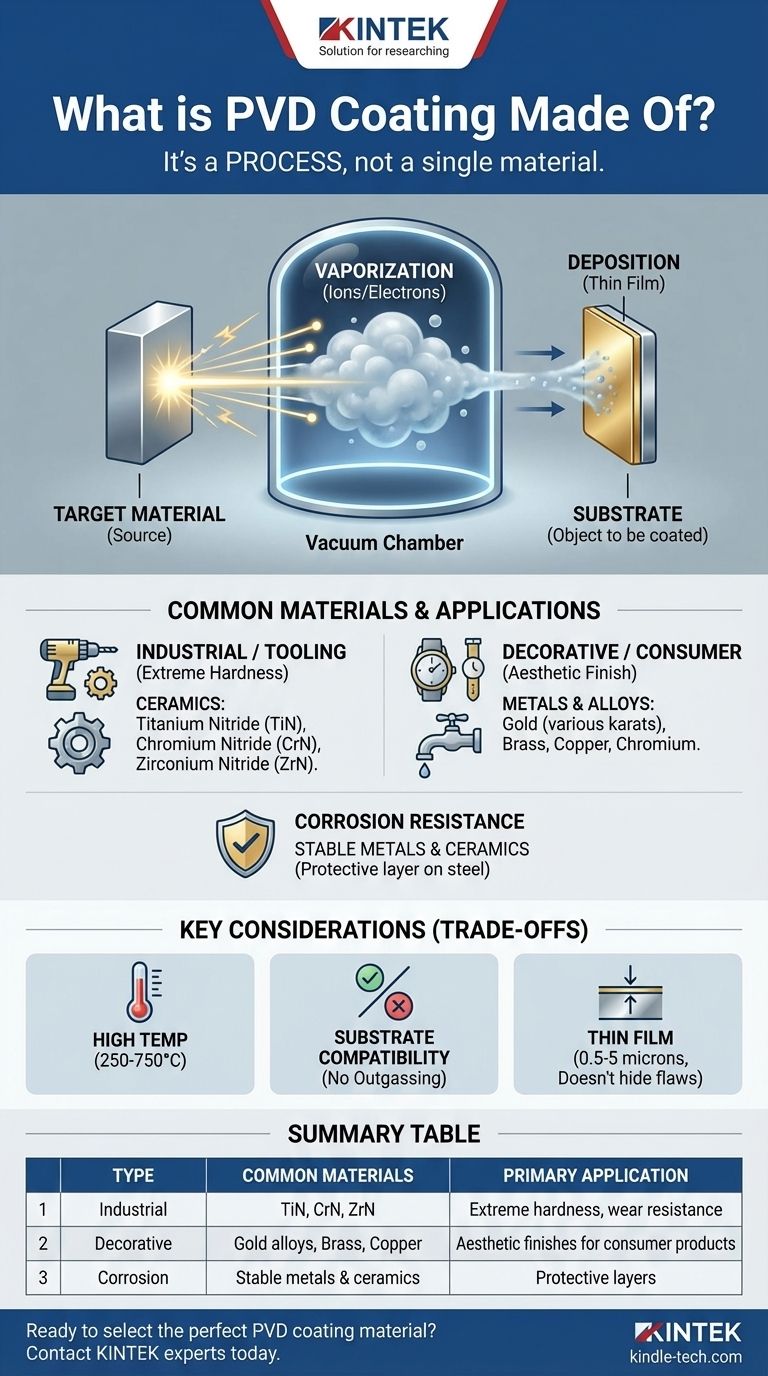
Crucially, PVD coating is not made of a single substance. It is a thin film composed of the specific material—or combination of materials—that is vaporized and deposited onto a product's surface. Common PVD coating materials range from industrial ceramics like Titanium Nitride (TiN) for durable tools to precious metals like gold for decorative finishes.
The most important concept to grasp is that PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) is a process, not a material. The final coating is made of whichever solid material is chosen as the "target" to be vaporized and bonded to the product's surface in a high-tech vacuum chamber.

How the Process Defines the Material
The composition of a PVD coating is a direct result of the deposition method. Understanding this process makes it clear why there is no single answer to what the coating is "made of."
The Role of the "Target" Material
The entire process begins with a solid source material, known as the target. This target is the raw ingredient for the coating.
The target is placed inside a vacuum chamber along with the object to be coated (the substrate).
Vaporization and Deposition
High-energy ions or electrons bombard the target, dislodging atoms and vaporizing them. This material vapor then travels through the vacuum chamber and condenses onto the substrate.
This action forms a very thin, tightly bonded film on the object's surface. The coating is, quite literally, made of the condensed target material.
A Molecular Bond, Not Paint
Unlike traditional plating or painting, PVD changes the properties of the metal on a molecular level.
The result is an extremely durable finish that is highly resistant to corrosion and oxidation, even though it may only be 0.5 to 5 microns thick.
Common Materials Used for PVD Coatings
The choice of target material is dictated by the desired outcome, whether it's extreme hardness, a specific color, or chemical resistance.
For Industrial and Tooling Applications
For applications requiring extreme hardness and wear resistance, such as drill bits or industrial components, ceramic materials are used.
The most common example is Titanium Nitride (TiN), which significantly increases the endurance and fatigue limit of the underlying metal. Other popular choices include Chromium Nitride (CrN) and Zirconium Nitride (ZrN).
For Decorative and Consumer Finishes
When appearance is the primary goal, metals and their alloys are used as the target material.
For "gold PVD," the coating can be made of brass, copper, or even real gold in various karats (9k, 18k, 24k). These coatings are frequently applied to stainless steel for products like watches, jewelry, and fixtures.
The Importance of the Substrate
The final performance also depends heavily on the substrate—the material being coated.
PVD works exceptionally well on all steel families, non-ferrous metals like copper and aluminum, and hard metals. The coating imparts surface properties, but the substrate provides the structural integrity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the PVD process has specific requirements and limitations that dictate its use.
High-Temperature Requirement
PVD is a high-temperature process, typically performed between 250°C and 750°C. This means the substrate material must be able to withstand these temperatures without deforming or degrading.
Not All Materials Can Be Coated
Because the process occurs in a high vacuum, certain materials that "outgas" (release vapors) are unsuitable.
For example, brass without a proper galvanic layer and most galvanized materials cannot be coated effectively with PVD.
A Thin-Film Solution
The PVD coating is exceptionally thin. While it creates a hard and resistant surface, it will not hide or correct underlying imperfections, scratches, or structural flaws in the base material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The material of a PVD coating is always chosen to achieve a specific engineering or aesthetic goal.
- If your primary focus is extreme durability and wear resistance: Opt for ceramic-based PVD coatings like Titanium Nitride (TiN) to create an exceptionally hard surface on tools and components.
- If your primary focus is a specific decorative color: Choose a metallic PVD target, such as a gold alloy, brass, or chromium, to achieve the desired visual finish for consumer products.
- If your primary focus is corrosion resistance: PVD is an excellent choice for applying a stable, non-reactive surface layer, particularly onto a base material like stainless steel.
Ultimately, the material of a PVD coating is a deliberate choice, selected to impart specific qualities of durability, color, or resistance onto a product's surface.
Summary Table:
| Coating Type | Common Materials | Primary Application |
|---|---|---|
| Industrial / Tooling | Titanium Nitride (TiN), Chromium Nitride (CrN), Zirconium Nitride (ZrN) | Extreme hardness, wear resistance for tools and components |
| Decorative / Consumer | Gold alloys (9k, 18k, 24k), Brass, Copper, Chromium | Aesthetic finishes for watches, jewelry, and fixtures |
| Corrosion Resistance | Various stable, non-reactive metals and ceramics | Protective surface layers on base materials like stainless steel |
Ready to select the perfect PVD coating material for your project?
At KINTEK, we specialize in lab equipment and consumables for advanced surface coating applications. Our expertise can help you:
- Achieve superior durability with ceramic-based coatings like TiN for your tools and industrial components.
- Create stunning decorative finishes with metallic PVD targets for your consumer products.
- Enhance corrosion resistance with stable, non-reactive surface layers.
Let us help you make the right material choice to meet your specific engineering or aesthetic goals. Contact our experts today to discuss your PVD coating needs and discover how KINTEK's solutions can elevate your product's performance and appearance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- Vacuum Cold Trap Direct Cold Trap Chiller
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process



















