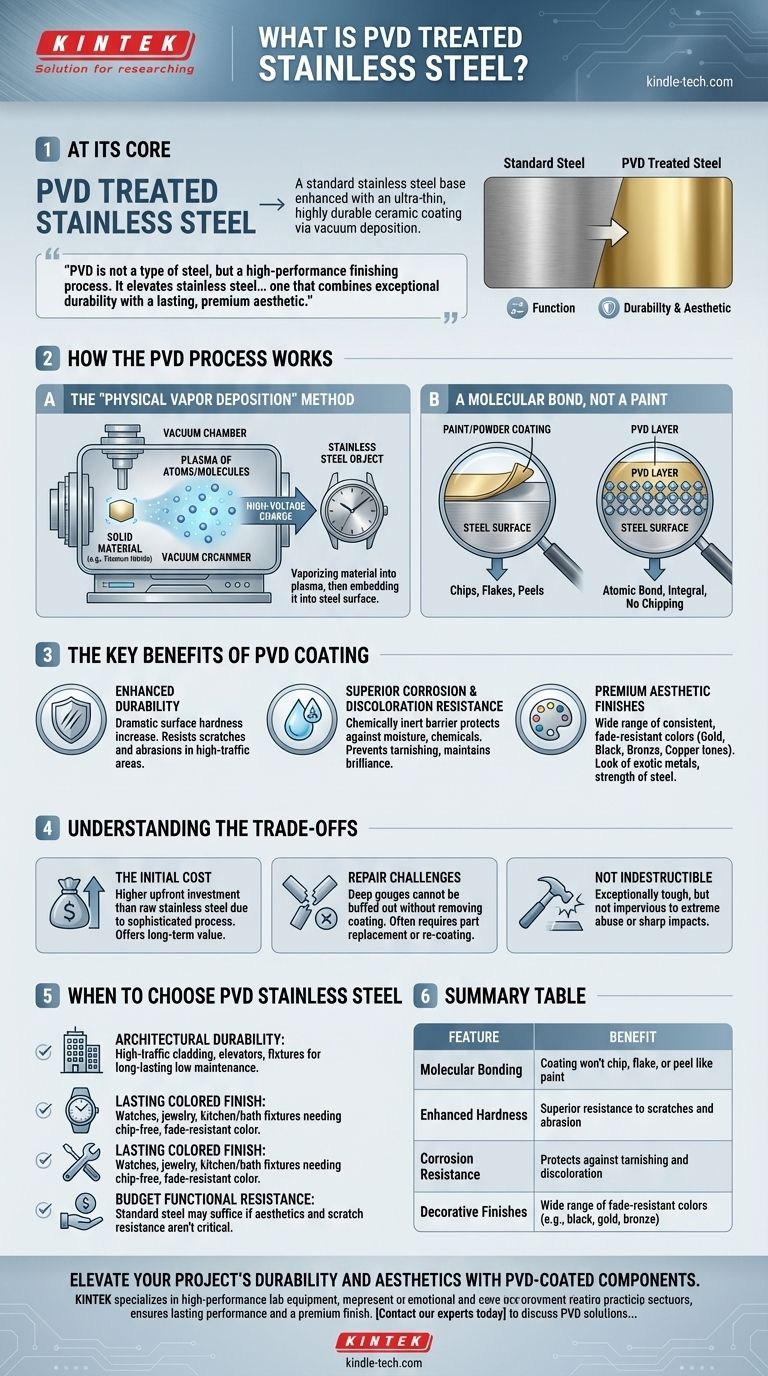
At its core, PVD treated stainless steel is a product where a standard stainless steel base is enhanced with an ultra-thin, highly durable ceramic coating. This treatment, applied through a vacuum deposition process, fundamentally changes the surface properties of the steel, granting it superior resistance to wear and allowing for a wide range of decorative colors without using paint.
PVD is not a type of steel, but a high-performance finishing process. It elevates stainless steel from a purely functional material to one that combines exceptional durability with a lasting, premium aesthetic.

How the PVD Process Works
To understand the value of PVD, you must first understand that it is a molecular bonding process, not a simple coating. It is performed in a high-tech vacuum chamber, which is what makes the finish so resilient.
The "Physical Vapor Deposition" Method
The process involves vaporizing a solid material (often a ceramic like titanium nitride) into a plasma of atoms or molecules. A high-voltage electrical charge then directs these particles toward the stainless steel object, where they embed themselves and form a thin, dense, and tightly bonded film on the surface.
A Molecular Bond, Not a Paint
Unlike painting or powder coating which sit on top of the steel, the PVD layer is bonded at an atomic level. This is why it doesn't chip, flake, or peel the way traditional coatings do. It becomes an integral part of the steel's surface.
The Key Benefits of PVD Coating
The reason PVD is specified for demanding applications is its ability to significantly upgrade the performance and appearance of the base stainless steel.
Enhanced Durability
The primary benefit is a dramatic increase in surface hardness. This makes the steel exceptionally resistant to the scratches and abrasions common in high-traffic areas or on frequently handled objects.
Superior Corrosion and Discoloration Resistance
The PVD coating is chemically inert and acts as a barrier, protecting the underlying stainless steel from environmental conditions, moisture, and chemicals. This prevents tarnishing and discoloration, maintaining the original brilliance and luster for far longer than untreated metal.
Premium Aesthetic Finishes
PVD allows stainless steel to take on a variety of colors—such as gold, black, bronze, and copper tones—that are consistent and fade-resistant. This provides the look of more exotic or expensive metals with the strength and cost-effectiveness of stainless steel.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While PVD offers significant advantages, it's essential to recognize its limitations to make an informed decision.
The Initial Cost
PVD treatment is a sophisticated process that adds to the final cost of the product. While it offers long-term value by reducing maintenance and replacement, the upfront investment is higher than for raw or brushed stainless steel.
Repair Challenges
The finish's incredible durability is also its primary drawback for repairs. A deep gouge that penetrates the PVD layer cannot be simply buffed out, as this would remove the colored coating in that spot. The entire part would often need to be replaced or completely re-coated.
Not Indestructible
While exceptionally tough, PVD coating is not impervious to damage. Sufficiently sharp or forceful impacts can still compromise the surface. Its value lies in resisting everyday wear, not extreme abuse.
When to Choose PVD Stainless Steel
Your choice should be guided by the balance you need between performance, appearance, and budget.
- If your primary focus is architectural durability: Choose PVD for high-traffic elements like cladding, elevators, door hardware, and public fixtures to ensure long-lasting appearance with minimal maintenance.
- If your primary focus is a lasting colored finish: Specify PVD for any product—from watches and jewelry to kitchen and bath fixtures—where you need a color that will not chip, fade, or tarnish over years of use.
- If your primary focus is purely functional corrosion resistance on a budget: Standard, untreated stainless steel may be sufficient if aesthetics and scratch resistance are not critical priorities.
Ultimately, PVD treated stainless steel is the definitive choice when you need a material that will not compromise on either durability or design.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Molecular Bonding | Coating won't chip, flake, or peel like paint |
| Enhanced Hardness | Superior resistance to scratches and abrasion |
| Corrosion Resistance | Protects against tarnishing and discoloration |
| Decorative Finishes | Wide range of fade-resistant colors (e.g., black, gold, bronze) |
Elevate your project's durability and aesthetics with PVD-coated components.
KINTEK specializes in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables, where material integrity is paramount. Whether you're developing architectural fixtures, medical devices, or consumer products, our expertise in surface treatment technologies ensures lasting performance and a premium finish.
Contact our experts today to discuss how PVD solutions can add value and longevity to your specific application.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What is an example of PECVD? RF-PECVD for High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications



















