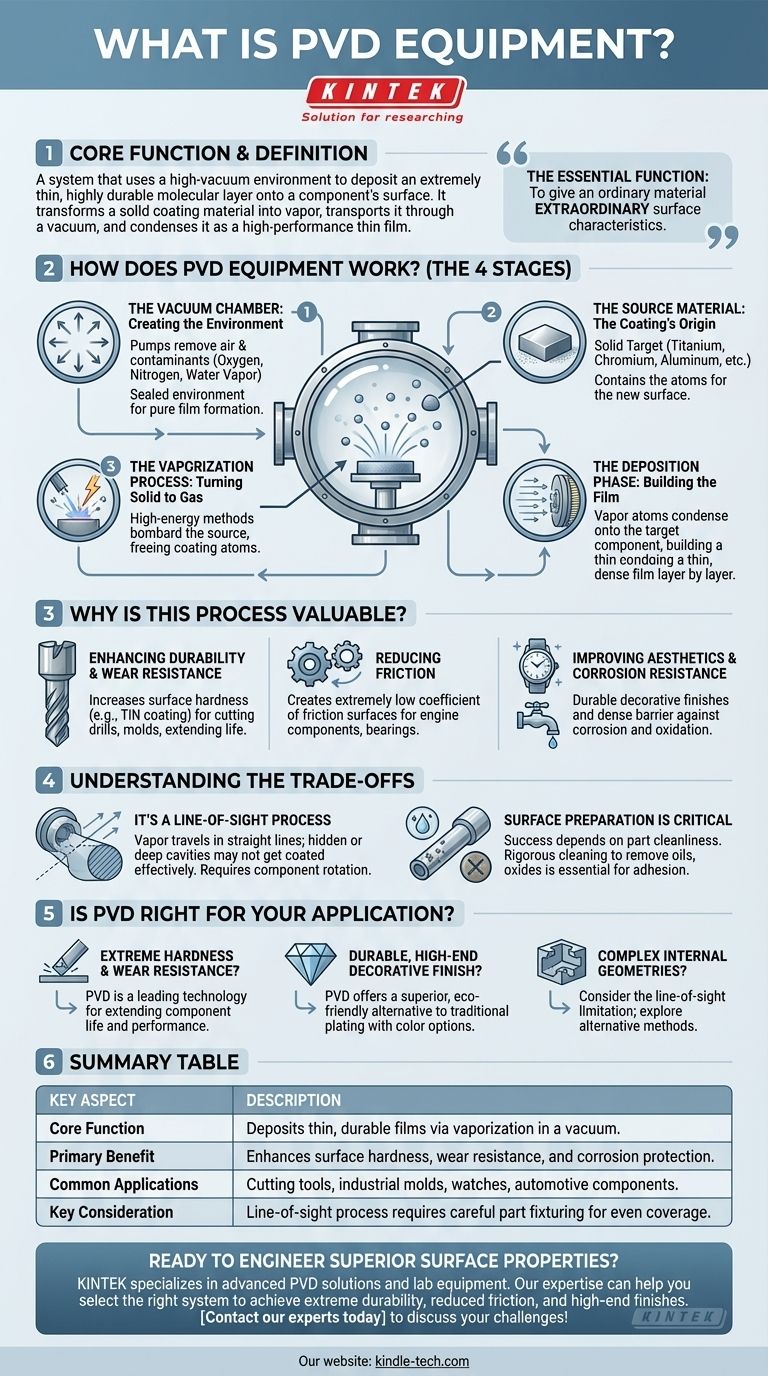
At its core, PVD equipment is a system that uses a high-vacuum environment to deposit an extremely thin but highly durable layer of material onto the surface of a component. This process, known as Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD), isn't a simple paint or plating; it's a molecular-level bonding technique that fundamentally enhances the properties of the base material.
The essential function of PVD equipment is to transform a solid coating material into a vapor, transport it through a vacuum, and have it condense onto a target object as a high-performance thin film. This allows engineers to give an ordinary material extraordinary surface characteristics.
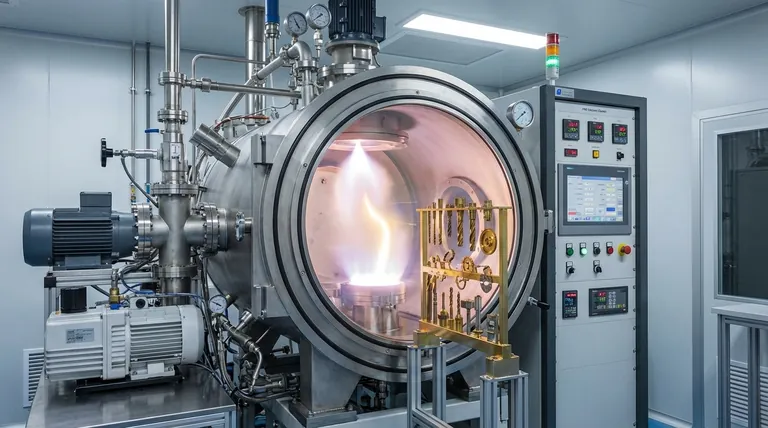

How Does PVD Equipment Fundamentally Work?
To understand what PVD equipment is, you must first understand the four critical stages of the process it facilitates. Each piece of the equipment is designed to execute one of these steps with extreme precision.
The Vacuum Chamber: Creating the Environment
The entire process takes place inside a sealed vacuum chamber. The first step is to pump out nearly all the air and other gases.
This vacuum is critical because it removes contaminants like oxygen, nitrogen, and water vapor that would otherwise react with the coating material and prevent a pure, dense film from forming.
The Source Material: The Coating's Origin
Inside the chamber, there is a source of the coating material, often a solid block, ingot, or powder of a specific metal or ceramic, such as titanium, chromium, or aluminum.
This source material contains the atoms that will ultimately form the new surface on your component.
The Vaporization Process: Turning Solid to Gas
This is the "Physical Vapor" step. High-energy methods are used to bombard the solid source material, causing atoms to be ejected from its surface and turn into a vapor or plasma.
While there are several methods, they all achieve the same goal: freeing the coating atoms so they can travel through the vacuum.
The Deposition Phase: Building the Film
The vaporized atoms travel in a straight line through the vacuum chamber until they strike the target component, which is strategically placed.
Upon impact, these atoms condense onto the component's surface, building a thin, highly-adherent, and densely packed film, layer by layer.
Why Is This Process So Valuable?
PVD equipment isn't used to apply a simple cosmetic layer; it's used to solve specific engineering challenges by fundamentally changing a component's surface properties.
Enhancing Durability and Wear Resistance
The most common application is creating incredibly hard surfaces. A PVD coating like Titanium Nitride (TiN) can dramatically increase the surface hardness of cutting tools, drills, and industrial molds, extending their operational life significantly.
Reducing Friction
PVD films can create surfaces with an extremely low coefficient of friction. This is vital for high-performance engine components, bearings, and other parts where minimizing energy loss and wear is critical.
Improving Aesthetics and Corrosion Resistance
PVD offers a far more durable alternative to traditional electroplating for decorative finishes on items like watches, faucets, and architectural hardware. The process also creates a dense barrier that protects the underlying material from corrosion and oxidation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the PVD process managed by this equipment has inherent characteristics that you must consider for any application.
It's a Line-of-Sight Process
Because the vaporized atoms travel in a straight line, surfaces that are hidden or in deep, narrow cavities will not get coated effectively. Parts often need to be rotated on complex fixtures to ensure even coverage.
Surface Preparation is Critical
The success of PVD coating is entirely dependent on the cleanliness of the part's surface. The equipment's antechambers and the pre-process workflow must include rigorous cleaning and drying steps to remove any oils, oxides, or residues. Poor preparation will lead to poor adhesion.
Is PVD the Right Choice for Your Application?
Choosing to use a PVD process means you're investing in surface engineering to achieve a specific performance outcome.
- If your primary focus is extreme hardness and wear resistance on tools or industrial parts: PVD is a leading technology for extending component life and improving performance.
- If your primary focus is a durable, high-end decorative finish: PVD offers a superior and more environmentally friendly alternative to traditional plating with a wide range of available colors.
- If your component has complex internal geometries that need coating: You must carefully consider the line-of-sight limitation and may need to explore alternative chemical deposition methods.
Ultimately, PVD equipment allows you to engineer the surface of a part, unlocking performance capabilities that the base material alone could never achieve.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Function | Deposits thin, durable films via vaporization in a vacuum. |
| Primary Benefit | Enhances surface hardness, wear resistance, and corrosion protection. |
| Common Applications | Cutting tools, industrial molds, watches, automotive components. |
| Key Consideration | Line-of-sight process requires careful part fixturing for even coverage. |
Ready to engineer superior surface properties for your components? KINTEK specializes in advanced PVD solutions and lab equipment. Our expertise can help you select the right system to achieve extreme durability, reduced friction, and high-end finishes. Contact our experts today to discuss how PVD technology can solve your specific application challenges!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What is hot press forging? Creating Complex, High-Strength Metal Components
- What is vacuum lamination? Achieve a Flawless, Durable Finish on Complex Shapes
- What is hot press moulding? Achieve Superior Density and Complex Shapes with Heat and Pressure
- What is the main function of hot press forming? Achieve Superior Strength & Precision in Manufacturing
- How does hot pressing work? Achieve Maximum Density for Advanced Materials



















